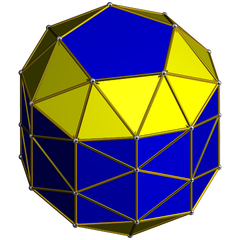
In geometry, a regular icosahedron is a convex polyhedron with 20 faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids, and the one with the most faces.
In geometry, a 4-polytope is a four-dimensional polytope. It is a connected and closed figure, composed of lower-dimensional polytopal elements: vertices, edges, faces (polygons), and cells (polyhedra). Each face is shared by exactly two cells. The 4-polytopes were discovered by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli before 1853.

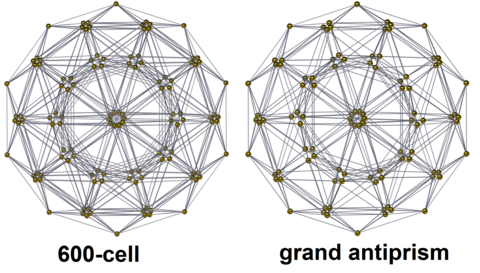
In geometry, the 600-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol {3,3,5}. It is also known as the C600, hexacosichoron and hexacosihedroid. It is also called a tetraplex (abbreviated from "tetrahedral complex") and a polytetrahedron, being bounded by tetrahedral cells.

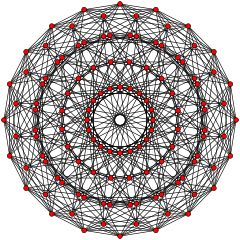
In geometry, the 120-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol {5,3,3}. It is also called a C120, dodecaplex (short for "dodecahedral complex"), hyperdodecahedron, polydodecahedron, hecatonicosachoron, dodecacontachoron and hecatonicosahedroid.

In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.

In geometry of 4 dimensions or higher, a double prism or duoprism is a polytope resulting from the Cartesian product of two polytopes, each of two dimensions or higher. The Cartesian product of an n-polytope and an m-polytope is an (n+m)-polytope, where n and m are dimensions of 2 (polygon) or higher.

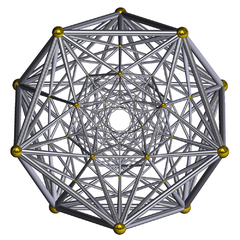
In geometry, the rectified 600-cell or rectified hexacosichoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 600 regular octahedra and 120 icosahedra cells. Each edge has two octahedra and one icosahedron. Each vertex has five octahedra and two icosahedra. In total it has 3600 triangle faces, 3600 edges, and 720 vertices.

In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of ten triangles for a total of twelve faces. Hence, it is a non-regular dodecahedron.

In geometry, the great icosahedron is one of four Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, with Schläfli symbol {3,5⁄2} and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of . It is composed of 20 intersecting triangular faces, having five triangles meeting at each vertex in a pentagrammic sequence.

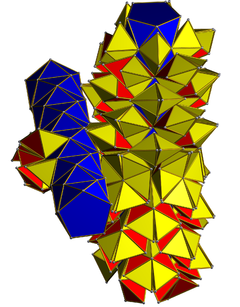
In geometry, the snub 24-cell or snub disicositetrachoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 120 regular tetrahedral and 24 icosahedral cells. Five tetrahedra and three icosahedra meet at each vertex. In total it has 480 triangular faces, 432 edges, and 96 vertices. One can build it from the 600-cell by diminishing a select subset of icosahedral pyramids and leaving only their icosahedral bases, thereby removing 480 tetrahedra and replacing them with 24 icosahedra.

In geometry, a truncated 5-cell is a uniform 4-polytope formed as the truncation of the regular 5-cell.
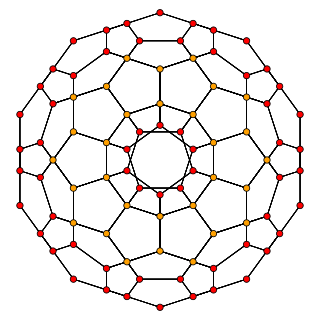
In four-dimensional geometry, a runcinated 120-cell is a convex uniform 4-polytope, being a runcination of the regular 120-cell.
In geometry, a uniform polytope of dimension three or higher is a vertex-transitive polytope bounded by uniform facets. The uniform polytopes in two dimensions are the regular polygons.

In 4-dimensional geometry, a uniform antiprismatic prism or antiduoprism is a uniform 4-polytope with two uniform antiprism cells in two parallel 3-space hyperplanes, connected by uniform prisms cells between pairs of faces. The symmetry of a p-gonal antiprismatic prism is [2p,2+,2], order 8p.

In geometry, a uniform 5-polytope is a five-dimensional uniform polytope. By definition, a uniform 5-polytope is vertex-transitive and constructed from uniform 4-polytope facets.

In four-dimensional geometry, a prismatic uniform 4-polytope is a uniform 4-polytope with a nonconnected Coxeter diagram symmetry group. These figures are analogous to the set of prisms and antiprism uniform polyhedra, but add a third category called duoprisms, constructed as a product of two regular polygons.

In the geometry of 4 dimensions, the 3-3 duoprism or triangular duoprism is a four-dimensional convex polytope. It can be constructed as the Cartesian product of two triangles and is the simplest of an infinite family of four-dimensional polytopes constructed as Cartesian products of two polygons, the duoprisms.

In geometry, the great duoantiprism is the only uniform star-duoantiprism solution p = 5,q = 5/3, in 4-dimensional geometry. It has Schläfli symbol {5}⊗{5/3},s{5}s{5/3} or ht0,1,2,3{5,2,5/3}, Coxeter diagram , constructed from 10 pentagonal antiprisms, 10 pentagrammic crossed-antiprisms, and 50 tetrahedra.