| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tensilon, Enlon |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | FDA Professional Drug Information |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Duration of action | 10–30 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
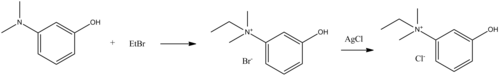
| Formula | C10H16NO+ |
| Molar mass | 166.244 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Edrophonium, formerly sold under the brand name Tensilon among others, is a readily reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It prevents breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and acts by competitively inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, mainly at the neuromuscular junction.