Notes
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note: The Guthrie classification is geographic and its groupings do not imply a relationship between the languages within them. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | This Bantu language-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| Kilombero | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Tanzania |
| Linguistic classification | Niger–Congo? |
| Glottolog | None |
The Kilombero languages are a group of Bantu languages of Tanzania established in Nurse (1988).
The languages, along with their Guthrie identifications, are:

Arabic is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE. It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the Arabian Peninsula bounded by eastern Egypt in the west, Mesopotamia in the east, and the Anti-Lebanon mountains and Northern Syria in the north, as perceived by ancient Greek geographers. The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic, also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ). Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 26 states and 1 disputed territory, the third most after English and French.
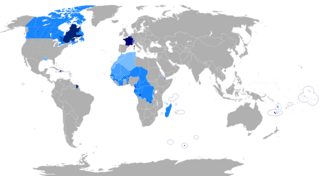
French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.

Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in North India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of Northern India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with the English language. It is an official language in 9 States and 3 Union Territories and an additional official language in 3 other States. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Italian is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. Italian is the closest national language to Latin, from which it descends via vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Taking into account both national and regional languages, it is seen that Italian and Sardinian are together the least differentiated from Latin. Italian is an official language in Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, and Vatican City. It has an official minority status in western Istria.

The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form. The IPA is used by lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguists, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators and translators.

A language is a structured system of communication used by humans, based on speech and gesture, sign, or often writing. The structure of language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is unique among known systems of animal communication in that it is not dependent on a single mode of transmission, it is highly variable between cultures and across time, and affords a much wider range of expression than other systems. It has the properties of productivity and displacement, and relies on social convention and learning.
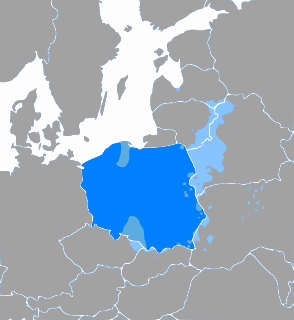
Polish is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group, written in Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by Polish minorities in other countries. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world – it is the sixth-most-spoken language of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T-V distinction pronouns, honorifics and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals.

The Romance languages are the modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin between the third and eighth centuries. They are a subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language family. The six most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian, Romanian, and Catalan. Italian is the closest national language to Latin, followed by Spanish, Romanian, Portuguese, and the most divergent being French. Taking into account all the Romance languages, including national and regional languages, Sardinian, Italian and Spanish are together the three least differentiated from Latin, also Occitan is closer to Latin than French. However, all Romance languages are closer to each other than to classical Latin.

Turkish, also referred to as Istanbul Turkish or Turkey Turkish, is the most widely spoken of the Turkic languages, with around 70 to 80 million speakers. It is the national language of Turkey. Significant smaller groups of Turkish speakers exist in Iraq, Syria, Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Northern Cyprus, Greece, the Caucasus, and other parts of Europe and Central Asia. Cyprus has requested that the European Union add Turkish as an official language, even though Turkey is not a member state.
Indian English (IE) is a class of varieties of the English language spoken in India, and among the Indian diaspora elsewhere in the world. English is used by the Indian government for communication along with Hindi, as enshrined in the Constitution. English is an official language of 7 states and 5 Union Territories and also additional official language of 7 states and 1 Union Territory. English is also the sole official language of the Judiciary of India, unless a state governor or legislature mandates the use of a regional language, or the president has given approval for the use of regional languages in courts.
RPL is a handheld calculator operating system and application programming language used on Hewlett-Packard's scientific graphing RPN calculators of the HP 28, 48, 49 and 50 series, but it is also usable on non-RPN calculators, such as the 38, 39 and 40 series.

The dollar sign is a symbol consisting of a capital "S" crossed with one or two vertical strokes, used to indicate the unit of various currencies around the world — including most currencies denominated "peso" and "dollar". The sign is also used as an element of several compound currency symbols, such as the Brazilian real (R$) and the Nicaraguan córdoba (C$).
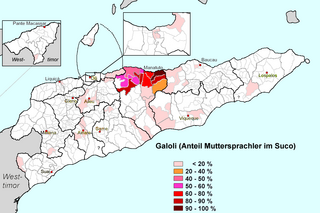
The Galoli, or Galolen, are a people of East Timor with a population of about 50,000, primarily along the northern coast of the district of Manatuto. To the west lies the Mambai people. There is an old colony on the southern coast of Wetar island, the Talo, who speak the Talur dialect.
Gogo is a Bantu language spoken by the Gogo people of Dodoma Region in Tanzania. The language is spoken throughout Dodoma Region and into the neighbouring district of Manyoni.
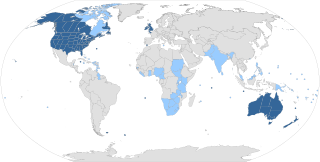
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, originally spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea which is not to be confused with East Anglia, the Eastern part of England which comprises the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Essex. English is most closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, while its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse, as well as Latin and French.

The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was the only practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.
The Northeast Bantu languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken in East Africa. In Guthrie's geographic classification, they fall within Bantu zones E50 plus E46 (Sonjo), E60 plus E74a (Taita), F21–22, J, G60, plus Northeast Coast Bantu. Some of these languages share a phonological innovation called Dahl's law that is unlikely to be borrowed as a productive process, though individual words reflecting Dahl's law have been borrowed into neighboring languages.

A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form of information storage and transfer. Writing systems require shared understanding between writers and readers of the meaning behind the sets of characters that make up a script. Writing is usually recorded onto a durable medium, such as paper or electronic storage, although non-durable methods may also be used, such as writing on a computer display, on a blackboard, in sand, or by skywriting. Reading a text can be accomplished purely in the mind as an internal process, or expressed orally.

The Sama language, Sinama, is the language of Sama-Bajau people of the Sulu Archipelago, Philippines; Sabah, Malaysia and parts of Indonesia. The Sama are one of the most widely dispersed peoples in Southeast Asia.