
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of one million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far Eastern Federal District, and is the world's largest country subdivision, covering over 3,083,523 square kilometers (1,190,555 sq mi). Yakutsk, which is the world's coldest major city, is its capital and largest city.

Bashkir or Bashkort is a Turkic language belonging to the Kipchak branch. It is co-official with Russian in Bashkortostan. It is spoken by 1.09 million native speakers in Russia, as well as in Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Estonia and other neighboring post-Soviet states, and among the Bashkir diaspora. It has three dialect groups: Southern, Eastern and Northwestern.

Tuvan or Tyvan is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in South Central Siberia, Russia. The language has borrowed a great number of roots from the Mongolian language, Tibetan and the Russian languages. There are small diaspora groups of Tuvan people that speak distinct dialects of Tuvan in China and Mongolia.
Three scripts are currently used for the Tatar language: Arabic, Cyrillic and Latin.

Faux Cyrillic, pseudo-Cyrillic, pseudo-Russian or faux Russian typography is the use of Cyrillic letters in Latin text, usually to evoke the Soviet Union or Russia, though it may be used in other contexts as well. It is a common Western trope used in book covers, film titles, comic book lettering, artwork for computer games, or product packaging which are set in or wish to evoke Eastern Europe, the Soviet Union, or Russia. A typeface designed to emulate Cyrillic is classed as a mimicry typeface.

Buryat or Buriat, known in foreign sources as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of Mongolian, and in pre-1956 Soviet sources as Buryat-Mongolian, is a variety of the Mongolic languages spoken by the Buryats and Bargas that is classified either as a language or major dialect group of Mongolian.
The Common Turkic alphabet is a project of a single Latin alphabet for all Turkic languages based on a slightly modified Turkish alphabet, with 34 letters recognised by the Organization of Turkic States. Its letters are as follows:

Dolgans are an ethnic group who mostly inhabit Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. They are descended from several groups, particularly Evenks, one of the Indigenous peoples of the Russian North. Dolgans are the most closely related to the Sakha. They adopted a Turkic language sometime after the 18th century. The 2010 Census counted 7,885 Dolgans. This number includes 5,517 in Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District.
Shor is a critically endangered Turkic language spoken by about 2,800 people in a region called Mountain Shoriya, in the Kemerovo Province in Southwest Siberia, although the entire Shor population in this area is over 12000 people. Presently, not all ethnic Shors speak Shor and the language suffered a decline from the late 1930s to the early 1980s. During this period the Shor language was neither written nor taught in schools. However, since the 1980s and 1990s there has been a Shor language revival. The language is now taught at the Novokuznetsk branch of the Kemerovo State University.

The Kyrgyz alphabets are the alphabets used to write the Kyrgyz language. Kyrgyz uses the following alphabets:

Three alphabets are used to write Kazakh: the Cyrillic, Latin and Arabic scripts. The Cyrillic script is used in Kazakhstan and Mongolia. An October 2017 Presidential Decree in Kazakhstan ordered that the transition from Cyrillic to a Latin script be completed by 2031. The Arabic script is used in Saudi Arabia, Iran, Afghanistan, and parts of China.

There are 4 stages in the history of Yakut writing systems:
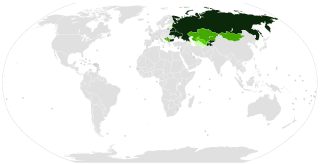
Numerous Cyrillic alphabets are based on the Cyrillic script. The early Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the 9th century AD and replaced the earlier Glagolitic script developed by the Bulgarian theologians Cyril and Methodius. It is the basis of alphabets used in various languages, past and present, Slavic origin, and non-Slavic languages influenced by Russian. As of 2011, around 252 million people in Eurasia use it as the official alphabet for their national languages. About half of them are in Russia. Cyrillic is one of the most-used writing systems in the world. The creator is Saint Clement of Ohrid from the Preslav literary school in the First Bulgarian Empire.
The Cyrillic script family contains many specially treated two-letter combinations, or digraphs, but few of these are used in Slavic languages. In a few alphabets, trigraphs and even the occasional tetragraph or pentagraph are used.
JCUKEN is the main Cyrillic keyboard layout for the Russian language in computers and typewriters. Earlier in Russia JIUKEN (ЙІУКЕН) layout was the main layout, but it was replaced by JCUKEN when the Russian alphabet reform of 1917 removed the letters Ѣ, І, Ѵ, and Ѳ. The letter Ъ had decreased in usage significantly after the reform.
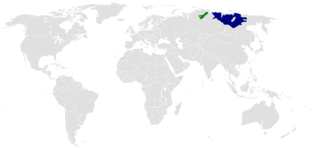
Yakutyə-KOOT, also known as Yakutian, Sakha, Saqa or Saxa, is a Turkic language belonging to Siberian Turkic branch and spoken by around 450,000 native speakers, primarily the ethnic Yakuts and one of the official languages of Sakha (Yakutia), a federal republic in the Russian Federation.
Marek Stachowski is a Polish linguist and etymologist specializing in Turkic languages, especially Yakut, Dolgan and Turkish. He is a professor at Jagiellonian University and the founding editor of the historical linguistics journal Studia Etymologica Cracoviensia.
The Komi language, a Uralic language spoken in the north-eastern part of European Russia, has been written in several different alphabets. Currently, Komi writing uses letters from the Cyrillic script. There have been five distinct stages in the history of Komi writing:
Khakass alphabets are the alphabets used to write the Khakas language.
Even alphabets are the alphabets used to write the Even language. During its existence, it functioned on different graphic bases and was repeatedly reformed. At present, Even writing functions in Cyrillic. There are three stages in the history of Even writing:












