Evidence for modern human presence in the northern and central highlands of Indochina, that constitute the territories of the modern Laotian nation-state dates back to the Lower Paleolithic. These earliest human migrants are Australo-Melanesians—associated with the Hoabinhian culture—and have populated the highlands and the interior, less accessible regions of Laos and all of South-east Asia to this day. The subsequent Austroasiatic and Austronesian marine migration waves affected landlocked Laos only marginally and direct Chinese and Indian cultural contact had a greater impact on the country.

Lao, sometimes referred to as Laotian, is a Kra–Dai language of the Lao people. It is spoken in Laos, where it is the official language for around 7 million people, as well as in northeast Thailand, where it is used by around 23 million people, usually referred to as Isan. Lao serves as a lingua franca among the citizens of Laos, who also speak approximately 90 other languages, many of which are unrelated to Lao.

The Mon are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand. The native language is Mon, which belongs to the Monic branch of the Austroasiatic language family and shares a common origin with the Nyah Kur language, which is spoken by the people of the same name that live in Northeastern Thailand. A number of languages in Mainland Southeast Asia are influenced by the Mon language, which is also in turn influenced by those languages.
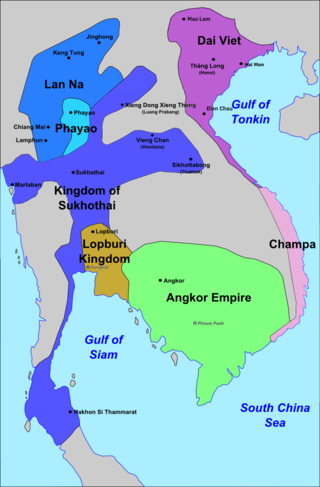
The Sukhothai Kingdom or the Northern Cities was a post-classical Thai kingdom (mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Si Inthrathit in 1238 and existed as an independent polity until 1438, when it fell under the influence of the neighboring Ayutthaya after the death of Borommapan.

The Lao people are a Tai ethnic group native to Southeast Asia, who speak the Lao language of the Kra–Dai languages. They are the majority ethnic group of Laos, making up 53.2% of the total population. The majority of Lao people adhere to Theravada Buddhism. They are closely related to other Tai people, especially with the Isan people, who are also speakers of Lao language, native to neighboring Thailand.

The Shan people, also known as the Tai Long or Tai Yai, are a Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia. The Shan are the biggest minority of Burma (Myanmar) and primarily live in the Shan State of this country, but also inhabit parts of Mandalay Region, Kachin State, Kayah State, Sagaing Region and Kayin State, and in adjacent regions of China, Laos, Assam and Megalaya, Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand. Though no reliable census has been taken in Burma since 1935, the Shan are estimated to number 4–6 million, with CIA Factbook giving an estimate of five million spread throughout Myanmar which is about 10% of the overall Burmese population.
The early history of Cambodia follows the prehistoric and protohistoric development of Cambodia as a country in mainland Southeast Asia. Thanks to archaeological work carried out since 2009 this can now be traced back to the Neolithic period. As excavation sites have become more numerous and modern dating methods are applied, settlement traces of all stages of human civil development from neolithic hunter-gatherer groups to organized preliterate societies are documented in the region.
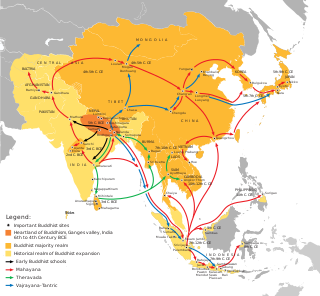
The history of Buddhism can be traced back to the 5th century BCE. Buddhism arose in Ancient India, in and around the ancient Kingdom of Magadha, and is based on the teachings of the renunciate Siddhārtha Gautama. The religion evolved as it spread from the northeastern region of the Indian subcontinent throughout Central, East, and Southeast Asia. At one time or another, it influenced most of Asia.
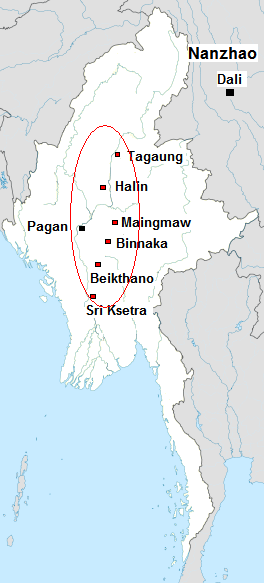
The Pyu city states were a group of city-states that existed from about the 2nd century BCE to the mid-11th century in present-day Upper Burma (Myanmar). The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant. The thousand-year period, often referred to as the Pyu millennium, linked the Bronze Age to the beginning of the classical states period when the Pagan Kingdom emerged in the late 9th century.

Thai people, Central Thai people or Siamese, T(h)ai Noi people, in a narrow sense, are a Tai ethnic group dominant in Central and Southern Thailand. Part of the larger Tai ethno-linguistic group native to Southeast Asia as well as Southern China and Northeast India, Thais speak the Sukhothai languages, which is classified as part of the Kra–Dai family of languages. The majority of Thais are followers of Theravada Buddhism.

The largest of the ethnic groups in Cambodia are the Khmer, who comprise approximately 90% of the total population and primarily inhabit the lowland Mekong subregion and the central plains. The Khmer historically have lived near the lower Mekong River in a contiguous arc that runs from the southern Khorat Plateau where modern-day Thailand, Laos and Cambodia meet in the northeast, stretching southwest through the lands surrounding Tonle Sap lake to the Cardamom Mountains, then continues back southeast to the mouth of the Mekong River in southeastern Vietnam.

Buddhism in Southeast Asia includes a variety of traditions of Buddhism including two main traditions: Mahāyāna Buddhism and Theravāda Buddhism. Historically, Mahāyāna Buddhism had a prominent position in this region, but in modern times most countries follow the Theravāda tradition. Southeast Asian countries with a Theravāda Buddhist majority are Thailand, Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar, all mainland countries.

Buddhist art is visual art produced in the context of Buddhism. It includes depictions of Gautama Buddha and other Buddhas and bodhisattvas, notable Buddhist figures both historical and mythical, narrative scenes from their lives, mandalas, and physical objects associated with Buddhist practice, such as vajras, bells, stupas and Buddhist temple architecture. Buddhist art originated in the north of the Indian subcontinent, in modern India, Pakistan and Afghanistan, with the earliest survivals dating from a few centuries after the historical life of Siddhartha Gautama from the 6th to 5th century BCE.

Before the Tai people's southward migration from Guangxi since the 4th century, the Indochinese peninsula had already been populated by Australo-Melanesians who by around 30,000 BP had spread into all sub-regions. They left traces of the first local culture - the Hoabinhian, a name assigned to an industry and cultural continuity of stone tools and flaked cobble artifacts that appears around 10,000 BP in caves and rock shelters first described in Hòa Bình, Vietnam, later also documented in Terengganu, Malaysia, Sumatra, Thailand, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia and Yunnan, southern China.

The peopling of Thailand refers to the process by which the ethnic groups that comprise the population of present-day Thailand came to inhabit the region.

Surin is a town in Thailand, capital of Surin Province, 431 km east-northeast of Bangkok. It is the site of the annual Surin Elephant Round-up. As of 2019, Surin has an estimated population of 39,179.

The Lavo Kingdom was a political entity (mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The original center of Lavo civilization was Lavo, but the capital shifted southward to Ayodhaya, the port city on the right side of the Ayutthaya island around the 11th century, whereupon the state was incorporated into the Ayutthaya Kingdom in the 14th century.
The prehistory of Burma (Myanmar) spanned hundreds of millennia to about 200 BCE. Archaeological evidence shows that the Homo erectus had lived in the region now known as Burma as early as 750,000 years ago, and the Homo sapiens about 11,000 BCE, in a Stone Age culture called the Anyathian. Named after the central dry zone sites where most of the early settlement finds are located, the Anyathian period was when plants and animals were first domesticated and polished stone tools appeared in Burma. Though these sites are situated in fertile areas, evidence shows these early people were not yet familiar with agricultural methods.

Southeast Asia was in the Indian sphere of cultural influence from 290 BCE to the 15th century CE, when Hindu-Buddhist influences were incorporated into local political systems. Kingdoms in the southeast coast of the Indian Subcontinent had established trade, cultural and political relations with Southeast Asian kingdoms in Burma, Bhutan, Sri Lanka ,Thailand, Indonesia, Malay Peninsula, Philippines, Cambodia and Champa. This led to the Indianisation and Sanskritisation of Southeast Asia within the Indosphere, Southeast Asian polities were the Indianised Hindu-Buddhist Mandala.

The Nyah Kur are an ethnic group native to Thailand in Southeast Asia. Closely related to the Mon people, the Nyah Kur are the descendants of the Mon of Dvaravati who did not flee westward or assimilate when their empire fell under the influence of the Khmer when Suryavarman I gained the throne in the early 11th century.