
The East Frisian Islands are a chain of islands in the North Sea, off the coast of East Frisia in Lower Saxony, Germany. The islands extend for some 90 kilometres (56 mi) from west to east between the mouths of the Ems and Jade / Weser rivers and lie about 3.5 to 10 km offshore. Between the islands and the mainland are extensive mudflats, known locally as Watten, which form part of the Wadden Sea. In front of the islands are Germany's territorial waters, which occupy a much larger area than the islands themselves. The islands, the surrounding mudflats and the territorial waters form a close ecological relationship. The island group makes up about 5% of the Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park.

Wittmund is a Landkreis (district) in the northwestern part of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated in East Frisia, on the North Sea coast. Neighboring districts are Friesland, Leer and Aurich.
Friesland is a district (Landkreis) in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Wesermarsch, Ammerland, Leer and Wittmund, and by the North Sea. The city of Wilhelmshaven is enclosed by—but not part of—the district.

Borkum is an island and a municipality in the Leer District in Lower Saxony, northwestern Germany. It is situated east of Rottumeroog and west of Juist.
Amrum is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants.

The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Islands or the Wadden Sea Islands, form an archipelago at the eastern edge of the North Sea in northwestern Europe, stretching from the northwest of the Netherlands through Germany to the west of Denmark. The islands shield the mudflat region of the Wadden Sea from the North Sea.
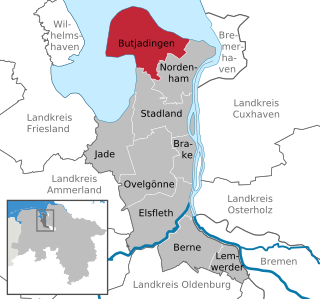
Butjadingen is a peninsula and municipality in the Wesermarsch district, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

The German Bight is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and Germany to the east. To the north and west it is limited by the Dogger Bank. The Bight contains the Frisian and Danish Islands. The Wadden Sea is approximately ten to twelve kilometres wide at the location of the German Bight. The Frisian islands and the nearby coastal areas are collectively known as Frisia. The southern portion of the bight is also known as the Heligoland Bight. Between 1949 and 1956 the BBC Sea Area Forecast used "Heligoland" as the designation for the area now referred to as German Bight.

Norderney is one of the seven populated East Frisian Islands off the North Sea coast of Germany.

Juist is an island and municipality in the district of Aurich in Lower Saxony in Germany. The island is one of seven East Frisian Islands at the edge of the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea in the southern North Sea. It is located between Borkum Island (west), Memmert Island (southwest) and Norderney (east). The island is 17 km (11 mi) long and from 500 metres (1,600 ft) to 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) wide, depending on the tide levels. There are two villages on the island: the main village Juist, and Loog. The island is separated from Norderney by the Norderneyer Seegatt.

Wangerooge is one of the 32 Frisian Islands in the North Sea located close to the coasts of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark. It is also a municipality in the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony in Germany.

Baltrum is a barrier island off the coast of East Frisia, in Germany, and is a municipality in the district of Aurich, Lower Saxony. It is located in-between the chain of the seven inhabited East Frisian Islands. Baltrum is the smallest island in this chain by area and inhabitants. It has a land area of 6.5 square kilometres, and a population in (2011) of just over 500 resident inhabitants.

Langeoog is one of the seven inhabited East Frisian Islands at the edge of the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea in the southern North Sea, located between Baltrum Island (west), and Spiekeroog (east). It is also a municipality in the district of Wittmund in Lower Saxony, Germany. The name Langeoog means Long Island in the Low German dialect.

Wenningstedt-Braderup is a municipality and seaside resort on the island of Sylt in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located north of the town of Westerland and is part of the Amt Landschaft Sylt. The local economy is dominated by tourism.

The single track Wangerooge Island Railway is an unelectrified narrow gauge railway with a track gauge of 1,000 mm located on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge off the northwestern coast of Germany. It is the most important means of transport on the island and is the only narrow gauge railway operated today by the Deutsche Bahn.

The Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park was established in 1986 and embraces the East Frisian Islands, mudflats and salt marshes between the Bay of Dollart on the border with the Netherlands in the west and Cuxhaven as far as the Outer Elbe shipping channel in the east. The national park has an area of about 345,800 hectares (1,335 sq mi). The National Park organisation is located in Wilhelmshaven. In June 2009, the National Park became a UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea and the Dutch Wadden Sea, highlighting its unique intertidal ecosystem and high biodiversity.

Minsener Oog, also Minser Oog or Minsener Oldeoog, is an uninhabited East Frisian island that belongs to the parish of Wangerooge in the north German district of Friesland in the state of Lower Saxony. It has been artificially enlarged through the construction of groynes.

























