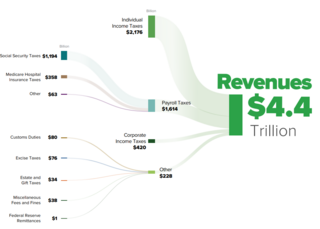
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
A property tax is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.
A capital gains tax (CGT) is the tax on profits realized on the sale of a non-inventory asset. The most common capital gains are realized from the sale of stocks, bonds, precious metals, real estate, and property.

In the United Kingdom, taxation may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government, devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion.
A wealth tax is a tax on an entity's holdings of assets or an entity's net worth. This includes the total value of personal assets, including cash, bank deposits, real estate, assets in insurance and pension plans, ownership of unincorporated businesses, financial securities, and personal trusts. Typically, wealth taxation often involves the exclusion of an individual's liabilities, such as mortgages and other debts, from their total assets. Accordingly, this type of taxation is frequently denoted as a netwealth tax.
A gift tax, known originally as inheritance tax, is a tax imposed on the transfer of ownership of property during the giver's life. The United States Internal Revenue Service says that a gift is "Any transfer to an individual, either directly or indirectly, where full compensation is not received in return."

In the United Kingdom, inheritance tax is a transfer tax. It was introduced with effect from 18 March 1986, replacing capital transfer tax. The UK has the fourth highest inheritance tax rate in the world, according to conservative think tank, the Tax Foundation, though only a very small proportion of the population pays it. 3.7% of deaths recorded in the UK in the 2020-21 tax year resulted in inheritance tax liabilities. Other countries such as China, Russia and India have no inheritance tax, whilst Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Norway and Israel have all chosen to abolish succession taxes.
International tax law distinguishes between an estate tax and an inheritance tax. An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate of a person who has died. However, this distinction is not always observed; for example, the UK's "inheritance tax" is a tax on the assets of the deceased, and strictly speaking is therefore an estate tax.
Taxation in Greece is based on the direct and indirect systems. The total tax revenue in 2017 was €47.56 billion from which €20.62 billion came from direct taxes and €26.94 billion from indirect taxes. The total tax revenue represented 39.4% of GDP in 2017. Taxes in Greece are collected by the Independent Authority for Public Revenue.
In economics, a gift tax is the tax on money or property that one living person or corporate entity gives to another. A gift tax is a type of transfer tax that is imposed when someone gives something of value to someone else. The transfer must be gratuitous or the receiving party must pay a lesser amount than the item's full value to be considered a gift. Items received upon the death of another are considered separately under the inheritance tax. Many gifts are not subject to taxation because of exemptions given in tax laws. The gift tax amount varies by jurisdiction, and international comparison of rates is complex and fluid.
In the United States, the estate tax is a federal tax on the transfer of the estate of a person who dies. The tax applies to property that is transferred by will or, if the person has no will, according to state laws of intestacy. Other transfers that are subject to the tax can include those made through a trust and the payment of certain life insurance benefits or financial accounts. The estate tax is part of the federal unified gift and estate tax in the United States. The other part of the system, the gift tax, applies to transfers of property during a person's life.
In Austria, taxes are levied by the state and the tax revenue in Austria was 42.7% of GDP in 2016 according to the World Bank The most important revenue source for the government is the income tax, corporate tax, social security contributions, value added tax and tax on goods and services. Another important taxes are municipal tax, real-estate tax, vehicle insurance tax, property tax, tobacco tax. There exists no property tax. The gift tax and inheritance tax were cancelled in 2008. Furthermore, self-employed persons can use a tax allowance of €3,900 per year. The tax period is set for a calendar year. However, there is a possibility of having an exception but a permission of the tax authority must be received. The Financial Secrecy Index ranks Austria as the 35th safest tax haven in the world.

Taxation in Italy is levied by the central and regional governments and is collected by the Italian Agency of Revenue. Total tax revenue in 2018 was 42.4% of GDP. The main earnings are income tax, social security, corporate tax and value added tax. All of these are collected at national level, but some differ across regions. Personal income taxation in Italy is progressive.
Taxes in Germany are levied at various government levels: the federal government, the 16 states (Länder), and numerous municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). The structured tax system has evolved significantly, since the reunification of Germany in 1990 and the integration within the European Union, which has influenced tax policies. Today, income tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) are the primary sources of tax revenue. These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure. The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
Taxes in Portugal are levied by both the national and regional governments of Portugal. Tax revenue in Portugal stood at 34.9% of GDP in 2018. The most important revenue sources include the income tax, social security contributions, corporate tax and the value added tax, which are all applied at the national level.
In Slovakia, taxes are levied by the state and local governments. Tax revenue stood at 19.3% of the country's gross domestic product in 2021. The tax-to-GDP ratio in Slovakia deviates from OECD average of 34.0% by 0.8 percent and in 2022 was 34.8% which ranks Slovakia 19th in the tax-to-GDP ratio comparison among the OECD countries. The most important revenue sources for the state government are income tax, social security, value-added tax and corporate tax.
The tax system of the Czech Republic is similar in its main features to the systems of developed and especially European countries.
Taxes in Poland are levied by both the central and local governments. Tax revenue in Poland is 33.9% of the country's GDP in 2017. The most important revenue sources include the income tax, Social Security, corporate tax and the value added tax, which are all applied on the national level.
UN pension is a retirement benefit provided to people who have worked directly for the United Nations organization. It is provided through the United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund (UNJSPF) under Article 28 of the Regulations, Rules and Pension Adjustment System of the United Nations Joint Staff Pension Fund.


