
The Lahontan Dam is a dam situated on the Carson River in the Carson Desert between Carson City, Nevada and Fallon, Nevada in the United States. Its impoundment is known as the Lahontan Reservoir or Lake Lahontan. It is currently operated by the Truckee-Carson Irrigation District.

With a height of 260.5 m (855 ft) Tehri Dam is the tallest dam in India and 12th tallest dam in the world. It is a multi-purpose rock and earth-fill embankment dam on the Bhagirathi River in New Tehri, Tehri Garhwal district in Uttarakhand, India. It is the primary dam of the THDC India Ltd. and the Tehri hydroelectric complex. Phase 1 was completed in 2006. The Tehri Dam withholds a reservoir for irrigation, municipal water supply and the generation of 1,000 megawatts (1,300,000 hp) of hydroelectricity. The dam's 1,000 MW variable-speed pumped-storage scheme is currently under construction with expected commissioning of first two units in 2023.

The Pejar Dam is an earth and rock-filled embankment dam with an uncontrolled spillway across the Wollondilly River, located in the Southern Tablelands region of New South Wales, Australia. The principal purpose of the dam is to supply potable water for the city of Goulburn. The impounded 9,000-megalitre reservoir is also called Pejar Dam.

GandhisagarDam is situated at a distance of 168 km from the District headquarter. The Dam is constructed on the Chambal River.

Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a masonry dam across the Krishna River at Nagarjuna Sagar which straddles the border between Palnadu district in Andhra Pradesh and Nalgonda district in Telangana. The dam provides irrigation water to the districts of Palnadu, Guntur, Nalgonda, Prakasam, Khammam, Krishna, and parts of West Godavari. It is also a source of electricity generation for the national grid.
The Shoalhaven Scheme is a dual-purpose water supply and Pumped-storage Hydroelectricity scheme located on the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia.
The Indira Sagar Dam is the largest dam in India, in terms of volume of water stored in the reservoir. It is located on the Narmada River at the town of Narmada Nagar, Punasa in the Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh in India. The foundation stone of the project was laid by the prime minister of India Indira Gandhi on 23 October 1984. The construction of the main dam started in 1992. The downstream projects of ISP are Omkareshwar, Maheshwar, and Sardar Sarovar Project. To build it, a town of 22,000 people and 100 villages was displaced.

The Srisailam Dam is constructed across the Krishna River in Nandyal district, Andhra Pradesh and Nagarkurnool district, Andhra Pradesh near Srisailam temple town and is the 2nd largest capacity working hydroelectric station in India.

The Rana Pratap Sagar Dam is a gravity masonry dam of 53.8 metres (177 ft) height built on the Chambal River at Rawatbhata in Rajasthan in India. It is part of integrated scheme of a cascade development of the river involving four projects starting with the Gandhi Sagar Dam in the upstream reach in Madhya Pradesh and the Jawahar Sagar Dam on the downstream with a terminal structure of the Kota Barrage in Rajasthan for irrigation.

Lake Qaraoun is an artificial lake or reservoir located in the southern region of the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon. It was created near Qaraoun village in 1959 by building a 61 m-high (200 ft) concrete-faced rockfill dam in the middle reaches of the Litani River. The reservoir has been used for hydropower generation, domestic water supply, and for irrigation of 27,500 ha.
Tilari (Forebay) Dam is situated in Dodamarg Taluka, in the Indian state of Maharashtra and the largest one is situated in Chandgad taluk of Kolhapur District in Maharashtra and is constructed on Tilari River as the result of a joint project by the Maharashtra and Goa governments. The water from this dam is distributed to both states. The dam is located near the border of Maharashtra and Karnataka and necessitated the relocation of several villages in the area. There are many reservoirs. The largest one is located near Belgaum in a village named Hajgoli in Maharashtra. The village is approximately 30 km from Belgaum and is a weekend spot for the people of that town.

The Maithon Dam is located at Maithon, 48 km from Dhanbad, in the state of Jharkhand India. It is 15,712 ft (4,789 m) long and 165 ft (50 m) high.

Jayakwadi dam is an earthen dam located on Godavari river at the site of Jayakwadi village in Paithan taluka of Aurangabad district in Maharashtra, India. It is a multipurpose project. The water is mainly used to irrigate agricultural land in the drought-prone Marathwada region of the state. It also provides water for drinking and industrial usage to nearby towns and villages and to the municipalities and industrial areas of Aurangabad and Jalna districts. The surrounding area of the dam has a garden and a bird sanctuary.

Perunchani Dam is an irrigation dam at Perunchani, in Kalkulam Taluk, Kanyakumari District, in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the dams of the Kodayar Irrigation System. As there was water deficiency in the Kodayar Irrigation System, Perunchani Dam was constructed in December 1952 to store flood water of the Paralayar River as an extension. It was built about 1 km (0.62 mi) upstream of the Puthen dam on the Paralayar River. The irrigation system became operational on 2 September 1953. It feeds the left bank irrigation canal system of the Puthen dam, which is the terminal structure of the system.
The Ingula Pumped Storage Scheme is a pumped-storage power station in the escarpment of the Little Drakensberg range straddling the border of the KwaZulu-Natal and Free State provinces, South Africa. It is about 22 km (14 mi) North-East of Van Reenen.
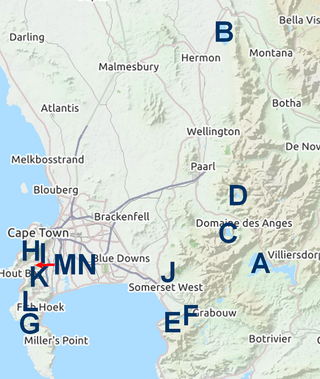
The Western Cape Water Supply System (WCWSS) is a complex water supply system in the Western Cape region of South Africa, comprising an inter-linked system of six main dams, pipelines, tunnels and distribution networks, and a number of minor dams, some owned and operated by the Department of Water and Sanitation and some by the City of Cape Town.

The Kannagawa Hydropower Plant (神流川発電所) is an under construction pumped-storage hydroelectric power plant near Minamiaiki in Nagano Prefecture and Ueno in Gunma Prefecture, Japan. The power plant utilizes the Minamiaiki River along with an upper and lower reservoir created by two dams, the upper Minamiaiki Dam and the lower Ueno Dam. The power station in between the two dams will contain six 470 megawatts (630,000 hp) pump-generators for a total installed capacity of 2,820 megawatts (3,780,000 hp). Unit 1 commenced commercial operation in 2005 and Unit 2 in 2012. When completed, the plant will have the second-largest pumped-storage power capacity in the world.
{{Infobox dam | name = Cheruthoni Dam | name_official = | image = Cheruthoni004.jpg | image_size = | image_caption = Cheruthoni dam | image_alt = | location_map = India#India Kerala#India Tamil Nadu | location_map_size = | location_map_caption = | coordinates | location = Idukki, [[Kerala] Only | status = O | construction_began = | opening = 1973 | demolished =

The Upper North Fork Feather River Project is a hydroelectric scheme in the Sierra Nevada of California, within Lassen and Plumas Counties. The project consists of three dams, five power plants, and multiple conduits and tunnels in the headwaters of the North Fork Feather River, a major tributary of the Feather—Sacramento River systems. The total installed capacity is 362.3 megawatts (MW), producing an annual average of 1,171.9 gigawatt hours (GWh). The project is also contracted for the delivery of irrigation water between March 31 and October 31 of each year. The project is owned and operated by Pacific Gas and Electric Company.

The Kanjirapuzha Dam, a masonry earth dam built for providing irrigation to a Cultural Command Area (CCA) of 9,713 hectares, is located in the Palakkad district in the Indian state of Kerala. The reservoir, which has three islands within it, also has an established commercial fisheries development programme operated by the Fisheries Department.















