
Lumpkin County is a county located in the north central portion of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 33,488. Its county seat is Dahlonega. Lumpkin County is included in the Atlanta-Sandy Springs-Roswell, Georgia Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Villa Rica is a city in Carroll and Douglas counties in the U.S. state of Georgia. Located roughly 30 miles west of Atlanta, a decision to develop housing on a large tract of land led to a major population boom at the turn of the 21st century: the population was 4,134 at the 2000 census; it had grown by 238%, to 13,956, at the 2010 census; and is estimated at 16,058 in 2019, nearly quadrupling its population in just 19 years.

Dahlonega is the county seat of Lumpkin County, Georgia, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city had a population of 5,242, and in 2018 the population was estimated to be 6,884.

The Dahlonega Mint was a former branch of the United States Mint built during the Georgia Gold Rush to help the miners get their gold assayed and minted, without having to travel to the Philadelphia Mint. It was located at in Dahlonega, Lumpkin County, Georgia. Coins produced at the Dahlonega Mint bear the "D" mint mark. That mint mark is used today by the Denver Mint, which opened in 1906, over four decades after the Dahlonega Mint closed. All coins from the Dahlonega Mint are gold, in the $1, $2.50, $3, and $5 denominations, and bear dates in the range 1838–1861.

Auraria is a ghost town in Lumpkin County, Georgia, United States, southwest of Dahlonega. Its name derives from aurum, the Latin word for gold. In its early days, it was also known variously as Dean, Deans, Nuckollsville, and Scuffle Town.

The Calhoun Mine is perhaps the oldest and best-known mine in Lumpkin County, Georgia. When gold was discovered in Lumpkin County in 1828, which led to the Georgia Gold Rush in 1829, it was discovered on 239 acres (0.97 km2) owned by Robert Obar. After at least two intermediary sales, the land was purchased by Senator John C. Calhoun of South Carolina, who was also the 7th Vice President of the United States. Calhoun started a mining company to mine the land and later allowed his son-in-law Thomas Green Clemson, the founder of Clemson University, to manage it. The ore deposit was a very rich deposit and, according to an 1856 letter from Clemson to his brother-in-law, was still producing significant quantities of gold nearly 30 years after its initial discovery on the land. This mine - along with the Consolidated Mine and the Loud Mine - were some of the most productive mines in the Georgia Gold Belt.

The Consolidated Mine was a gold mine in Lumpkin County, Georgia, United States, just east of Dahlonega. Like most of the area around Dahlonega, the placer mining on the land on which the mine is located probably started during the Georgia Gold Rush. By 1880, the placer deposits were exhausted and the land was down to hard rock. Gold was soon discovered in a huge quartz vein system, and mined. "The richest acre" was mined deep into the ground, and the resulting shaft became known as the "Glory Hole.”

The Georgia State Capitol is an architecturally and historically significant building in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. The building has been named a National Historic Landmark which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. As the primary office building of Georgia's government, the capitol houses the offices of the governor, lieutenant governor, and secretary of state on the second floor, chambers in which the General Assembly, consisting of the Georgia State Senate and Georgia House of Representatives, meets annually from January to April. The fourth floor houses visitors' galleries overlooking the legislative chambers and a museum located near the rotunda in which a statue of Miss Freedom caps the dome.
Crisson Mine was a gold mine in Lumpkin County, Georgia, USA, located just east of Dahlonega. Like many mines in the area, the property probably started as a placer mine during the Georgia Gold Rush. Once the placer deposits had been exhausted, an open pit gold mine was established in 1847 and commercial operations continued until the early 1980s. A small stamp mill was also established here. Much of the gold used for the gold leaf dome of the Georgia State Capitol was mined at this mine, which was among the most productive mines in the Georgia Gold Belt. The mine is located just north of the site of the Consolidated Mine, which is itself north of the Calhoun Mine.

The largest quantities of gold found in the eastern United States were found in the Georgia Gold Belt, extending from eastern Alabama to Rabun County, Georgia. The biggest concentration of gold was found in White, Lumpkin, and northern Cherokee counties in Georgia. The gold in the Georgia Gold Belt was close to 24 karat (100%) purity. Most of the gold was found in eroded rock (saprolite) and mixed in with quartz.

Maldon is a town in Victoria, Australia, in the Shire of Mount Alexander local government area. It has been designated "Australia's first notable town" and is notable for its 19th-century appearance, maintained since gold-rush days. At the 2016 census, Maldon had a population of 1,513.
The Chestatee River is a 32.76-mile-long (52.72 km) river in the Appalachian Mountains of northern Georgia, USA.

Historic Westville is a history museum representing a 19th-century Georgia town in Columbus, Georgia, United States.

The Georgia Gold Rush was the second significant gold rush in the United States and the first in Georgia, and overshadowed the previous rush in North Carolina. It started in 1829 in present-day Lumpkin County near the county seat, Dahlonega, and soon spread through the North Georgia mountains, following the Georgia Gold Belt. By the early 1840s, gold became difficult to find. Many Georgia miners moved west when gold was found in the Sierra Nevada in 1848, starting the California Gold Rush. Since the 16th century, American Indians in Georgia told European explorers that the small amounts of gold which they possessed came from mountains of the interior. Some poorly documented accounts exist of Spanish or French mining gold in North Georgia between 1560 and 1690, but they are based on supposition and on rumors passed on by Indians. In summing up known sources, W.S. Yeates observed: "Many of these accounts and traditions seem to be quite plausible. Nevertheless, it is hardly probable that the Spaniards would have abandoned mines which were afterwards found to be quite profitable, as those in North Georgia."
The Free Jim Mine was a Georgia Gold Rush gold mine located in the town of Dahlonega in Lumpkin County, Georgia, United States. The mine was started by a free African American named James Boisclair, who arrived in the area in the 1830s from Augusta, Georgia. Apparently, Boisclair discovered gold on a tract of land but, under state law, could not purchase the land since he was black, except through a guardian. A local resident, Joseph J. Singleton became his custodian, consequently allowing Boisclair to purchase the land and start what would become known as the Free Jim Mine. The mine was operated by Bosclair for some years. Boisclair left Georgia following news of the California Gold Rush.

Matthew FlemingStephenson (1802–1882) was an American miner, geologist, and mineralogist based in the US state of Georgia. He was one of the first collectors of lazulite, rutile, pyrophyllite, and other minerals. A phrase he said while encouraging people not to leave Georgia for the California Gold Rush, "There's gold in them thar hills", is commonly referenced in American popular culture.
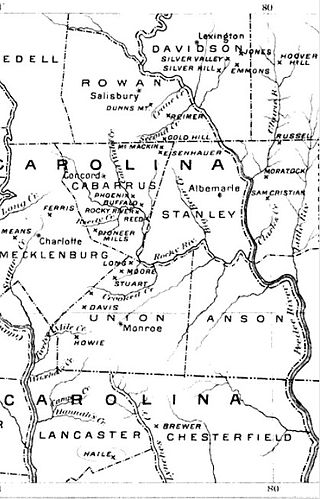
The Carolina Gold Rush, the first gold rush in the United States, followed the discovery of a large gold nugget in North Carolina in 1799, by a 12-year-old boy named Conrad Reed. He spotted the nugget while playing in Meadow Creek on his family's farm in Cabarrus County, North Carolina. Conrad took the 17-pound (7.7 kg) gold nugget home to show his father. However, gold was not commonly seen in their community and the value of the nugget was not understood. The nugget was used as a door stop in the family's home for several years. In 1802, Conrad's father, John Reed, showed the rock to a jeweler, who recognized it as gold and offered to buy it. Reed, still unaware of the real value of his "doorstop," sold it to the jeweler for US$3.50.

Northeast Georgia is a region of Georgia in the United States. The northern part is also in the north Georgia mountains, while the southern part is still hilly but much flatter in topography. Northeast Georgia is also served by the Asheville/Spartanburg/Greenville/Anderson market.

The Old Lumpkin County Jail is a historic jail building in Dahlonega, Georgia. The two-story brick jail was built in 1884. The first floor is now used by the Lumpkin County Historical Society and the second floor has been largely maintained in historic condition. Tours are given during Gold Rush Days in October. Bill Miner a.k.a. the Gentleman Bandit and Grey Fox were held in the jail. The county build a newer jail in 1964. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on September 13, 1985. It is located on Clarksville Street.

Price Memorial Hall, also known as the Price Memorial Building, is a historic site in Dahlonega, Georgia. The hall was built on the site of the U.S. government's federal branch mint built in 1836. It burned down in 1878 and the university, one of the first Federal Land Grant Colleges, had its hall built on the foundation. A historical marker is located on the site.






















