Related Research Articles

Estradiol valerate (EV), sold for use by mouth under the brand name Progynova and for use by injection under the brand names Delestrogen and Progynon Depot among others, is an estrogen medication. It is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels, hormone therapy for transgender people, and in hormonal birth control. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. The medication is taken by mouth or by injection into muscle or fat once every 1 to 4 weeks.
Combined injectable contraceptives (CICs) are a form of hormonal birth control for women. They consist of monthly injections of combined formulations containing an estrogen and a progestin to prevent pregnancy.

Estradiol benzoate (EB), sold under the brand name Progynon-B among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Estradiol benzoate is used in veterinary medicine as well. When used clinically, the medication is given by injection into muscle usually two to three times per week.

Estradiol cypionate (EC), sold under the brand name Depo-Estradiol among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for trans women, and in hormonal birth control for women. It is given by injection into muscle once every 1 to 4 weeks.

Estradiol undecylate, also known as estradiol undecanoate and formerly sold under the brand names Delestrec and Progynon Depot 100 among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been used as a part of hormone therapy for transgender women. Although estradiol undecylate has been used in the past, it was discontinued and hence is no longer available. The medication has been given by injection into muscle usually once a month.
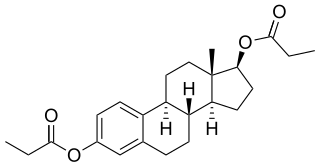
Estradiol dipropionate (EDP), sold under the brand names Agofollin, Di-Ovocylin, and Progynon DP among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It has also been used in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Although widely used in the past, estradiol dipropionate has largely been discontinued and is mostly no longer available today. It appears to remain in use only in Japan, Macedonia, and Australia. Estradiol dipropionate is given by injection into muscle at intervals ranging from once or twice a week to once every week and a half to two weeks.

Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH), also known as hydroxyprogesterone enanthate (OHPE) and sold under the brand names H.O.P., Lutogil A.P., and Lutogyl A.P. among others, is a progestin medication used for progestogenic indications. It has been formulated both alone and in together with estrogens, androgens/anabolic steroids, and other progestogens in several combination preparations. OHPH is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals.

A steroid ester is an ester of a steroid. They include androgen esters, estrogen esters, progestogen esters, and corticosteroid esters. Steroid esters may be naturally occurring/endogenous like DHEA sulfate or synthetic like estradiol valerate. Esterification is useful because it is often able to render the parent steroid into a prodrug of itself with altered chemical properties such as improved metabolic stability, water solubility, and/or lipophilicity. This, in turn, can enhance pharmacokinetics, for instance by improving the steroid's bioavailability and/or conferring depot activity and hence an extended duration with intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.

Testosterone isobutyrate, sold under the brand names Agovirin-Depot and Perandren M among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid medication and a testosterone ester which is used for indications such as low testosterone levels in men and delayed puberty in boys. It is available only in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The medication is administered by injection into muscle once every 1 to 2 weeks in males. Unlike most other testosterone esters, which are provided as oil solutions, testosterone isobutyrate is formulated as a microcrystalline aqueous suspension.

Testosterone phenylacetate is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester. Analogously to estradiol benzoate having been one of the first estrogen esters to be introduced, testosterone phenylacetate was one of the first testosterone esters to be introduced. However, since its introduction, it has largely been replaced by other esters, such as testosterone propionate.
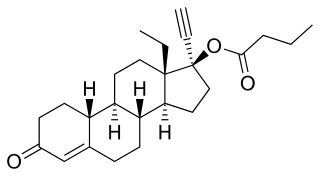
Levonorgestrel butanoate (LNG-B), or levonorgestrel 17β-butanoate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development as a long-acting injectable contraceptive. It is the C17β butanoate ester of levonorgestrel, and acts as a prodrug of levonorgestrel in the body. The drug is at or beyond the phase III stage of clinical development, but has not been marketed at this time. It was first described in the literature, by the WHO, in 1983, and has been under investigation for potential clinical use since then.

Estradiol cypionate/medroxyprogesterone acetate (EC/MPA), sold under the brand name Cyclofem among others, is a form of combined injectable birth control. It contains estradiol cypionate (EC), an estrogen, and medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), a progestin. It is recommended for short-term use and is given once a month by injection into a muscle.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.

The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.

Estradiol benzoate/progesterone (EB/P4), sold under the brand names Duogynon and Sistocyclin among others, is a combination medication of estradiol benzoate (EB), an estrogen, and progesterone (P4), a progestogen. It has been formulated both as short-acting oil solutions and long-acting microcrystalline aqueous suspensions and is given by injection into muscle either once or continuously at regular intervals.

The pharmacokinetics of progesterone, concerns the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration of progesterone.

Estradiol benzoate/testosterone isobutyrate (EB/TiB), sold under the brand names Femandren M and Folivirin, is an injectable combination medication of estradiol benzoate (EB), an estrogen, and testosterone isobutyrate (TiB), an androgen/anabolic steroid, which is used in menopausal hormone therapy for women. It is provided in the form of 1 mL ampoules containing 2.5 mg estradiol benzoate and 25 mg testosterone isobutyrate in a microcrystalline aqueous suspension and is administered by intramuscular injection once every 4 to 6 weeks. EB/TiB reportedly has a duration of about 14 to 21 days.
Estrone/progesterone/testosterone (E1/P4/T), sold under the brand name Tristeron or Tristerone, is an injectable combination medication of estrone (E1), an estrogen, progesterone (P4), a progestogen, and testosterone (T), an androgen/anabolic steroid, which was used in the treatment of functional uterine bleeding in women. It contained 6 mg estrone, 50 mg progesterone, and 25 mg testosterone in microcrystalline aqueous suspension and was administered by intramuscular injection. The medication was manufactured by Wyeth and was marketed by 1951. It is no longer available.
References
- ↑ Alan C. Sartorelli; David G. Johns (27 November 2013). Antineoplastic and Immunosuppressive Agents. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 181–. ISBN 978-3-642-65806-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Heinrich Kahr (8 March 2013). Konservative Therapie der Frauenkrankheiten: Anzeigen, Grenzen und Methoden Einschliesslich der Rezeptur. Springer-Verlag. pp. 20–22. ISBN 978-3-7091-5694-0.
- 1 2 Hans Schuermann; Rudolf Doepfmer (13 March 2013). Fertilitätsstörungen beim Manne. Springer-Verlag. pp. 260–. ISBN 978-3-642-94784-1.
- ↑ William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 385–394. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ↑ Hermann M. Behre; Gerhard F. Weinbauer; Eberhard Nieschlag (13 February 1996). "Testosterone Buciclate". In Shalender Bhasin; Henry L. Gabelnick; Jeffrey M. Spieler (eds.). Pharmacology, Biology, and Clinical Applications of Androgens: Current Status and Future Prospects. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 471–480. ISBN 978-0-471-13320-9.
Testosterone buciclate is applied intramuscularly as a microcrystalline aqueous suspension. [...] After air milling [...] of crystalline testosterone buciclate to a particle size of at least 75% in the range of 10 - 50 μm, the drug was [...] suspended in sterile, aqueous suspension vehicle [...].
- ↑ William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 314–322. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- 1 2 3 Hans Hermann Julius Hager; Walther Kern; Paul Heinz List; Hermann Josef Roth (29 July 2013). Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Ärzte und Medizinalbeamte: Wirkstoffgruppen II Chemikalien und Drogen (A-AL). Springer-Verlag. pp. 109, 141, 178. ISBN 978-3-662-25655-8.
- 1 2 3 Willibald Pschyrembel (15 June 2011). Praktische Gynäkologie: für Studierende und Ärzte. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 598, 600, 601. ISBN 978-3-11-150424-7.
- ↑ AMA Drug Evaluations . Americal Medical Association. 1971. p. 318.
- ↑ Drug Topics Redbook. Topics Publishing Company. 1976. p. 580.
- ↑ John Christian Krantz; Charles Jelleff Carr; Domingo M. Aviado (1972). Krantz and Carr's Pharmacologic principles of medical practice: a textbook on pharmacology and therapeutics for students and practitioners of medicine, pharmacy, and dentistry. Williams & Wilkins. p. 1258. ISBN 9780683002928.
- ↑ Marion E. Howard (1949). Modern Drug Encyclopedia and Therapeutic Index. Drug Publications. p. 697.
- ↑ Vademecum International. J. Morgan Jones Publications. 1959. p. 147.
- ↑ Frederick H. Meyers; Ernest Jawetz; Alan Goldfien (1978). Review of Medical Pharmacology. Lange Medical Pub. p. 400. ISBN 978-0-87041-151-9.
- ↑ Arthur Osol; Robertson Pratt (1973). The United States dispensatory. Lippincott. p. 498. ISBN 978-0-397-55901-5.
The following dosages for estradiol in the form of aqueous suspension injected intramuscularly, or pellets implanted subcutaneously, are recommended by a leading maunfacturer: Menopausal syndrome.—In average cases, 1 mg. intramuscularly 2 or 3 times weekly for 2 or 3 weeks; in more severe cases, 1 to 1.5 mg. Thereafter dosage is reduced to the minimum requirement, usually within the range of 0.5 to 1 mg. of estradiol twice weekly.
- ↑ Louis Sanford Goodman (1980). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics . Macmillan. p. 1428. ISBN 978-0-02-344720-4.
Estradiol, U.S.P. (AQUADiOL, PROGYNON, others), is available in aqueous suspension containing 0.5 or 1 mg/ml for intramuscular injection and as 25-mg pellets for subcutaneous implantation. Various esters of estradiol (benzoate, cypionate, enanthate, propionate, undecylate, and valerate) are prepared in aqueous suspensions or oily solutions for slow release after intramuscular injection. These preparations contain 0.5 to 40 mg/ml and are sold under various trade names (DELESTROGEN, DEPO-ESTRADIOL, OVOCYLIN, many others). Polyestradiol phosphate (ESTRADURIN) is also available for intramuscular use in prostatic carcinoma. Various sulfate esters of Estrone, U.S.P., are available in tablets containing 0.75 to 6 mg (OGEN, others). These esters and estrone are also supplied under various trade names in aqueous suspension and oily solution containing 1 to 5 mg/ml for intramuscular injection.
- ↑ https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/anda/pre96/85239_Estrone%20Suspension_Medr.pdf [ bare URL PDF ]
- 1 2 3 Sang GW (April 1994). "Pharmacodynamic effects of once-a-month combined injectable contraceptives". Contraception. 49 (4): 361–85. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90033-7. PMID 8013220.
The exact formulation and the size of the microcrystals is most important for duration of action. The smaller particles are more rapidly dissolved than larger ones and, hence, MPA appears more rapidly in the circulation, with more rapid elimination from the body. This is also true for the once-a-month formulation, Cyclofem. From our laboratory's data, the distribution of particle size of Cyclofem is showed in Table 2. [...] TABLE 2. Distribution of particle size of crystalline steroids in Cyclofem (aqueous suspension). Size of particle (μm): ≤4: 0.3%. 5–6: 7.3%. 6–8: 16.7%. 8–10: 29.0%. 10–13: 29.7%. 13–16: 9.9%. 16–20: 0.5%. >20: 0.1%. [...] Mego-E, containing megestrol acetate 25 mg in combination with 3.5 mg 17B-estradiol in 1 ml of aqueous microcrystalline suspension with a defined particle size range, [...]
- ↑ Garza-Flores J, Hall PE, Perez-Palacios G (1991). "Long-acting hormonal contraceptives for women". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40 (4–6): 697–704. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(91)90293-e. PMID 1958567. S2CID 26021562.
- ↑ Gabelnick, Henry L.; Hall, Peter E. (1987). "Long-acting methods for fertility regulation". Journal of Controlled Release. 6 (1): 387–394. doi:10.1016/0168-3659(87)90092-7. ISSN 0168-3659.
- ↑ Antal, E; Dick, C; Wrightiii, C; Welshman, I; Block, E (1989). "Comparative bioavailability of two medroxyprogesterone acetate suspensions". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 54 (1): 33–39. doi:10.1016/0378-5173(89)90162-2. ISSN 0378-5173.
- ↑ Pharmacy International. McGraw-Hill International Corporation. 1950. p. 34.
- ↑ Garza-Flores J (April 1994). "Pharmacokinetics of once-a-month injectable contraceptives". Contraception. 49 (4): 347–59. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(94)90032-9. PMID 8013219.
- ↑ Bagade O, Pawar V, Patel R, Patel B, Awasarkar V, Diwate S (2014). "Increasing use of long-acting reversible contraception: safe, reliable, and cost-effective birth control" (PDF). World J Pharm Pharm Sci. 3 (10): 364–392. ISSN 2278-4357. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-10. Retrieved 2019-06-09.
- ↑ Ufer, Joachim (1968). "Die therapeutische Anwendung der Gestagene beim Menschen" [Therapeutic Use of Progestagens in Humans]. Die Gestagene [Progestogens]. Springer-Verlag. pp. 1026–1124. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-99941-3_7. ISBN 978-3-642-99941-3.
C. Dysfunktionelle Uterusblutungen. [...] 1. Depotinjektionen. 1. Originalmethode nach KAUFMANN und OBER. Es wird 1 Amp. mit 200 mg Progesteron und 10 mg Oestradiol-Monobenzoat als Kristallsuspension (Sistocyclin) injiziert [676, 678, 679, 295, 482, 365, 434, 563, 400]. [...] Beispiele. KAUFMANN et al. [485]: 400 mg Progesteron + 20 mg Oestradiolmonobenzoat Kristallsuspension. ELERT [224] U. HERRMANN [363]: 200 mg Progesteron + 10 mg Oestradiolmono benzoat Kristallsuspension.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). www.indufar.com.py. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Kubíková, Drahomíra (2014). "Menopauzální symptomy a hormonální substituční terapie" [Menopausal symptoms and hormone replacement therapy]. Praktické Lékárenství (in Czech). 10 (2): 68–73. ISSN 1801-2434.
- ↑ Marek Josef; a kolektiv (14 May 2010). Farmakoterapie vnitřních nemocí: 4., zcela přepracované a doplněné vydání. Grada Publishing a.s. pp. 380–. ISBN 978-80-247-9524-9.
In addition, testosterone isobutyrate in FOLIVIRIN, Biotika, an injection containing 25 mg testosterone isobutyrate and 2.5 mg estradiol benzoate is available. It is applied every 4-6 weeks depending on the effect.
- ↑ Georg Arends; Heinrich Zörnig; Hermann Hager; Georg Frerichs, Walther Kern (14 December 2013). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis: Für Apotheker, Arzneimittelhersteller, Drogisten, Ärzte u. Medizinalbeamte. Springer-Verlag. pp. 1163–. ISBN 978-3-662-36329-4.
- ↑ Hormone und Psyche die Endokrinologie des Alternden Menschen: Fünftes Symposion der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Endokrinologie Freiburg (Breisgau), den 7. bis 9. März 1957. Springer-Verlag. 9 March 2013. pp. 55–. ISBN 978-3-642-87014-9.