See also
Y-DNA Q-M242 Subclades
Y-DNA Backbone Tree
| |||
Footnotes
| |||
| Haplogroup Q-M25 | |
|---|---|
| Possible time of origin | 24,300 [95% CI 22,100 <-> 26,700] years before present (YFull v6.02 [1] ) |
| Coalescence age | 16,400 [95% CI 14,900 <-> 18,000] years before present (YFull v6.02 [1] ) |
| Possible place of origin | Central Asia |
| Ancestor | Q-F1096(F1215) |
| Defining mutations | M25 |
Haplogroup Q-M25, also known as Q1a1b is a subclade or branch of human Y-DNA haplogroup Q-F1096 (Q1a1), which is, in turn, a subclade of Q-MEH2 (Q1a). In human genetics, each Y-DNA haplogroup constitutes a biological paternal lineages back to a shared common male ancestor.
Q-M25 has descendants in modern populations across all of Eurasia. Only one detailed study on the Y-DNA on Turkmens from Turkmenistan has taken place. [2] Haplogroup Q is found in minority Turkmen tribes living in Afghanistan at percentages of about 32%, [3] and another study found that 42.6% of Iranian Turkmens have haplogroup Q-M25 (also known as Q1a1b). [4]
Q-M25 has not been detected in pre-Columbian populations in the Americas.
Q-M25 has been detected in the Northeast of East Asia, in South Asia, and across Central Asia. [5] [6] [7] Though present at low frequencies, it may be one of the more widely distributed branches of Q-M242 in Asia.
| Population | Sampling Location | Paper | N | Percentage | SNP Tested |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turkmen | Golestan, Iran | Grugni 2012 [4] | 29/68 | ~42.6% | M25 & M143 |
| Turkmen | Jawzjan, Afghanistan | Di Cristofaro 2013 [3] | 23/74 | ~31.1% | M25 & M346/ (cf)Q1a3(currently Q1a2)=2/74 (Q total=33.8%) |
| Mixed | Central Asia & Siberia | Underhill 2000 [6] | 6/184 | ~3.26% | M25 & M143 |
| Kalmyk | Malyarchuk 2011 [5] | 1/60 | ~1.70% | M25 | |
| Han | Shanxi | Zhong 2010 [7] | 1/56 | ~1.79% | M25 |
| Uyghur | Xinjiang | Zhong 2010 [7] | 1/71 | ~1.41% | M25 |
| Uyghur | Xinjiang | Zhong 2010 [7] | 1/50 | ~2.00% | M25 |
| Uzbek | Jawzjan, Afghanistan | Di Cristofaro 2013 [3] | 1/94 | ~1.06% | M25 |
| Mongol | Mongolia | Di Cristofaro 2013 [3] | 1/160 | ~0.63% | M25 |
The frequency of Q-M25 varies greatly across West Asia. An extreme peak is seen in the Turkmen of Golestan. [4] Across the whole of Iran it varies from over 9 percent of the population in the north to only 2 to 3 percent of the population in the south. [8] The frequency of Q-M25 drops to only about 1 percent of the population of Lebanon's Muslims, and it is absent from the non-Muslim population there. [9] However, its presence in the Marsh Arabs(related to Sumer) of Iraq hints that Q-M25's West Asian history extends beyond a single localized recent founder. [10]
| Population | Sampling Location | Paper | N | Percentage | SNP Tested |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marsh Arabs | Al-Zahery 2011 [10] | 1/143 | ~0.70% | M25/ (cf)Q1b-M378=2.1% | |
| Iraqis | Al-Zahery 2011 [10] | 0/154 | ~0.00% | M25/ (cf)Q1b-M378=1.9% | |
| Iranians | Iran (North) | Regueiro 2006 [8] | 3/33 | ~9.09% | M25 |
| Iranians | Mazandaran | Di Cristofaro 2013 [3] | 1/13 | ~7.69% | M25 |
| Iranians | Iran (South) | Regueiro 2006 [8] | 3/117 | ~2.56% | M25 |
| Iranians | Esfahan | Di Cristofaro 2013 [3] | 1/42 | ~2.38% | M25 |
| Azeris | Iran (Azeri) | Grugni 2012 [4] | 1/63 | ~1.60% | M25 |
| Turkmens | Golestan | Grugni 2012 [4] | 29/68 | ~42.6% | M25 |
| Lebanese (Non-Muslim) | Lebanon | Zalloua 2008 [9] | 0/482 | ~0.00% | M25 |
| Lebanese (Muslim) | Lebanon | Zalloua 2008 [9] | 4/432 | ~0.93% | M25 |
Q-M25 is present across modern Turkey [11] and in Eastern Europe.
| Population | Paper | N | Percentage | SNP Tested | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East Anatolia | Cinnioglu 2004 [11] | 1/82 | ~1.20% | M25 |
Haplogroup Q-M25 is defined by the presence of the M25 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) as well as the M143, L714, and L716 SNPs.
This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft tree Proposed Tree for haplogroup Q-M25.

In human genetics, Haplogroup J-M172 or J2 is a Y-chromosome haplogroup which is a subclade (branch) of haplogroup J-M304. Haplogroup J-M172 is common in modern populations in Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Southern Europe, Northwestern Iran and North Africa. It is thought that J-M172 may have originated between the Caucasus, Anatolia and/or Western Iran.

Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Archipelago, the Caucasus, Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia.
Haplogroup I is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is believed to have originated about 21,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) period in West Asia. The haplogroup is unusual in that it is now widely distributed geographically, but is common in only a few small areas of East Africa, West Asia and Europe. It is especially common among the El Molo and Rendille peoples of Kenya, various regions of Iran, the Lemko people of Slovakia, Poland and Ukraine, the island of Krk in Croatia, the department of Finistère in France and some parts of Scotland and Ireland.

Haplogroup B (M60) is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup common to paternal lineages in Africa. It is a primary branch of the haplogroup BT.

Haplogroup F, also known as F-M89 and previously as Haplogroup FT, is a very common Y-chromosome haplogroup. The clade and its subclades constitute over 90% of paternal lineages outside of Africa.
Haplogroup P also known as P-F5850 or K2b2 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup in human genetics. P-F5850 is a branch of K2b, which is a branch of Haplogroup K2 (K-M526).
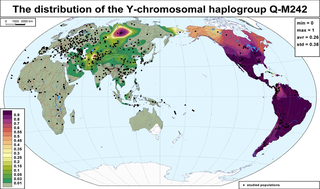
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has one primary subclade, Haplogroup Q1 (L232/S432), which includes numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations.
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346.

In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome. Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).

The Lurs are an Iranian people living in western Iran. The four Luri branches are the Bakhtiari, Mamasani, Kohgiluyeh and Lur proper, who are principally linked by the Luri language.
Haplogroup IJ (M429/P125) is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, an immediate descendant of Haplogroup IJK. IJK is a branch of Haplogroup HIJK.

Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
Haplogroup Q-M346 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q. Haplogroup Q-M346 is defined by the presence of the M346 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP).
Listed here are notable ethnic groups and populations from Western Asia, Egypt and South Caucasus by human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups based on relevant studies. The samples are taken from individuals identified with the ethnic and linguistic designations in the first two columns, the third column gives the sample size studied, and the other columns give the percentage of the particular haplogroup. Some old studies conducted in the early 2000s regarded several haplogroups as one haplogroup, e.g. I, G and sometimes J were haplogroup 2, so conversion sometimes may lead to unsubstantial frequencies below.
Haplogroup Q-L54 is a subclade of Y-DNA haplogroup Q-L53. Q1a3a-L54 is defined by the presence of the L54 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP).
Haplogroup Q-L275 or Haplogroup Q2 is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup believed to have originated in Eurasia. Haplogroup Q-L275 is defined by the presence of the L275 single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Haplogroup Q-L275 can be identified through genealogical DNA testing.
Haplogroup Q-M120, also known as Q1a1a1, is a Y-DNA haplogroup. It is the only primary branch of haplogroup Q1a1a (F746/NWT01). The lineage is most common amongst modern populations in eastern Eurasia.
Haplogroup Q-M323 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q-M346. Haplogroup Q-M323 is defined by the presence of the M323 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP).
Haplogroup K2b (P331), also known as MPS is a human y-chromosome haplogroup that is thought to be less than 3,000 years younger than K, and less than 10,000 years younger than F, meaning it probably is around 50,000 years old, according to the age estimates of Tatiana Karafet et al. 2014.
Haplogroup Q-L804 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-L804 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Currently Q-L804 is Q1b1a1b below Q1b-M346.