Related Research Articles

The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal.
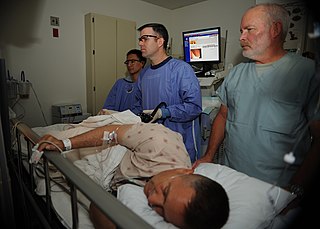
Colonoscopy or coloscopy is a medical procedure involving the endoscopic examination of the large bowel (colon) and the distal portion of the small bowel. This examination is performed using either a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera, which is mounted on a flexible tube and passed through the anus.

A polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be sessile.

An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure. Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may transform to become malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner. Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.

A rectal prolapse occurs when walls of the rectum have prolapsed to such a degree that they protrude out of the anus and are visible outside the body. However, most researchers agree that there are 3 to 5 different types of rectal prolapse, depending on whether the prolapsed section is visible externally, and whether the full or only partial thickness of the rectal wall is involved.

Gardner's syndrome is a subtype of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Gardner syndrome is an autosomal dominant form of polyposis characterized by the presence of multiple polyps in the colon together with tumors outside the colon. The extracolonic tumors may include osteomas of the skull, thyroid cancer, epidermoid cysts, fibromas, as well as the occurrence of desmoid tumors in approximately 15% of affected individuals.
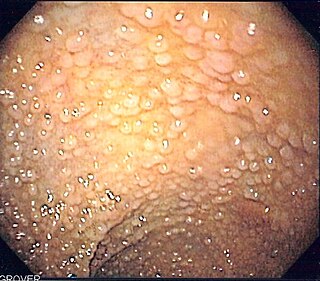
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when they are left untreated. Three variants are known to exist, FAP and attenuated FAP are caused by APC gene defects on chromosome 5 while autosomal recessive FAP is caused by defects in the MUTYH gene on chromosome 1. Of the three, FAP itself is the most severe and most common; although for all three, the resulting colonic polyps and cancers are initially confined to the colon wall. Detection and removal before metastasis outside the colon can greatly reduce and in many cases eliminate the spread of cancer.
Rectal bleeding refers to bleeding in the rectum, thus a form of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. There are many causes of rectal hemorrhage, including inflamed hemorrhoids, rectal varices, proctitis, stercoral ulcers, and infections. Diagnosis is usually made by proctoscopy, which is an endoscopic test.

Fundic gland polyposis is a medical syndrome where the fundus and the body of the stomach develop many fundic gland polyps. The condition has been described both in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and attenuated variants (AFAP), and in patients in whom it occurs sporadically.

Colonic polypectomy is the removal of colorectal polyps in order to prevent them from turning cancerous.

Juvenile polyposis syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition characterized by the appearance of multiple juvenile polyps in the gastrointestinal tract. Polyps are abnormal growths arising from a mucous membrane. These usually begin appearing before age 20, but the term juvenile refers to the type of polyp, not to the age of the affected person. While the majority of the polyps found in juvenile polyposis syndrome are non-neoplastic, hamartomatous, self-limiting and benign, there is an increased risk of adenocarcinoma.

A colorectal polyp is a polyp occurring on the lining of the colon or rectum. Untreated colorectal polyps can develop into colorectal cancer.

A sessile serrated lesion (SSL) is a premalignant flat lesion of the colon, predominantly seen in the cecum and ascending colon.
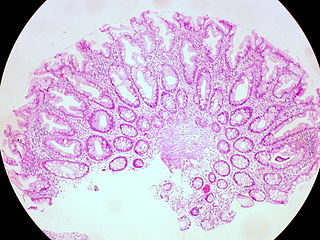
A hyperplastic polyp is a type of gastric polyp or colorectal polyp.
Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome or SRUS is a chronic disorder of the rectal mucosa. It commonly occurs with varying degrees of rectal prolapse. The condition is thought to be caused by different factors, such as long term constipation, straining during defecation, and dyssynergic defecation. Treatment is by normalization of bowel habits, biofeedback, and other conservative measures. In more severe cases various surgical procedures may be indicated. The condition is relatively rare, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 people per year. It affects mainly adults aged 30–50. Females are affected slightly more often than males. The disorder can be confused clinically with rectal cancer or other conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, even when a biopsy is done.

Serrated polyposis syndrome (SPS), previously known as hyperplastic polyposis syndrome, is a disorder characterized by the appearance of serrated polyps in the colon. While serrated polyposis syndrome does not cause symptoms, the condition is associated with a higher risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). The lifelong risk of CRC is between 25 and 40%. SPS is the most common polyposis syndrome affecting the colon, but is under recognized due to a lack of systemic long term monitoring. Diagnosis requires colonoscopy, and is defined by the presence of either of two criteria: five or more serrated lesions/polyps proximal to the rectum, or more than 20 serrated lesions/polyps of any size distributed throughout the colon with five proximal to the rectum.
Polymerase proofreading-associated polyposis (PPAP) is an autosomal dominant hereditary cancer syndrome, which is characterized by numerous polyps in the colon and an increased risk of colorectal cancer. It is caused by germline mutations in DNA polymerase ε (POLE) and δ (POLD1). Affected individuals develop numerous polyps called colorectal adenomas. Compared with other polyposis syndromes, Polymerase proofreading-associated polyposis is rare. Genetic testing can help exclude similar syndromes, such as Familial adenomatous polyposis and MUTYH-associated polyposis. Endometrial cancer, duodenal polyps and duodenal cancer may also occur.

Traditional serrated adenoma is a premalignant type of polyp found in the colon, often in the distal colon. Traditional serrated adenomas are a type of serrated polyp, and may occur sporadically or as a part of serrated polyposis syndrome. Traditional serrated adenomas are relatively rare, accounting for less than 1% of all colon polyps. Usually, traditional serrated adenomas are found in the distal colon and are usually less than 10 mm in size.

Segmental colitis associated with diverticulosis (SCAD) is a condition characterized by localized inflammation in the colon, which spares the rectum and is associated with multiple sac-like protrusions or pouches in the wall of the colon (diverticulosis). Unlike diverticulitis, SCAD involves inflammation of the colon between diverticula, while sparing the diverticular orifices. SCAD may lead to abdominal pain, especially in the left lower quadrant, intermittent rectal bleeding and chronic diarrhea.
Gardner fibroma (GF) is a benign fibroblastic tumor. GF tumors typically develop in the dermis and adjacent subcutaneous tissue lying just below the dermis. These tumors typically occur on the back, abdomen, and other superficial sites but in rare cases have been diagnoses in internal sites such as the retroperitoneum and around the large blood vessels in the upper thoracic cavity. The World Health Organization, 2020, classified Gardner fibroma as a benign tumor in the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
References
- ↑ Popović M, Knežević A, Škopelja JD, Đolai M (2022). "JUVENILE POLYP IN ADULTS". Acta Clinica Croatica. 61 (2): 354–358. doi: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.02.23 . PMC 9934046 . PMID 36818922.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brosens, LA; Langeveld, D; van Hattem, WA; Giardiello, FM; Offerhaus, GJ (28 November 2011). "Juvenile polyposis syndrome". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 17 (44): 4839–44. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i44.4839 . PMC 3235625 . PMID 22171123.
- 1 2 Fox, VL; Perros, S; Jiang, H; Goldsmith, JD (September 2010). "Juvenile polyps: recurrence in patients with multiple and solitary polyps". Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 8 (9): 795–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.05.010 . PMID 20580940.
- 1 2 Nugent, KP; Talbot, IC; Hodgson, SV; Phillips, RK (September 1993). "Solitary juvenile polyps: not a marker for subsequent malignancy". Gastroenterology. 105 (3): 698–700. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(93)90885-g. PMID 8395444.
- 1 2 Hood, B; Bigler, S; Bishop, P; Liu, H; Ahmad, N; Renault, M; Nowicki, M (October 2011). "Juvenile polyps and juvenile polyp syndromes in children: a clinical and endoscopic survey". Clinical Pediatrics. 50 (10): 910–5. doi:10.1177/0009922811407177. PMID 21576185. S2CID 8295632.
- ↑ "Familial Juvenile Polyposis". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- 1 2 Durno, CA (April 2007). "Colonic polyps in children and adolescents". Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology. 24 (4): 233–239. doi: 10.1155/2007/401674 . PMC 2657698 . PMID 17431512.
- ↑ Olafsdottir, I; Nemeth, A; Lörinc, E; Toth, E; Agardh, D (January 2016). "Value of Fecal Calprotectin as a Biomarker for Juvenile Polyps in Children Investigated With Colonoscopy". Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. 62 (1): 43–6. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000893 . PMID 26147630. S2CID 19284840.