Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison.

Poison is something that causes harm. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense.

Soman is an extremely toxic chemical substance. It is a nerve agent, interfering with normal functioning of the mammalian nervous system by inhibiting the enzyme cholinesterase. It is an inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. As a chemical weapon, it is classified as a weapon of mass destruction by the United Nations according to UN Resolution 687. Its production is strictly controlled, and stockpiling is outlawed by the Chemical Weapons Convention of 1993 where it is classified as a Schedule 1 substance. Soman was the third of the so-called G-series nerve agents to be discovered along with GA (tabun), GB (sarin), and GF (cyclosarin).

Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.

Chlorfenvinphos is the common name of an organophosphorus compound that was widely used as an insecticide and an acaricide. The molecule itself can be described as an enol ester derived from dichloroacetophenone and diethylphosphonic acid. Chlorfenvinphos has been included in many products since its first use in 1963. However, because of its toxic effect as a cholinesterase inhibitor it has been banned in several countries, including the United States and the European Union. Its use in the United States was cancelled in 1991.

Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles.

Aminopterin, the 4-amino derivative of folic acid, is an antineoplastic drug with immunosuppressive properties often used in chemotherapy. Aminopterin is a synthetic derivative of pterin. Aminopterin works as an enzyme inhibitor by competing for the folate binding site of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. Its binding affinity for dihydrofolate reductase effectively blocks tetrahydrofolate synthesis. This results in the depletion of nucleotide precursors and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.

Aldicarb is a carbamate insecticide which is the active substance in the pesticide Temik. It is effective against thrips, aphids, spider mites, lygus, fleahoppers, and leafminers, but is primarily used as a nematicide. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. In case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure.

Coumatetralyl is an anticoagulant of the 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist type used as a rodenticide.

Azinphos-methyl (Guthion) is a broad spectrum organophosphate insecticide manufactured by Bayer CropScience, Gowan Co., and Makhteshim Agan. Like other pesticides in this class, it owes its insecticidal properties to the fact that it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.

Phosmet is a phthalimide-derived, non-systemic, organophosphate insecticide used on plants and animals. It is mainly used on apple trees for control of codling moth, though it is also used on a wide range of fruit crops, ornamentals, and vines for the control of aphids, suckers, mites, and fruit flies.

Diphenadione is a vitamin K antagonist that has anticoagulant effects and is used as a rodenticide against rats, mice, voles, ground squirrels and other rodents. The chemical compound is an anti-coagulant with active half-life longer than warfarin and other synthetic 1,3-indandione anticoagulants.

Bromadiolone is a potent anticoagulant rodenticide. It is a second-generation 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative and vitamin K antagonist, often called a "super-warfarin" for its added potency and tendency to accumulate in the liver of the poisoned organism. When first introduced to the UK market in 1980, it was effective against rodent populations that had become resistant to first generation anticoagulants.

α-Naphthylthiourea (ANTU) is an organosulfur compound with the formula C10H7NHC(S)NH2. This a white, crystalline powder although commercial samples may be off-white. It is used as a rodenticide and as such is fairly toxic. Naphthylthiourea is available as 10% active baits in suitable protein- or carbohydrate-rich materials and as a 20% tracking powder.
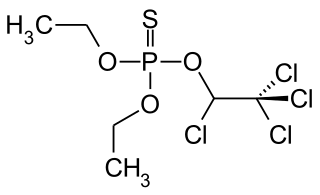
Chlorethoxyfos is an organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide. It is registered for the control of corn rootworms, wireworms, cutworms, seed corn maggot, white grubs and symphylans on corn. The insecticide is sold under the trade name Fortress by E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Company.

Carbophenothion also known as Stauffer R 1303 as for the manufacturer, Stauffer Chemical, is an organophosphorus chemical compound. It was used as a pesticide for citrus fruits under the name of Trithion. Carbophenothion was used as an insecticide and acaricide. Although not used anymore it is still a restricted use pesticide in the United States. The chemical is identified in the US as an extremely hazardous substance according to the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.

Ethoprophos (or ethoprop) is an organophosphate ester with the formula C8H19O2PS2. It is a clear yellow to colourless liquid that has a characteristic mercaptan-like odour. It is used as an insecticide and nematicide and it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.

Terbufos is a chemical compound used in insecticides and nematicides. Terbufos is part of the chemical family of organophosphates. It is a clear, colourless to pale yellow or reddish-brown liquid and sold commercially as granulate.

A poison can be any substance that is harmful to the body. It can be swallowed, inhaled, injected or absorbed through the skin. Poisoning is the harmful effect that occurs when too much of that substance has been taken. Poisoning is not to be confused with envenomation.
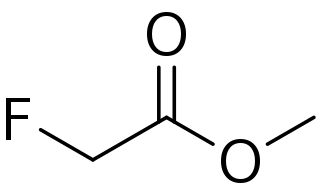
Methyl fluoroacetate (MFA) is an extremely toxic methyl ester of fluoroacetic acid. It is a colorless, odorless liquid at room temperature. It is used as a laboratory chemical and as a rodenticide. Because of its extreme toxicity, MFA was studied for potential use as chemical weapon. The general population is not likely to be exposed to methyl fluoroacetate. People who use MFA for work, however, can breathe in or have direct skin contact with the substance.



















