
Rhys ap Gruffydd or ap Gruffudd was the ruler of the kingdom of Deheubarth in south Wales from 1155 to 1197. Today, he is commonly known as The Lord Rhys, in Welsh Yr Arglwydd Rhys, although this title may have not been used in his lifetime. He usually used the title "Proprietary Prince of Deheubarth" or "Prince of South Wales", but two documents have been discovered in which he uses the title "Prince of Wales" or "Prince of the Welsh". Rhys was one of the most successful and powerful Welsh princes, and, after the death of Owain Gwynedd of Gwynedd in 1170, the dominant power in Wales.

Ceredigion, historically Cardiganshire, is a county in the west of Wales. It borders Gwynedd across the Dyfi estuary to the north, Powys to the east, Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. Aberystwyth is the largest settlement and, together with Aberaeron, is an administrative centre of Ceredigion County Council.

Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda Wledig, was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of Western Europe.

Ceredig ap Cunedda, was king of Ceredigion in Wales.

Cardigan is a town and community in the county of Ceredigion, Wales. Positioned on the tidal reach of the River Teifi at the point where Ceredigion meets Pembrokeshire, Cardigan was the county town of the historic county of Cardiganshire. Cardigan is the second-largest town in Ceredigion. The largest town, Aberystwyth, is one of the two administrative centres; the other is Aberaeron.

Cenarth is a village, parish and community in Carmarthenshire, on the border between Ceredigion and Carmarthenshire, and close to the border with Pembrokeshire, Wales. It stands on the banks of the River Teifi, 6 miles (9.7 km) east of Cardigan and 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Newcastle Emlyn, and features the Cenarth Falls, a popular visitor attraction, and several other listed structures including an 18th-century corn mill incorporating the National Coracle Centre.

The River Teifi in Wales forms the boundary for most of its length between the counties of Ceredigion and Carmarthenshire, and for the final 3 miles (4.8 km) of its total length of 76 miles (122 km), the boundary between Ceredigion and Pembrokeshire. Its estuary is northwest of Cardigan, known in Welsh as Aberteifi, meaning 'mouth of the Teifi'. Teifi has formerly been anglicised as "Tivy".

Llanddewi Brefi is a village, parish and community of approximately 500 people in Ceredigion, Wales. The village is notable for the famous Synod of Brefi held here in the sixth century. A number of miraculous events are said to have occurred during the synod, most notably by Saint David Welsh: Dewi Sant, patron saint of Wales. Today, it is one of the largest parishes in Wales and lies 7 miles (11 km) north-east of Lampeter between Tregaron and Llanfair Clydogau.
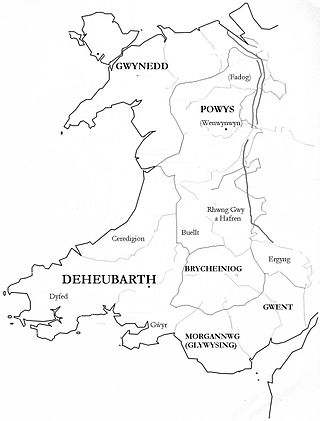
Seisyllwg was a petty kingdom of medieval Wales. It is unclear when it emerged as a distinct unit, but according to later sources it consisted of the former Kingdom of Ceredigion plus the region known as Ystrad Tywi. Thus it covered the modern county of Ceredigion, part of Carmarthenshire, and the Gower Peninsula. It is evidently named after Seisyll, king of Ceredigion in the 7th or early 8th century, but it is unknown if he was directly responsible for its establishment. In the 10th century Seisyllwg became the centre of power for Hywel Dda, who came to rule most of Wales. In 920 Hywel merged Seisyllwg with the Kingdom of Dyfed to form the new kingdom of Deheubarth.
Maelgwn ap Rhys was prince of part of the kingdom of Deheubarth in south west Wales.
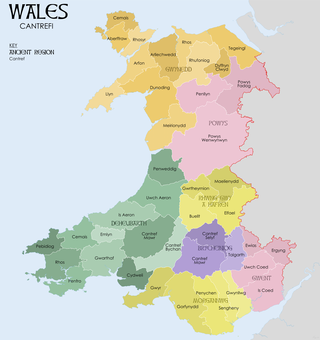
A cantref was a medieval Welsh land division, particularly important in the administration of Welsh law.

The Battle of Crug Mawr, sometimes referred to as the Battle of Cardigan, took place in September or October 1136, as part of a struggle between the Welsh and Normans for control of Ceredigion, West Wales.

Rhys Gryg, real name Rhys ap Rhys, also known as Rhys Fychan, was a Welsh prince who ruled part of the Kingdom of Deheubarth.

Creuddyn was a medieval commote and, later, a lordship in Ceredigion, Wales. It was located between the rivers Ystwyth and Rheidol, and was one of the three commotes of Cantref Penweddig. The name, of Old Welsh origin, probably refers to the Pen Dinas hill fort, anciently known as Dinas Maelor. The natural centre of the commote was Llanfihangel y Creuddyn where five roads meet at the village. The name survives in the name of a rural community and church of the same name; however the modern community is much smaller than the medieval commote.
Angharad ferch Meurig was a 9th-century Welsh noblewoman. She was the wife of Rhodri the Great of Gwynedd, and mother of Anarawd, Cadell ap Rhodri, and Merfyn.
Gwgon ap Meurig was a 9th-century king of Ceredigion and Ystrad Tywi in southwest Wales.

Saint Tysul was a 5th-century pre-canonical saint and patron saint of the churches of Llandysul in Ceredigion (Cardiganshire) and Llandyssil in Maldwyn (Montgomeryshire), Powys. Tysul’s full name was Tysul ap Corun ap Cunedda – or son of Corun, son of Cunedda. His feast day is 31 January.

Cemaes Head is a headland and nature reserve in north Pembrokeshire. It lies in the community of St Dogmaels, within the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park. To the west and north it overlooks Cardigan Bay, and to the east Cardigan Island and the estuary of the River Teifi.
Saint Meleri was a late 5th century Welsh saint and Queen of Ceredigion.

















