Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent.

Thallium(I) chloride, also known as thallous chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula TlCl. This colourless salt is an intermediate in the isolation of thallium from its ores. Typically, an acidic solution of thallium(I) sulfate is treated with hydrochloric acid to precipitate insoluble thallium(I) chloride. This solid crystallizes in the caesium chloride motif.
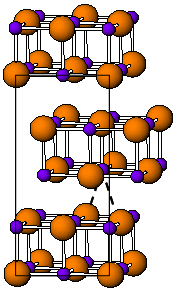
Thallium(I) iodide is a chemical compound with the formula TlI. It is unusual in being one of the few water-insoluble metal iodides, along with AgI, CuI, SnI2, SnI4, PbI2 and HgI2.
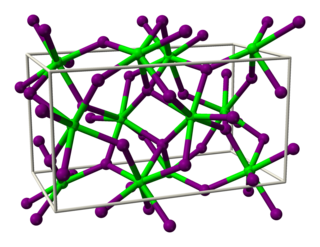
Strontium iodide (SrI2) is a salt of strontium and iodine. It is an ionic, water-soluble, and deliquescent compound that can be used in medicine as a substitute for potassium iodide . It is also used as a scintillation gamma radiation detector, typically doped with europium, due to its optical clarity, relatively high density, high effective atomic number (Z=48), and high scintillation light yield. In recent years, europium-doped strontium iodide (SrI2:Eu2+) has emerged as a promising scintillation material for gamma-ray spectroscopy with extremely high light yield and proportional response, exceeding that of the widely used high performance commercial scintillator LaBr3:Ce3+. Large diameter SrI2 crystals can be grown reliably using vertical Bridgman technique and are being commercialized by several companies.
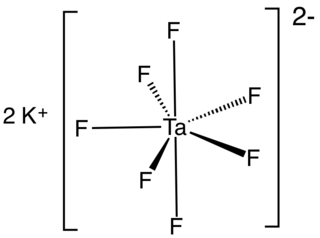
Potassium heptafluorotantalate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2[TaF7]. It is the potassium salt of the heptafluorotantalate anion [TaF7]2−. This white, water-soluble solid is an intermediate in the purification of tantalum from its ores and is the precursor to the metal.
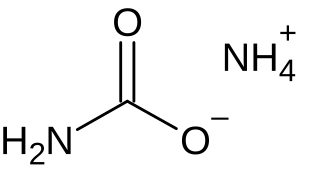
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.
Langbeinites are a family of crystalline substances based on the structure of langbeinite with general formula M2M'2(SO4)3, where M is a large univalent cation, and M' is a small divalent cation. The sulfate group, SO2−4, can be substituted by other tetrahedral anions with a double negative charge such as tetrafluoroberyllate, selenate, chromate, molybdate, or tungstates. Although monofluorophosphates are predicted, they have not been described. By redistributing charges other anions with the same shape such as phosphate also form langbeinite structures. In these the M' atom must have a greater charge to balance the extra three negative charges.

Monofluorophosphate is an anion with the formula PO3F2−, which is a phosphate group with one oxygen atom substituted with a fluoride atom. The charge of the ion is −2. The ion resembles sulfate in size, shape and charge, and can thus form compounds with the same structure as sulfates. These include Tutton's salts and langbeinites. The most well-known compound of monofluorophosphate is sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly used in toothpaste.
Yttrium iodide is a binary inorganic compound, a salt of yttrium and hydroiodic acid with the formula YI
3. The compound forms colorless crystals, soluble in water.

A transition metal nitrate complex is a coordination compound containing one or more nitrate ligands. Such complexes are common starting reagents for the preparation of other compounds.
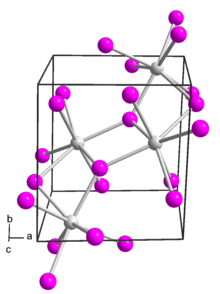
Neodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium with the formula NdI3. Neodymium uses the +3 oxidation state in the compound. The anhydrous compound is a green powdery solid at room temperature.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium with hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula PrI3, with green crystals. It is soluble in water.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
Europium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing europium and iodine with the chemical formula EuI3.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.