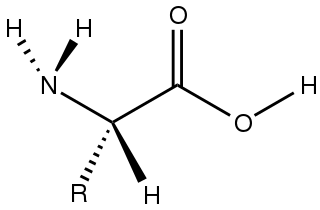
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid in which at least one hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group, as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology.
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure. They are widely distributed in nature, being important constituents of animal lipid metabolism, and they play an important role in the human diet and in human physiology. The three types of omega−3 fatty acids involved in human physiology are α-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA can be found in plants, while DHA and EPA are found in algae and fish. Marine algae and phytoplankton are primary sources of omega−3 fatty acids. DHA and EPA accumulate in fish that eat these algae. Common sources of plant oils containing ALA include walnuts, edible seeds, and flaxseeds, while sources of EPA and DHA include fish and fish oils, as well as algae oil.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

Monosodium glutamate (MSG), also known as sodium glutamate, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese in this glutamic acid form. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.

Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated –NH+
3 form under physiological conditions, while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated −COO− under physiological conditions. Aspartic acid has an acidic side chain (CH2COOH) which reacts with other amino acids, enzymes and proteins in the body. Under physiological conditions (pH 7.4) in proteins the side chain usually occurs as the negatively charged aspartate form, −COO−. It is a non-essential amino acid in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it as needed. It is encoded by the codons GAU and GAC.

Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula B(OH)3. It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salts, and can react with alcohols to form borate esters.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.

Dipsacus is a genus of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae. The members of this genus are known as teasel, teazel or teazle. The genus includes about 15 species of tall herbaceous biennial plants growing to 1–2.5 metres (3.3–8.2 ft) tall. Dipsacus species are native to Europe, Asia and northern Africa.
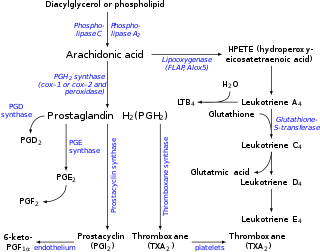
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a sub-category of oxylipins, i.e. oxidized fatty acids of diverse carbon units in length, and are distinguished from other oxylipins by their overwhelming importance as cell signaling molecules. Eicosanoids function in diverse physiological systems and pathological processes such as: mounting or inhibiting inflammation, allergy, fever and other immune responses; regulating the abortion of pregnancy and normal childbirth; contributing to the perception of pain; regulating cell growth; controlling blood pressure; and modulating the regional flow of blood to tissues. In performing these roles, eicosanoids most often act as autocrine signaling agents to impact their cells of origin or as paracrine signaling agents to impact cells in the proximity of their cells of origin. Eicosanoids may also act as endocrine agents to control the function of distant cells.

Calcium citrate is the calcium salt of citric acid. It is commonly used as a food additive (E333), usually as a preservative, but sometimes for flavor. In this sense, it is similar to sodium citrate. Calcium citrate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements. Calcium makes up 24.1% of calcium citrate (anhydrous) and 21.1% of calcium citrate (tetrahydrate) by mass. The tetrahydrate occurs in nature as the mineral Earlandite.
Phosphorus oxoacid is a generic name for any acid whose molecule consists of atoms of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen. There is a potentially infinite number of such compounds. Some of them are unstable and have not been isolated, but the derived anions and organic groups are present in stable salts and esters. The most important ones—in biology, geology, industry, and chemical research—are the phosphoric acids, whose esters and salts are the phosphates.
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements.
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids :
4-Hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase is an enzyme that uses p-coumaric acid to produce 4-ethylphenol.
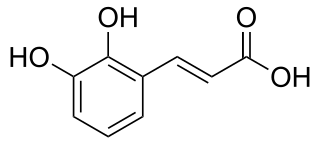
2,3-Dihydroxycinnamic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid. It is an isomer of caffeic acid.
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.













