
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term piracy generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and outer space. Piracy usually excludes crimes committed by the perpetrator on their own vessel, as well as privateering, which implies authorization by a state government.

The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.
Maritime security is an umbrella term informed to classify issues in the maritime domain that are often related to national security, marine environment, economic development, and human security. This includes the world's oceans but also regional seas, territorial waters, rivers and ports, where seas act as a “stage for geopolitical power projection, interstate warfare or militarized disputes, as a source of specific threats such as piracy, or as a connector between states that enables various phenomena from colonialism to globalization”. The theoretical concept of maritime security has evolved from a narrow perspective of national naval power projection towards a buzzword that incorporates many interconnected sub-fields. The definition of the term maritime security varies and while no internationally agreed definition exists, the term has often been used to describe both existing, and new regional and international challenges to the maritime domain. The buzzword character enables international actors to discuss these new challenges without the need to define every potentially contested aspect of it. Maritime security is of increasing concern to the global shipping industry, where there are a wide range of security threats and challenges. Some of the practical issues clustered under the term of maritime security include crimes such as piracy, armed robbery at sea, trafficking of people and illicit goods, illegal fishing or marine pollution. War, warlike activity, maritime terrorism and interstate rivalry are also maritime security concerns.

The Piracy Act 1837 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It abolished the death penalty for most offences of piracy, but created a new offence often known as piracy with violence, which was punishable with death. This offence still exists in the United Kingdom and in the Republic of Ireland, but is no longer punishable by death in either country.
Maritime Security Regimes are codes and conventions of behavior agreed upon by coastal states to provide a degree of security within territorial waters and on the high seas.

Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea affects a number of countries in West Africa as well as the wider international community. By 2011, it had become an issue of global concern. Pirates in the Gulf of Guinea are often part of heavily armed criminal enterprises, who employ violent methods to steal oil cargo. In 2012, the International Maritime Bureau, Oceans Beyond Piracy and the Maritime Piracy Humanitarian Response Program reported that the number of vessels attacks by West African pirates had reached a world high, with 966 seafarers attacked during the year. According to the Control Risks Group, pirate attacks in the Gulf of Guinea had by mid-November 2013 maintained a steady level of around 100 attempted hijackings in the year, a close second behind the Strait of Malacca in Southeast Asia. Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea continues to be a concern to the shipping industry, which is affected significantly. At the same time, governments in the region generally highlight that the fight against piracy requires a broad understanding of maritime security throughout the Gulf of Guinea.
Piracy off the coast of Somalia occurs in the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and Somali Sea, in Somali territorial waters and other surrounding places and has a long and troubled history with different perspectives from different communities. It was initially a threat to international fishing vessels, expanding to international shipping since the consolidation of states phase of the Somali Civil War around 2000.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1918, adopted unanimously on April 27, 2010, after recalling resolutions 1814 (2008), 1816 (2008), 1838 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1846 (2008), 1851 (2008) and 1897 (2008) on Somalia, the Council called on countries to criminalise piracy within their national laws.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1950, adopted unanimously on November 23, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Somalia, including resolutions 1814 (2008), 1816 (2008), 1838 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1846 (2008), 1851 (2008), 1897 (2009) and 1918 (2010); the Council re-authorised states to intervene in acts of piracy by Somali pirates at sea for a further period of twelve months.

Piracy in the 21st century has taken place in a number of waters around the world, including the Gulf of Guinea, Strait of Malacca, Sulu and Celebes Seas, Indian Ocean, and Falcon Lake.
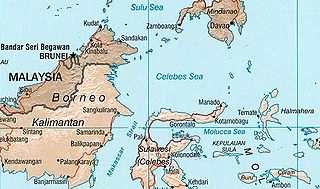
The Sulu and Celebes Seas, a semi-enclosed sea area and porous region that covers an area of space around 1 million square kilometres, have been subject to illegal maritime activities since the pre-colonial era and continue to pose a maritime security threat to bordering nations up to this day. While piracy has long been identified as an ubiquitous challenge, being historically interwoven with the region, recent incidents also include other types of maritime crimes such as kidnapping and the trafficking of humans, arms and drugs. Attacks mostly classify as 'armed robbery against ships' according to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea as they occur in maritime zones that lie under the sovereignty of a coastal state. Incidents in the Sulu and Celebes Seas specifically involve the abduction of crew members. Since March 2016, the Information Sharing Centre (ISC) of the Regional Cooperation Agreement on Combating Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in Asia (ReCAAP) reports a total of 86 abuctions, leading to the issue of a warning for ships transpassing the area.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1897 was unanimously adopted on 30 November 2009.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1816 was unanimously adopted on 2 June 2008.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1846 was unanimously adopted on 2 December 2008.
In keeping with the Paris Principles definition of a child soldier, the Roméo Dallaire Child Soldiers Initiative defines a child pirate as any person below 18 years of age who is or who has been recruited or used by a pirate gang in any capacity, including children – boys and/or girls – used as gunmen in boarding parties, hostage guards, negotiators, ship captains, messengers, spies or for sexual purposes, whether at sea or on land. It does not only refer to a child who is taking or has taken a direct part in kinetic criminal operations.

Offshore installation security is the protection of maritime installations from intentional harm. As part of general maritime security, offshore installation security is defined as the installation's ability to combat unauthorized acts designed to cause intentional harm to the installation. The security of offshore installations is vital as not only may a threat result in personal, economic, and financial losses, but it also concerns the strategic aspects of the petroleum market and geopolitics.
Maritime terrorism in Southeast Asia refers to acts of extreme maritime violence committed with political motives within the Southeast Asian region. Despite seaborne terrorist attacks accounting for only 2% of all international terrorist incidents from 1978 to 2008, according to RAND's Terrorism Database, Southeast Asia has proven a hotbed of maritime terrorism. Due to the high frequency of pirates in the region, many Southeast Asian-based terrorist groups have appropriated piratical tactics in carrying out their violent political struggles. In 2003, the International Maritime Bureau reported that out of the 445 actual or attempted piratical attacks on merchant vessels, 189 occurred in Southeast Asia, which was more cases than either Africa or Latin America, with 121 attacks occurring in Indonesian waters and 35 attacks occurring in Malaysian and Singaporean waters. In 2004, while the number of actual and attempted attacks fell to 325, Southeast Asia remained at the top of the regional rankings, with 93 incidents occurring in Indonesian waters. Between 2014 and 2018, 242 attacks occurred in Southeast Asia, with the majority occurring in Indonesian waters. The most popular weapons of choice among Southeast Asian maritime terrorists have been explosive devices and firearms, which were used in roughly 60% of maritime attacks in the region.
As a practice of piracy, petro-piracy, also sometimes called oil piracy or petrol piracy, is defined as “illegal taking of oil after vessel hijacks, which are sometimes executed with the use of motorships” with huge potential financial rewards. Petro-piracy is mostly a practice that is connected to and originates from piracy in the Gulf of Guinea, but examples of petro-piracy outside of the Gulf of Guinea is not uncommon. At least since 2008, the Gulf of Guinea has been home to pirates practicing petro-piracy by targeting the region's extensive oil industry. Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea has risen in the last years to become the hot spot of piracy globally with 76 actual and attempted attacks, according to the International Maritime Bureau (IMB). Most of these attacks in the Gulf of Guinea take place in inland or territorial waters, but recently pirates have been proven to venture further out to sea, e.g. crew members were kidnapped from the tanker David B. 220 nautical miles outside of Benin. Pirates most often targets vessels carrying oil products and kidnappings of crew for ransom. IMB reports that countries in the Gulf of Guinea, Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Togo, Congo, and, especially, Nigeria, have experienced petro-piracy and kidnappings of crew as the most common trends of piracy attacks in the Gulf of Guinea.
Piracy kidnappings occur during piracy, when people are kidnapped by pirates or taken hostage. Article 1 of the United Nations International Convention against the Taking of Hostages defines a hostage-taker as "any person who seizes or detains and threatens to kill, to injure, or to continue to detain another person in order to compel a third party namely, a State, an international intergovernmental organization, a natural or Juridical person, or a group of people, to do or abstain from doing any act as an explicit or implicit condition tor the release of the hostage commits the offense of taking of hostages ("hostage-taking") within the meaning of this Convention." Kidnappers often try to obtain the largest financial reward possible in exchange for hostages, but piracy kidnappings can also be politically motivated.












