
This is a list of sites in Minnesota which are included in the National Register of Historic Places. There are more than 1,700 properties and historic districts listed on the NRHP; each of Minnesota's 87 counties has at least 2 listings. Twenty-two sites are also National Historic Landmarks.

The Old Dutch Parsonage is a historical house built in 1751, moved about 1913 and now located at 65 Washington Place, Somerville, Somerset County, New Jersey, United States. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on January 25, 1971, and noted as "an excellent example of mid-18th-century Flemish Bond brick structure".

Knox's Headquarters State Historic Site, in the town of New Windsor in Orange County, New York, consists of the Georgian house of the Ellison family, built in 1754 by immigrant William Bull of Hamptonburgh, NY, and the grounds around it. The site is located on Old Forge Hill Road, just south of Route 94 east of Vails Gate.

The Claybank Brick Plant National Historic Site, located near Claybank, Saskatchewan at the foot of the Dirt Hills in the RM of Elmsthorpe No. 100, was an operational brick manufacturing plant from 1914–1989. Bricks manufactured at the site have been used to construct prominent Canadian buildings such as the Bessborough Hotel in Saskatoon and the Chateau Frontenac in Quebec City. The site was designated as a National Historic Site in 1996 and remains one of Canada’s greatest examples of early twentieth century industrialism.

The Alliance Clay Product Company District is a historic district in Alliance, Ohio, United States. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978, it includes twelve contributing properties.

Stonum, also called Stoneham, is a historic house at 900 Washington Avenue in New Castle, Delaware. Its main section built about 1750, it was the country home of George Read (1733-1798), a signer of the Declaration of Independence. His advocacy enabled Delaware to become the first state ratifying the declaration. The house was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1973. It is the only building standing associated with this Founding Father.

The Dixie Coca-Cola Bottling Company Plant, also known as Baptist Student Center, or Baptist Collegiate Ministry, Georgia State University, is a historic building at 125 Edgewood Avenue in Atlanta, Georgia. Built in 1891, it was the headquarters and bottling plant of the Dixie Coca-Cola Bottling Company, and the place where the transition from Coca-Cola as a drink served at a soda fountain to a mass-marketed bottled soft drink took place. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1983, and is one of the only buildings in Atlanta dating to Coca-Cola's early history. Since 1966 the building has been the Baptist Student Ministry location for Georgia State University.

The Johnson County Courthouse in Buffalo, Wyoming was built in 1884. The Italianate style building adjoins the former Johnson County Library, which is also listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
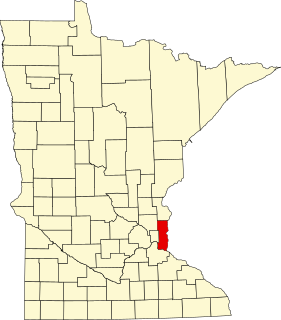
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Washington County, Minnesota. It is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Washington County, Minnesota, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.
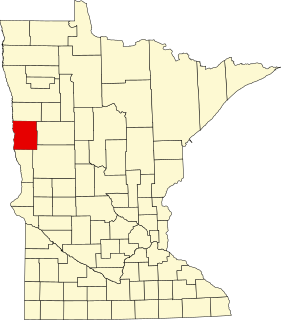
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Clay County, Minnesota. It is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Clay County, Minnesota, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.

The United Brick Corporation Brick Complex, also known as the New York Avenue Brickworks, is a historic industrial site. It is located on the 2800 block of New York Avenue, NE in Washington, D.C. on the grounds of the United States National Arboretum. The site sits on federal land, and access by the public is restricted.

Coplay Cement Company Kilns, also known as the Saylor Park Industrial Museum, is an open-air historic site located at Coplay, Pennsylvania in Lehigh County, Pennsylvania. The nine kilns were built in 1892-1893, and used for the production of Portland cement. They are constructed of locally produced red brick, and are known as Schoefer vertical kilns. They were shut down in 1904. The Coplay Cement Company donated the kilns and surrounding land to Lehigh County in 1975, for a cement industry museum. It is operated as a partnership between the County of Lehigh, which owns and maintains the site, and the Lehigh County Historical Society, which provides educational services. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

The Birch Creek Charcoal Kilns are a group of beehive-shaped clay charcoal kilns near Leadore, Idaho, built in 1886. They were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972.

Guignard Brick Works is a historic industrial site and national historic district located in Cayce, Lexington County, South Carolina. The brick works was established by the Guignard family in 1801 and over the years produced brick for many buildings in Columbia, South Carolina and throughout the South. The complex includes four brick beehive kilns, a historic brick office, and remnants of other industrial features of the brick works. Three of the four remaining kilns were built around 1920, the other was built in 1932. Clay for brickmaking was obtained from banks of the nearby Congaree River.

Pamplin Pipe Factory, also known as Merrill and Ford, The Akron Smoking Pipe Factory, and The Pamplin Smoking Pipe and Manufacturing Company, is a historic factory and archaeological site located at Pamplin, Appomattox County, Virginia. Located on the property are a wood-framed factory building, a deteriorating brick kiln, and a collapsed brick chimney. It began operation about 1879 and was at one time the largest clay pipe manufacturer in the United States.

White and Company's Goose Lake Stoneware Manufactury is an archaeological site located at 5010 N. Jugtown Road in the Goose Lake Prairie State Natural Area, near Morris, Illinois. The site, as well as the nearby tile works site, was part of a large White and Company plant used to manufacture stoneware and tile. The manufactury, which operated from 1855 to 1866, was one of the earliest large-scale stoneware plants in Illinois. The company chose the site for its plant due to the abundant clay resources around Goose Lake, which it used in its products. A town known as Jugtown was settled nearby for the plant's employees; the town reached a population of 114 by 1860. The stoneware site now mainly contains waste products from the stoneware production process, including kiln furniture and waster sherds.

The Charles "Bullet" Dean Hyten House is a historic house at 211 South Main Street in Benton, Arkansas. It is a single-story Bungalow-style structure, with a hip roof that extends over its front porch. The porch is supported by square columns set on brick piers, with decorative metal latticework between the columns. Built in 1922, the house significant as the only surviving house associated with Charles Hyten and Niloak pottery. Hyten and Arthur Dovey together created a pottery process in 1909 that achieved swirling of different colors and types of clay, yet held together without shattering when baked in a kiln. The process was patented by Hyten in 1928. It was the basis of the Arts and crafts movement-era Niloak's Art pottery line.

The Moses King Brick and Tile Works is a historic brickworks located at 738 North Coal Street in Colchester, Illinois. The complex includes King's Folk Victorian home, four of the original seven beehive kilns, the factory building and its drying tunnels, two exhaust stacks, and various outbuildings. Moses King established the brickworks on his own land, which held one of the county's richest clay deposits, in 1881. The brickworks was a major part of Colchester's clay industry, which developed as a way of using excess coal from the city's more prominent coal mining industry; it eventually became one of the city's main economic drivers, along with coal and the railroad. While coal and clay both declined in Colchester in the twentieth century, the brickworks survived as a producer of buff brick, ultimately becoming the last surviving brickworks in the city. It closed in the 1960s when buff brick declined in favor of colored brick, which could be more easily obtained from other sources.

The Broadway–Phelps Park Historic District is located in Decorah, Iowa, United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976. The original boundaries of the historic district is composed of seven blocks of a residential area and the city's oldest park. It is located on a prominent hill in the heart of Decorah. Contributing properties include five churches, three government buildings, a museum, brick kiln, a carriage house, and 36 private residences. Contributing sites include the city park square and the river bluff. The historic buildings were built from the 1850s to the early 1900s. Most of the structures are two or more stories, and were built in limestone, sandstone, or brick. The Ellsworth-Porter House is individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places. In 2022, the historic district boundaries were increased to include two more properties.

The Ernest McCarty Oliver House, in LaFayette, Alabama, is a Victorian house built in 1895. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.
























