
Plumas County is a county in the Sierra Nevada of California, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 19,790. The county seat is Quincy, and the only incorporated city is Portola. The largest community in the county is East Quincy. The county was named for the Spanish Río de las Plumas, which flows through it.

Carlsbad is a city in and the county seat of Eddy County, New Mexico, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 26,138. Carlsbad is centered at the intersection of U.S. Routes 62/180 and 285, and is the principal city of the Carlsbad-Artesia Micropolitan Statistical Area, which has a total population of 55,435. Located in the southeastern part of New Mexico, Carlsbad straddles the Pecos River and sits at the eastern edge of the Guadalupe Mountains.

Cloudcroft is a village in Otero County, New Mexico, United States, and is located within the Lincoln National Forest. The population was 674 at the 2010 census. Despite being located in an otherwise arid region, its high elevation allows for a mild summer that makes it a popular tourist attraction in west Texas and southern New Mexico. It was named by Fodor's in 2002 as the Number 3 "Most Overlooked and Underrated Destination Spot." Tourism remains the primary economic driver of the village.

The Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest (HTNF) is the principal U.S. National Forest in the U.S. state of Nevada, and has a smaller portion in Eastern California. With an area of 6,289,821 acres (25,454.00 km2), it is the largest U.S. National Forest outside of Alaska.

The Chihuahuan Desert is a desert and ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of West Texas, the middle and lower Rio Grande Valley, the lower Pecos Valley in New Mexico, and a portion of southeastern Arizona, as well as the central and northern portions of the Mexican Plateau. It is bordered on the west by the Sonoran Desert and the extensive Sierra Madre Occidental range, along with northwestern lowlands of the Sierra Madre Oriental range. On the Mexican side, it covers a large portion of the state of Chihuahua, along with portions of Coahuila, north-eastern Durango, the extreme northern part of Zacatecas, and small western portions of Nuevo León. With an area of about 501,896 km2 (193,783 sq mi), it is the largest desert in North America.

Guadalupe Mountains National Park is an American national park in the Guadalupe Mountains, east of El Paso, Texas. The mountain range includes Guadalupe Peak, the highest point in Texas at 8,751 feet (2,667 m), and El Capitan used as a landmark by travelers on the route later followed by the Butterfield Overland Mail stagecoach line. The ruins of a stagecoach station stand near the Pine Springs visitor center. The restored Frijole Ranch contains a small museum of local history and is the trailhead for Smith Spring. The park covers 86,367 acres in the same mountain range as Carlsbad Caverns National Park, about 25 miles (40 km) to the north in New Mexico. The Guadalupe Peak Trail winds through pinyon pine and Douglas-fir forests as it ascends over 3,000 feet (910 m) to the summit of Guadalupe Peak, with views of El Capitan and the Chihuahuan Desert.

Mescalero or Mescalero Apache is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-central New Mexico.

The Guadalupe Mountains are a mountain range located in West Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The range includes the highest summit in Texas, Guadalupe Peak, 8,751 ft (2,667 m), and the "signature peak" of West Texas, El Capitan, both of which are located within Guadalupe Mountains National Park. The Guadalupe Mountains are bordered by the Pecos River valley and Llano Estacado to the east and north, Delaware Mountains to the south, and Sacramento Mountains to the west. One of the clearest exposures of a prehistoric reef is preserved in the mountain range's bedrock geology. Bedrock contains fossils of reef-dwelling organisms from the Permian period, and the geology is widely studied, mostly by stratigraphers, paleontologists, and Paleoecologists.

The Sacramento Mountains are a mountain range in the south-central part of the U.S. state of New Mexico, lying just east of Alamogordo in Otero County. From north to south, the Sacramento Mountains extend for 85 miles (137 km), and from east to west they encompass 42 miles (68 km).
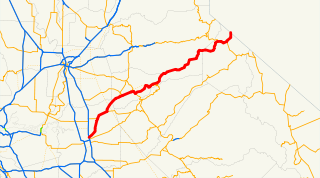
State Route 88, also known as the Carson Pass Highway, is a state highway in the U.S. state of California. It travels in an east–west direction from Stockton in the San Joaquin Valley, crossing the Sierra Nevada at Carson Pass, and ending at the Nevada state line, whereupon it becomes Nevada State Route 88, eventually terminating at U.S. Route 395.

Carson National Forest is a national forest in northern New Mexico, United States. It encompasses 6,070 square kilometers and is administered by the United States Forest Service. The Forest Service's "mixed use" policy allows for its use for recreation, grazing, and resource extraction.

The General Revision Act of 1891, also known as the Forest Reserve Act of 1891, was a federal legislation signed in 1891 by President Benjamin Harrison. The General Revision Act of 1891 reversed previous policy initiatives, such as the Timber Culture Act of 1873, in which land fraud was readily achievable by wealthy individuals and corporations. The acquisition of vast mineral and timber resources in the western United States was often cited as a governing motive for such individuals and corporations to claim land rights for future settlement and resource depletion activities. The legacy of the General Revision Act of 1891 is frequently credited as its serving as a catalyst to a series of federal land reform initiatives, notably under President Theodore Roosevelt. From the Reclamation Act of 1902 to the formation of the United States Forest Service in 1905, the General Revision Act of 1891 acted as a critical first piece of federal legislation granting increased plots of publicly allotted land and decreased extraction rights to privately held western land owners in the early 20th century.

Lincoln National Forest is a unit of the U.S. Forest Service located in southern New Mexico. Established by Presidential Proclamation in 1902 as the Lincoln Forest Reserve, the 1,103,897 acres (4,467.31 km2) forest begins near the Texas border and contains lands in parts of Chaves, Eddy, Lincoln, and Otero counties. The three Ranger Districts within the forest contain all or part of four mountain ranges, and include a variety of different environmental areas, from desert to heavily forested mountains and sub-alpine grasslands. Established to balance conservation, resource management, and recreation, the lands of the Lincoln National Forest include important local timber resources, protected wilderness areas, and popular recreation and winter sports areas. The forest headquarters is located in Alamogordo, N.M. with local offices in Carlsbad, Cloudcroft, and Ruidoso.

ConservAmerica, formerly known as Republicans for Environmental Protection (REP), is a national nonprofit organization formed in 1995. REP's stated purpose is to strengthen the Republican Party's stance on environmental issues and support efforts to conserve natural resources and protect human and environmental health. Incorporated in Illinois, its headquarters are in Sturgis, Michigan.

The Santa Fe National Forest is a protected national forest in northern New Mexico in the Southwestern United States. It was established in 1915 and covers 1,558,452 acres (6,306.83 km2). Elevations range from 5,300 feet (1600 m) to 13,103 feet (4000 m) at the summit of Truchas Peak, located within the Pecos Wilderness. The Jemez, Coyote, and Cuba districts are located in the Jemez Mountains; the Pecos/Las Vegas district is located in the Sangre de Cristo Mountains; and the Española district is located in both mountain ranges. In descending order of land area the forest lies in parts of Rio Arriba, San Miguel, Sandoval, Santa Fe, Mora, and Los Alamos counties. Forest headquarters are located in the city of Santa Fe.

Carlsbad Caverns National Park is an American national park in the Guadalupe Mountains of southeastern New Mexico. The primary attraction of the park is the show cave, Carlsbad Cavern. Visitors to the cave can hike in on their own via the natural entrance or take an elevator from the visitor center.

Alamo National Forest is a disestablished National Forest in southern New Mexico. The Forest was established on July 2, 1908, by an Executive Order (908) signed by President Theodore Roosevelt that consolidated two existing U.S. Forest Service units, the Guadalupe National Forest, established on April 19, 1907, to protect a part of the Guadalupe Mountains north of the Texas border, and the Sacramento National Forest, established on April 24, 1907, to preserve the heavily forested Sacramento Mountains east of Alamogordo. The new forest encompassed approximately 800,000 acres of public land and was divided into a number of Ranger districts, including the Carson Seep district in the former Guadalupe forest and the Fresnal, La Luz, Mayhill and Weed districts in the former Sacramento forest. The Forest boundaries were enlarged on March 2, 1909, by Presidential Proclamation when Roosevelt removed timber-rich land from the adjacent Mescalero Apache Reservation and added them to the forest. These lands were returned to the Mescalero Apache three years later on March 1, 1912, by an Executive Order (1481) signed by President William Howard Taft, who noted his desire to “restore the Mescalero Apache Indian Reservation in all respects to the status existing prior to the said proclamation of March 2, 1909, as though the inclusion of the lands within the Alamo National Forest had not been ordered.” The final change of boundaries came on April 3, 1916, when President Woodrow Wilson issued a proclamation both adding to and eliminating lands from the forest area. A little over a year later the Alamo National Forest was disestablished by Executive Order (2633) and the forest’s lands transferred to the nearby Lincoln National Forest, a former Forest Reserve first established in 1902 to protect lands around Capitan and Lincoln. Under this new administration the Carson Seep Ranger District was renamed the Guadalupe Ranger District, and the Fresnal district was renamed the Cloudcroft district. The Mayhill and Weed districts retained their names until 1961 when the Cloudcroft, Mayhill, and Weed districts were consolidated into the current Sacramento Ranger District.

Sacramento National Forest is a former National Forest in southern New Mexico. The Forest was established by Presidential proclamation on April 24, 1907 to preserve the timber-rich lands in the southern Sacramento Mountains around Cloudcroft and Mayhill. Led by inaugural Forest Supervisor C. H. Hinderer, the forest was headquartered in Alamogordo. Fourteen months later, on July 2, 1908, President Roosevelt issued Executive Order 908. which consolidated the Sacramento with the nearby Guadalupe National Forest to create the Alamo National Forest. Arthur M. Neal, the last supervisor of the independent Guadalupe forest became the initial supervisor for the new Alamo National Forest, with his headquarters in Alamogordo. Under this new administrative scheme the former Sacramento National Forest was divided into a number of individual Ranger Districts within the Alamo National Forest, including Fresnal, La Luz, Mayhill, and Weed. On June 6, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson issued Executive Order 2633, which disestablished the Alamo National Forest and transferred all of its lands to the nearby Lincoln National Forest. As a result of this order, some areas of the former Sacramento National Forest, like La Luz Ranger District, lost their independent status, others were renamed, such as the Fresnal district, which became the Cloudcroft Ranger District, and others, like Mayhill and Weed, retained their original names and designations. In 1961, the Cloudcroft, Mayhill and Weed Ranger Districts were consolidated and given their current designation, the Sacramento Ranger District of the Lincoln National Forest.
Sioux National Forest was a National Forest (NF) established by Executive Order 908 on July 1, 1908. The order called for the consolidation of the following national forests and forest units into a single entity:
The Rio Bonito is a small river in the Sierra Blanca mountains of southern New Mexico, United States. The headwaters of the river start in the Lincoln National Forest on the slopes of Sierra Blanca and travel eastward until they merge with the south fork of the Rio Bonito just west of Bonito Lake, a man-made reservoir. After passing through the reservoir, the river continues in a generally eastward direction passing through the historic Fort Stanton and the home of Billy the Kid, Lincoln, New Mexico. 10 miles (16 km) past Lincoln the Rio Bonito merges with the Rio Ruidoso in the town of Hondo, New Mexico where the two rivers join to form the Rio Hondo which then flows towards the Pecos River. Though not reaching the Pecos except during floods.

















