



Coulson is a ghost town located in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States, on the north bank of the Yellowstone River, approximately one mile east of present-day downtown Billings. [1] [2]




Coulson is a ghost town located in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States, on the north bank of the Yellowstone River, approximately one mile east of present-day downtown Billings. [1] [2]

Yellowstone County is the most populous county in the U.S. state of Montana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 164,731. Its county seat is Billings, the state's most populous city. Like the nearby park, Yellowstone County is named after the Yellowstone River which roughly bisects the county, flowing southwest to northeast. The river, in turn, was named for the yellow sandstone cliffs in what is now Yellowstone County.

Huntley is a census-designated place (CDP) in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States. The population was 411 at the 2000 census. Huntley lent its name to the Huntley Project, a federal irrigation project that began delivering water to the arid district in 1907. Today, Huntley is an eastern suburb of Billings and is located east of Shepherd and west of Worden.

Laurel is a city in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States. It is the third largest community in the Billings Metropolitan Statistical Area, and is located in the Yellowstone Valley, as an east–west terminal division point of the Burlington-Northern Railroad. The population was 7,222 at the 2020 census.
Lockwood is a census-designated place (CDP) in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States. It is not an organized city or town. Lockwood had the largest growth rate in the state of Montana with 57.8% growth since 2000. The 2020 census put Lockwood's population at 7,195. Lockwood is a suburb of Billings and is the second largest community in the Billings Metropolitan Area. Annexation of Lockwood to Billings has been studied; however, the June 2009 Billings City Council Annexation Plan states that the city has no plans to annex Lockwood in the foreseeable future. Lockwood is the site of a major Exxon refinery.

Shepherd is a census-designated place (CDP) in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States. The population was 193 at the 2000 census. Shepherd is a Billings suburb located to the northeast. The unincorporated town was named after R.E. Shepherd, a prominent early settler and owner of the Billings Land and Irrigation Company and the Merchants National Bank. The post office opened in 1915.

Worden is a census-designated place (CDP) in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States. The population was 506 at the 2000 census. Worden, along with Ballantine, Huntley, and Pompey's Pillar, is part of the Huntley Project, an irrigation district established by the United States Bureau of Reclamation in 1907.
There are 45 streams named Willow Creek in the U.S. state of Montana.


The Western Heritage Center is a regional museum located in historic downtown Billings, Montana, United States. The museum is housed in the historic Parmly Billings Memorial Library, built in 1901. The building is a stately Richardsonian Romanesque structure with twin towers, listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The Western Heritage Center displays original exhibits about south-central Montana and the Northern Plains and houses oral histories and artifacts about the history of the Yellowstone River Valley. The museum celebrated its fiftieth anniversary in 2021.
The Yellowstone Art Museum (YAM) in downtown Billings, Montana is the largest contemporary art museum in Montana.

The Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition of 1869 was the first organized expedition to explore the region that became Yellowstone National Park. The privately financed expedition was carried out by David E. Folsom, Charles W. Cook and William Peterson of Diamond City, Montana, a gold camp in the Confederate Gulch area of the Big Belt Mountains east of Helena, Montana. The journals kept by Cook and Folsom, as well as their personal accounts to friends were of significant inspirational value to spur the organization of the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition which visited Yellowstone in 1870.
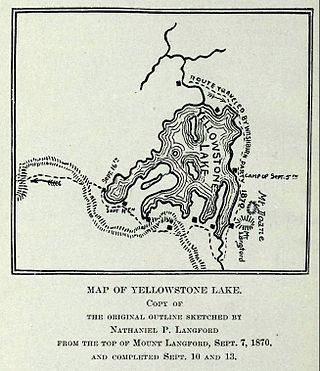
The Washburn Expedition of 1870 explored the region of northwestern Wyoming that two years later became Yellowstone National Park. Led by Henry D. Washburn and Nathaniel P. Langford, and with a U.S. Army escort headed by Lt. Gustavus C. Doane, the expedition followed the general course of the Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition made the previous year.
Yellowstone Christian College is a four-year, confessional Christian liberal arts college with 2 campuses in Billings, Montana and Kalispell, Montana. The college is affiliated with the Montana Southern Baptist Convention. Founded in 1974, it was called Yellowstone Baptist College until 2010.
Pryor Mountains National Forest was established as the Pryor Mountains Forest Reserve by the U.S. Forest Service in Montana on November 6, 1906 by the U.S. Forest Service with 78,732 acres (318.62 km2). It became a National Forest on March 4, 1907. On July 1, 1908 it was combined with part of Yellowstone National Forest to establish Beartooth National Forest. The name was discontinued.
Mountview Cemetery is a city-owned cemetery and was established in 1920 and was merged with Billings Cemetery in Billings, Montana, and is the largest cemetery in the region, with over 25,000 burials and interments.
Rimrock is a populated place located in Yellowstone County, Montana, United States at 45.802°N 108.703°W.
The Billings Bench Water Association Canal, also referred to as the Billings Canal, is an irrigation canal that starts at the Yellowstone River in Laurel, Montana, runs through Billings, Montana, under the Rims and ends at the Yellowstone River near Shepherd, Montana.