Related Research Articles

Ambrosius Aurelianus was a war leader of the Romano-British who won an important battle against the Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century, according to Gildas. He also appeared independently in the legends of the Britons, beginning with the 9th-century Historia Brittonum. Eventually, he was transformed by Geoffrey of Monmouth into the uncle of King Arthur, the brother of Arthur's father Uther Pendragon, as a ruler who precedes and predeceases them both. He also appears as a young prophet who meets the tyrant Vortigern; in this guise, he was later transformed into the wizard Merlin.

Magnus Maximus was a Celtiberian who became Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian.

Flavius Valerius Constantius "Chlorus", also called Constantius I, was Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as caesar from 293 to 305 and then ruling as augustus until his death. Constantius was also father of Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor of Rome. The nickname Chlorus was first popularized by Byzantine-era historians and not used during the emperor's lifetime.

Gratian was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian was raised to the rank of Augustus as a child and inherited the West after his father's death in 375. He nominally shared the government with his infant half-brother Valentinian II, who was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia on Valentinian's death. The East was ruled by his uncle Valens, who was later succeeded by Theodosius I.

Valentinian II was a Roman emperor in the western part of the Roman empire between AD 375 and 392. He was at first junior co-ruler of his half-brother, was then sidelined by a usurper, and only after 388 sole ruler, albeit with limited de facto powers.

Constantine III was a common Roman soldier who was declared emperor in Roman Britain in 407 and established himself in Gaul. He was recognised as co-emperor of the Roman Empire from 409 until 411.

Coel, also called Coel Hen and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a c. 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman Britain and the progenitor of several kingly lines in Yr Hen Ogledd, a region of the Brittonic-speaking area of what is now northern England and southern Scotland.

Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda Wledig, was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of Western Europe.

Historia regum Britanniae, originally called De gestis Britonum, is a pseudohistorical account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the kings of the Britons over the course of two thousand years, beginning with the Trojans founding the British nation and continuing until the Anglo-Saxons assumed control of much of Britain around the 7th century. It is one of the central pieces of the Matter of Britain.
Eudaf Hen is a figure of Welsh tradition. He is remembered as a King of the Britons and the father of Elen Luyddog and Conan Meriadoc in sources such as the Welsh prose tale The Dream of Macsen Wledig and Geoffrey of Monmouth's Latin chronicle Historia Regum Britanniae. He also figures into Welsh genealogies. Geoffrey of Monmouth calls him Octavius, a corruption and faux-Latinization of Old Welsh/Breton Outham. According to the medieval Welsh genealogy from Mostyn MS. 117, Eudaf was a direct ancestor of King Arthur.
Trahern is a legendary King of the Britons in Geoffrey of Monmouth's fictional Historia Regum Britanniae.
Caradocus, according to Geoffrey of Monmouth's Historia regum Britanniae, a pseudohistorical account of the kings of the Britons, was the duke of Cornwall under the reign of Octavius, who became king of Cornwall and died during the Emperor Magnus Maximus' reign.

Dionotus was a legendary king of Cornwall in Geoffrey of Monmouth's Historia regum Britanniae, an account of the rulers of Britain based on ancient Welsh sources and disputed by many historians. Dionotus succeeding his brother Caradocus, and was regent of Britain during the campaigns in Gaul of Emperor Magnus Maximus. The curious thing about this king is that the Welsh chronicles, which parallel most of Geoffrey of Monmouth's book, do not mention this king by name. However, Geoffrey uses Latin versions of Welsh names so he could be referring to Dynod, duke of Cornwall, or Anwn Dynod, Maximus's own son.

The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances. In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew troops from northern and western Britain, probably leaving local warlords in charge. In 407, usurper Constantine III took the remaining mobile Roman soldiers to Gaul in response to the crossing of the Rhine in late 406, leaving the island a victim to barbarian attacks. Around 410, the Romano-British expelled the Roman magistrates from Britain. Roman Emperor Honorius replied to a request for assistance with the Rescript of Honorius, telling the Roman cities to see to their own defence, a tacit acceptance of temporary British self-government. Honorius was fighting a large-scale war in Italy against the Visigoths under their leader Alaric, with Rome itself under siege. No forces could be spared to protect distant Britain. Though it is likely that Honorius expected to regain control over the provinces soon, by the mid-6th century Procopius recognised that Roman control of Britannia was entirely lost.
Conan Meriadoc is a legendary British Celtic leader credited with founding Brittany. Versions of his story circulated in both Brittany and Great Britain from at least the early 12th century, and supplanted earlier legends of Brittany's foundation. His story is known in two major versions, which appear in the Welsh text known as The Dream of Macsen Wledig, and in Geoffrey of Monmouth's Historia Regum Britanniae. Both texts associate him with Magnus Maximus, a Roman usurper against the Valentinianic dynasty who was widely regarded as having deprived Britain of its defences when he took its legions to claim the imperial throne. Conan's cousin or sister, Saint Elen, is said to have been Macsen Wledic's wife.
Marcus was a Roman usurper who was proclaimed Emperor of Roman Britain. He was killed later that same year in a subsequent mutiny.
Gratian or Gratianus was a Roman usurper in Roman Britain from 406-407.

The Theodosian dynasty was a Roman imperial family that produced five Roman emperors during Late Antiquity, reigning over the Roman Empire from 379 to 457. The dynasty's patriarch was Theodosius the Elder, whose son Theodosius the Great was made Roman emperor in 379. Theodosius's two sons both became emperors, while his daughter married Constantius III, producing a daughter that became an empress and a son also became emperor. The dynasty of Theodosius married into, and reigned concurrently with, the ruling Valentinianic dynasty, and was succeeded by the Leonid dynasty with the accession of Leo the Great.
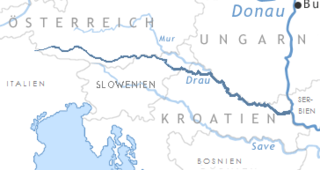
The Battle of the Save was fought in 388 between the forces of Roman usurper Magnus Maximus and the Eastern Roman Empire. Emperor Theodosius I defeated Magnus Maximus's army in battle. Later Maximus was captured and executed at Aquileia.

The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of ancient Rome from the fall of the Roman Republic in 27 BC until the abdication of Romulus Augustulus in AD 476 in the West, and the Fall of Constantinople in the East in AD 1453. Ancient Rome became a territorial empire while still a republic, but was then ruled by Roman emperors beginning with Augustus, becoming the Roman Empire following the death of the last republican dictator, the first emperor's adoptive father Julius Caesar.
References
- ↑ Monmouth, Geoffrey of (2007-12-11). The History of the Kings of Britain. Broadview Press. ISBN 978-1-77048-142-8.