
Sylt is a former island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian Islands and is the largest island in North Frisia. The northernmost island of Germany, it is known for its tourist resorts, notably Westerland, Kampen and Wenningstedt-Braderup, as well as for its 40-kilometre-long (25-mile) sandy beach. It is frequently covered by the media in connection with its exposed situation in the North Sea and its ongoing loss of land during storm tides. Since 1927, Sylt has been connected to the mainland by the Hindenburgdamm causeway. In later years, it has been a resort for the German jet set and tourists in search of occasional celebrity sightings.

Ameland is a municipality and one of the West Frisian Islands off the north coast of the Netherlands. It consists mostly of sand dunes and is the third major island of the West Frisians. It neighbours islands Terschelling to the west and Schiermonnikoog to the east. This includes the small Engelsmanplaat and Rif sandbanks to the east.

The East Frisian Islands are a chain of islands in the North Sea, off the coast of East Frisia in Lower Saxony, Germany. The islands extend for some 90 kilometres (56 mi) from west to east between the mouths of the Ems and Jade / Weser rivers and lie about 3.5 to 10 km offshore. Between the islands and the mainland are extensive mudflats, known locally as Watten, which form part of the Wadden Sea. In front of the islands are Germany's territorial waters, which occupy a much larger area than the islands themselves. The islands, the surrounding mudflats and the territorial waters form a close ecological relationship. The island group makes up about 5% of the Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park.

Wittmund is a Landkreis (district) in the northwestern part of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated in East Frisia, on the North Sea coast. Neighboring districts are Friesland, Leer and Aurich.
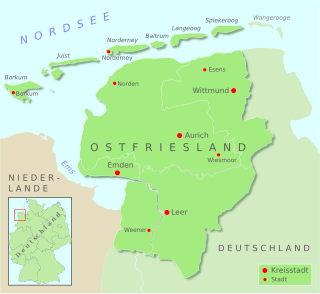
East Frisia or East Friesland is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia and to the west of Landkreis Friesland.

Borkum is an island and a municipality in the Leer District in Lower Saxony, northwestern Germany. It is situated east of Rottumeroog and west of Juist.
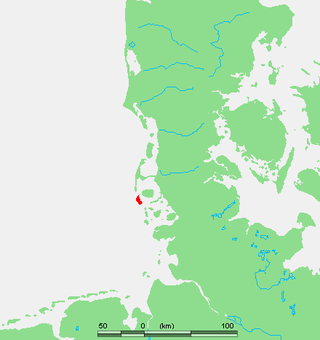
Amrum is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants.

The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Islands or the Wadden Sea Islands, form an archipelago at the eastern edge of the North Sea in northwestern Europe, stretching from the northwest of the Netherlands through Germany to the west of Denmark. The islands shield the mudflat region of the Wadden Sea from the North Sea.
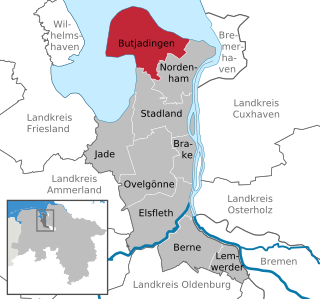
Butjadingen is a peninsula and municipality in the Wesermarsch district, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

Wittmund is a town and capital of the district of Wittmund, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

Norderney is one of the seven populated East Frisian Islands off the North Sea coast of Germany.

Juist is an island and municipality in the district of Aurich in Lower Saxony in Germany. The island is one of seven East Frisian Islands at the edge of the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea in the southern North Sea. It is located between Borkum Island (west), Memmert Island (southwest) and Norderney (east). The island is 17 km (11 mi) long and from 500 metres (1,600 ft) to 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) wide, depending on the tide levels. There are two villages on the island: the main village Juist, and Loog. The island is separated from Norderney by the Norderneyer Seegatt.

Papenburg is a city in the district of Emsland, Lower Saxony, Germany, situated at the river Ems. It is known for its large shipyard, the Meyer-Werft, which specializes in building cruise liners.

Garbsen is a town in the district of Hanover, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the river Leine, approx. 11 km northwest of Hanover. The name Garbsen can be traced back to 1223. Today's 13 city districts have partly developed independently until the city of Garbsen was formed within its current boundaries during the regional reform in 1974.

Wangerooge is one of the 32 Frisian Islands in the North Sea located close to the coasts of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark. It is also a municipality in the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony in Germany.

Baltrum is a barrier island off the coast of East Frisia, in Germany, and is a municipality in the district of Aurich, Lower Saxony. It is located in-between the chain of the seven inhabited East Frisian Islands. Baltrum is the smallest island in this chain by area and inhabitants. It has a land area of 6.5 square kilometres, and a population in (2011) of just over 500 resident inhabitants.

Spiekeroog is one of the East Frisian Islands, off the North Sea coast of Germany. It is situated between Langeoog to its west, and Wangerooge to its east. The island belongs to the district of Wittmund, in Lower Saxony in Germany. The only village on the island is also called Spiekeroog. The island is part of the Wadden Sea World Heritage Site by the UNESCO and the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park.

The single track Wangerooge Island Railway is an unelectrified narrow gauge railway with a track gauge of 1,000 mm located on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge off the northwestern coast of Germany. It is the most important means of transport on the island and is the only narrow gauge railway operated today by the Deutsche Bahn.

Minsener Oog, also Minser Oog or Minsener Oldeoog, is an uninhabited East Frisian island that belongs to the parish of Wangerooge in the north German district of Friesland in the state of Lower Saxony. It has been artificially enlarged through the construction of groynes.





























