Related Research Articles

Tswana, also known by its native name Setswana, and previously spelled Sechuana in English, is a Bantu language spoken in Southern Africa by about 8.2 million people. It belongs to the Bantu language family within the Sotho-Tswana branch of Zone S (S.30), and is closely related to the Northern Sotho and Southern Sotho languages, as well as the Kgalagadi language and the Lozi language.
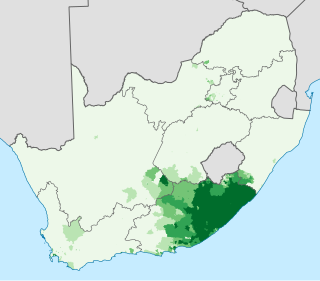
Xhosa also isiXhosa as an endonym, is a Nguni language and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 8.2 million people and by another 11 million as a second language in South Africa, mostly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Gauteng and Northern Cape. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.

Southern Ndebele, also known as Transvaal Ndebele or South Ndebele, is an African language belonging to the Nguni group of Bantu languages, spoken by the Ndebele people of South Africa.

The Swazi or siSwati language is a Bantu language of the Nguni group spoken in Eswatini and South Africa by the Swati people. The number of speakers is estimated to be in the region of 2.4 million. The language is taught in Eswatini and some South African schools in Mpumalanga, particularly former KaNgwane areas. Siswati is an official language of Eswatini, and is also one of the eleven official languages of South Africa.
The Nguni languages are a group of closely related Bantu languages spoken in southern Africa by the Nguni peoples. Nguni languages include Xhosa, Zulu, Ndebele, and Swati. The appellation "Nguni" derives from the Nguni cattle type. Ngoni is an older, or a shifted, variant.

The Swazi or Swati are a Bantu ethnic group in Southern Africa, inhabiting Eswatini, a sovereign kingdom in Southern Africa. EmaSwati are part of the Nguni-language speaking peoples whose origins can be traced through archaeology to East Africa where similar traditions, beliefs and cultural practices are found.
Elandspark is a suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is located in Region 9.
Atholl Gardens is a suburb of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is located in Region E.
Phuthi (Síphùthì) is a Nguni Bantu language spoken in southern Lesotho and areas in South Africa adjacent to the same border. The closest substantial living relative of Phuthi is Swati, spoken in Eswatini and the Mpumalanga province of South Africa. Although there is no contemporary sociocultural or political contact, Phuthi is linguistically part of a historic dialect continuum with Swati. Phuthi is heavily influenced by the surrounding Sesotho and Xhosa languages, but retains a distinct core of lexicon and grammar not found in either Xhosa or Sesotho, and found only partly in Swati to the north.

South African Bantu-speaking peoples are the majority of black South Africans. Occasionally grouped as Bantu, the term itself is derived from the word for "people" common to many of the Bantu languages. The Oxford Dictionary of South African English describes its contemporary usage in a racial context as "obsolescent and offensive" because of its strong association with white minority rule with their apartheid system. However, Bantu is used without pejorative connotations in other parts of Africa and is still used in South Africa as the group term for the language family.
An indaba is an important conference held by the izinDuna of the Zulu and Xhosa peoples of South Africa. Indabas may include only the izinDuna of a particular community, or they may be held with representatives of other communities.
Nguni people are a group of closely related Bantu ethnic groups native to South Africa, with off-shoots in neighbouring countries in Southern Africa. Swazi people live in both South Africa and Eswatini, while Northern Ndebele people live in both South Africa and Zimbabwe.
The Hlubi are an Nguni ethnic group of Southern Africa, with the majority of population found in KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.

The Xhosa people, or Xhosa-speaking people are a Nguni ethnic group whose traditional homeland is primarily the Eastern Cape, South Africa. They are the second largest race group in Southern Africa and are native speakers of the IsiXhosa language.
The Southern Bantu languages are a large group of Bantu languages, largely validated in Janson (1991/92). They are nearly synonymous with Guthrie's Bantu zone S, apart from the exclusion of Shona and the inclusion of Makhuwa. They include all of the major Bantu languages of South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, and Mozambique, with outliers such as Lozi in Zambia and Namibia, and Ngoni in Zambia, Tanzania and Malawi.
Bhaca, or IsiBhaca (Baca) is a Bantu language of South Africa. Traditionally considered a dialect of Swati, it is closer to Zulu, Phuthi and Xhosa. It is spoken southeast of Lesotho, where Sotho, Xhosa and Zulu meet, mainly around Mount Frere, Mzimkhulu, and to a lesser extent in Mount Ayliff, Matatiele, Harding, Bulwer, Underberg, Highflats, Umzinto, Umzumbe and Ixopo.
Lala is a Bantu language of South Africa, claimed to be extinct in some sources. As of 1999, however, there were still a number of communities of speakers in the coastal regions of the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. Although it is a Tekela Nguni language, for sociological reasons it is often considered a dialect of Zulu, whereas it differs quite markedly in phonology and to a degree in morphology, and with a large portion of its lexicon derived from Xhosa and the IsiZansi Tekela variety of the lower South Coast.
Nhlangwini (Hlangwane) is a Bantu language of South Africa. It is located along the border between Xhosa and Zulu, but is more closely related to Swazi. The Nhlangwini people are found in KZN South Coast, Ixopo,uMzimkhulu and Matatiele in areas called Mzongwana and Makhoba.
Several braille alphabets are used in South Africa. For English, Unified English Braille has been adopted. Nine other languages have been written in braille: Afrikaans, Ndebele, Sesotho, Northern Sotho, Swazi, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, and Zulu. All print alphabets are restricted to the basic Latin alphabet, with diacritics in some cases; the braille alphabets are likewise basic braille with additional letters to render the diacritics.

Matiwane, son of Masumpa, was the chief of an independent Nguni-speaking tribe, the amaNgwane, a people named after Matiwane's ancestor Ngwane. The amaNgwane lived at the headwaters of the White Umfolozi, in what is now northern KwaZulu-Natal. The cunning of Matiwane would keep the amaNgwane one step ahead of the ravages of the rising Zulu kingdom, but their actions also set the Mfecane in motion. After his tribe was ousted from their homeland by Zwide or Shaka, Matiwane and his army preyed on neighboring tribes and became vagrant marauders. Eventually he fled South into lands occupied by Xhosa States, which got his whole tribe annihilated at the Battle of Mbholompo. As a refugee Matiwane was at the mercy of the Basutos and Swazis, but eventually had to seek refuge with king Dingane, successor to Shaka. This despotic ruler put Matiwane to death shortly after Matiwane sought his protection.
References
- ↑ "Isizwe SamaHlubi: Submission to the Commission on Traditional Leadership Disputes and Claims: Draft 1" (PDF). July 2004. Retrieved 28 July 2011.
- 1 2 Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- ↑ Swazi at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)