Related Research Articles

The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems.

Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.

The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The human pituitary gland is oval shaped, about the size of a chickpea, and weighs 0.5 grams (0.018 oz) on average.

Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face due to facial plethora, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness.
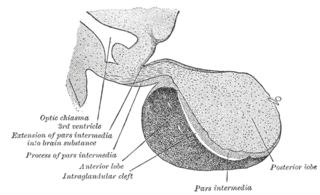
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis). The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels.
Cushing's disease is one cause of Cushing's syndrome characterised by increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary. This is most often as a result of a pituitary adenoma or due to excess production of hypothalamus CRH that stimulates the synthesis of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Pituitary adenomas are responsible for 80% of endogenous Cushing's syndrome, when excluding Cushing's syndrome from exogenously administered corticosteroids. The equine version of this disease is Pituitary pars intermedia dysfunction.

An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure. Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner. Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.
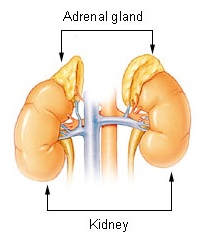
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes to organ failure and shock. Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow.

Hypopituitarism is the decreased (hypo) secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. If there is decreased secretion of one specific pituitary hormone, the condition is known as selective hypopituitarism. If there is decreased secretion of most or all pituitary hormones, the term panhypopituitarism is used.

Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%.
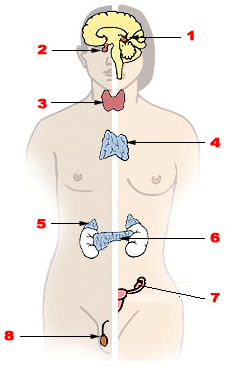
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testicles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.
Nelson's syndrome is a disorder that occurs in about one in four patients who have had both adrenal glands removed to treat Cushing's disease. In patients with pre-existing adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-secreting pituitary adenomas, loss of adrenal feedback following bilateral adrenalectomy can trigger the rapid growth of the tumor, leading to visual symptoms and hyperpigmentation. The severity of the disease is dependent upon the effect of ACTH release on the skin, pituitary hormone loss from mass compression, as well as invasion into surrounding structures around the pituitary gland.
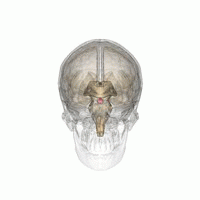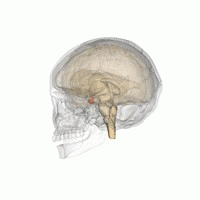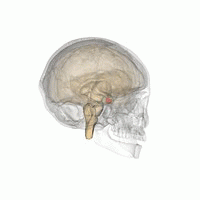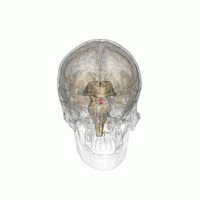
Hyperpituitarism is a condition due to the primary hypersecretion of pituitary hormones; it typically results from a pituitary adenoma. In children with hyperpituitarism, disruption of growth regulation is rare, either because of hormone hypersecretion or because of manifestations caused by local compression of the adenoma.
Pituitary apoplexy is bleeding into or impaired blood supply of the pituitary gland. This usually occurs in the presence of a tumor of the pituitary, although in 80% of cases this has not been diagnosed previously. The most common initial symptom is a sudden headache, often associated with a rapidly worsening visual field defect or double vision caused by compression of nerves surrounding the gland. This is often followed by acute symptoms caused by lack of secretion of essential hormones, predominantly adrenal insufficiency.

Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Transsphenoidal surgery is a type of surgery in which an endoscope or surgical instruments are inserted into part of the brain by going through the nose and the sphenoid bone into the sphenoidal sinus cavity. Transsphenoidal surgery is used to remove tumors of the pituitary gland..

A pituitary disease is a disorder primarily affecting the pituitary gland.

Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure.
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is a minimally invasive technique used mainly in neurosurgery and otolaryngology. A neurosurgeon or an otolaryngologist, using an endoscope that is entered through the nose, fixes or removes brain defects or tumors in the anterior skull base. Normally an otolaryngologist performs the initial stage of surgery through the nasal cavity and sphenoid bone; a neurosurgeon performs the rest of the surgery involving drilling into any cavities containing a neural organ such as the pituitary gland. The use of endoscope was first introduced in Transsphenoidal Pituitary Surgery by R Jankowsky, J Auque, C Simon et al. in 1992 G.

Adrenalism describes the condition of an excessive or substandard secretion of hormones related to the adrenal glands, which are found directly superior to the kidneys. Adrenalism can be further distinguished as hyperadrenalism, referring to the excessive secretion of hormones, and hypoadrenalism, referring to the insufficient secretion of hormones.
References
- ↑ Jaffe, CA (2006). "Clinically non-functioning pituitary adenoma". Pituitary. 9 (4): 317–21. doi:10.1007/s11102-006-0412-9. PMID 17082898. S2CID 2169345.
- ↑ Buchfelder, M; Schlaffer, S (2010). "Pituitary surgery for Cushing's disease" (PDF). Neuroendocrinology. 92 (Suppl 1): 102–6. doi: 10.1159/000314223 . PMID 20829628.
- ↑ "Discussion on Simmonds's Disease. [ Summary ]". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 41 (4): 187–195. April 1948. doi: 10.1177/003591574804100401 . ISSN 0035-9157.
- 1 2 "Pituitary service: Transsphenoidal hypophysectomy" (PDF). uclh.nhs.uk. June 2014. Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- ↑ "Dramatically Increased Intestinal Absorption of Cholesterol Following Hypophysectomy Is Normalized by Thyroid Hormone". Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-15. Retrieved 2013-10-15.
- ↑ Gaillard, Frank. "Transsphenoidal hypophysectomy | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- ↑ "Stereotactic Radiosurgery - Treatments - For Patients - UR Neurosurgery - University of Rochester Medical Center". www.urmc.rochester.edu. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- ↑ Swearingers. Manuel of medical surgical nursing: A care planning Resource. 7th Edition