
The ionosphere is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about 48 km (30 mi) to 965 km (600 mi) above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. It also affects GPS signals that travel through this layer.

The magnetopause is the abrupt boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding plasma. For planetary science, the magnetopause is the boundary between the planet's magnetic field and the solar wind. The location of the magnetopause is determined by the balance between the pressure of the dynamic planetary magnetic field and the dynamic pressure of the solar wind. As the solar wind pressure increases and decreases, the magnetopause moves inward and outward in response. Waves along the magnetopause move in the direction of the solar wind flow in response to small-scale variations in the solar wind pressure and to Kelvin–Helmholtz instability.
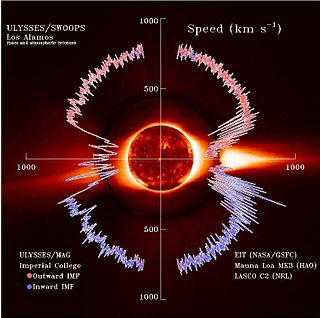
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

An aurora , also commonly known as the northern lights or southern lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions. Auroras display dynamic patterns of brilliant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky.
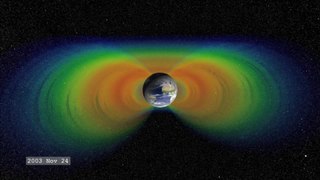
The Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The belts are named after James Van Allen, who published an article describing the belts in 1958.

Kristian Olaf Bernhard Birkeland was a Norwegian space physicist, inventor, and professor of physics at the Royal Fredriks University in Oslo. He is best remembered for his theories of atmospheric electric currents that elucidated the nature of the aurora borealis. In order to fund his research on the aurorae, he invented the electromagnetic cannon and the Birkeland–Eyde process of fixing nitrogen from the air. Birkeland was nominated for the Nobel Prize seven times.

Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the varying conditions within the Solar System and its heliosphere. This includes the effects of the solar wind, especially on the Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Though physically distinct, space weather is analogous to the terrestrial weather of Earth's atmosphere. The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and popularized in the 1990s. Later, it prompted research into "space climate", the large-scale and long-term patterns of space weather.

A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave.

The magnetosphere of Saturn is the cavity created in the flow of the solar wind by the planet's internally generated magnetic field. Discovered in 1979 by the Pioneer 11 spacecraft, Saturn's magnetosphere is the second largest of any planet in the Solar System after Jupiter. The magnetopause, the boundary between Saturn's magnetosphere and the solar wind, is located at a distance of about 20 Saturn radii from the planet's center, while its magnetotail stretches hundreds of Saturn radii behind it.

Cluster II was a space mission of the European Space Agency, with NASA participation, to study the Earth's magnetosphere over the course of nearly two solar cycles. The mission was composed of four identical spacecraft flying in a tetrahedral formation. As a replacement for the original Cluster spacecraft which were lost in a launch failure in 1996, the four Cluster II spacecraft were successfully launched in pairs in July and August 2000 onboard two Soyuz-Fregat rockets from Baikonur, Kazakhstan. In February 2011, Cluster II celebrated 10 years of successful scientific operations in space. In February 2021, Cluster II celebrated 20 years of successful scientific operations in space. As of March 2023, its mission was extended until September 2024. The China National Space Administration/ESA Double Star mission operated alongside Cluster II from 2004 to 2007.

A Birkeland current is a set of electrical currents that flow along geomagnetic field lines connecting the Earth's magnetosphere to the Earth's high latitude ionosphere. In the Earth's magnetosphere, the currents are driven by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of plasma through the magnetosphere. The strength of the Birkeland currents changes with activity in the magnetosphere. Small scale variations in the upward current sheets accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis.
Space physics, also known as space plasma physics, is the study of naturally occurring plasmas within Earth's upper atmosphere and the rest of the Solar System. It includes the topics of aeronomy, aurorae, planetary ionospheres and magnetospheres, radiation belts, and space weather. It also encompasses the discipline of heliophysics, which studies the solar physics of the Sun, its solar wind, the coronal heating problem, solar energetic particles, and the heliosphere.

The magnetosphere of Jupiter is the cavity created in the solar wind by Jupiter's magnetic field. Extending up to seven million kilometers in the Sun's direction and almost to the orbit of Saturn in the opposite direction, Jupiter's magnetosphere is the largest and most powerful of any planetary magnetosphere in the Solar System, and by volume the largest known continuous structure in the Solar System after the heliosphere. Wider and flatter than the Earth's magnetosphere, Jupiter's is stronger by an order of magnitude, while its magnetic moment is roughly 18,000 times larger. The existence of Jupiter's magnetic field was first inferred from observations of radio emissions at the end of the 1950s and was directly observed by the Pioneer 10 spacecraft in 1973.
Dynamics Explorer was a NASA mission, launched on 3 August 1981, and terminated on 28 February 1991. It consisted of two unmanned satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.

A substorm, sometimes referred to as a magnetospheric substorm or an auroral substorm, is a brief disturbance in the Earth's magnetosphere that causes energy to be released from the "tail" of the magnetosphere and injected into the high latitude ionosphere. Visually, a substorm is seen as a sudden brightening and increased movement of auroral arcs. Substorms were first described in qualitative terms by Kristian Birkeland which he called polar elementary storms. Sydney Chapman used the term substorm about 1960 which is now the standard term. The morphology of aurora during a substorm was first described by Syun-Ichi Akasofu in 1964 using data collected during the International Geophysical Year.
The impact of the solar wind onto the magnetosphere generates an electric field within the inner magnetosphere - the convection field. Its general direction is from dawn to dusk. The co-rotating thermal plasma within the inner magnetosphere drifts orthogonal to that field and to the geomagnetic field Bo. The generation process is not yet completely understood. One possibility is viscous interaction between solar wind and the boundary layer of the magnetosphere (magnetopause). Another process may be magnetic reconnection. Finally, a hydromagnetic dynamo process in the polar regions of the inner magnetosphere may be possible. Direct measurements via satellites have given a fairly good picture of the structure of that field. A number of models of that field exists.
In the height region between about 85 and 200 km altitude on Earth, the ionospheric plasma is electrically conducting. Atmospheric tidal winds due to differential solar heating or due to gravitational lunar forcing move the ionospheric plasma against the geomagnetic field lines thus generating electric fields and currents just like a dynamo coil moving against magnetic field lines. That region is therefore called ionospheric dynamo region. The magnetic manifestation of these electric currents on the ground can be observed during magnetospheric quiet conditions. They are called Sq-variations and L-variations (L=lunar) of the geomagnetic field. Additional electric currents are generated by the varying magnetospheric electric convection field. These are the DP1-currents and the polar DP2-currents. Finally, a polar-ring current has been derived from the observations which depends on the polarity of the interplanetary magnetic field. These geomagnetic variations belong to the so-called external part of the geomagnetic field. Their amplitudes reach at most about 1% of the main internal geomagnetic field Bo.

Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the atmosphere of the Sun. They take many forms, including solar wind, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, coronal heating and sunspots.

A space hurricane is a huge, funnel-like, spiral geomagnetic storm that occurs above the polar Ionosphere of Earth, during extremely quiet conditions. They are related to the aurora borealis phenomenon, as the electron precipitation from the storm's funnel produces gigantic, cyclone-shaped auroras. Scientists believe that they occur in the polar regions of planets with magnetic fields.

Dynamics Explorer 1 was a NASA high-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981, and terminated on 28 February 1991. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.















