
Manchester Piccadilly is the main railway station of the city of Manchester, in the metropolitan county of Greater Manchester, England. Opened originally as Store Street in 1842, it was renamed Manchester London Road in 1847 and became Manchester Piccadilly in 1960. Located to the south-east of the city centre, it hosts long-distance intercity and cross-country services to national destinations including London, Birmingham, Nottingham, Glasgow, Edinburgh, Cardiff, Bristol, Exeter, Plymouth, Reading, Southampton and Bournemouth; regional services to destinations in Northern England including Liverpool, Leeds, Sheffield, Newcastle and York; and local commuter services around Greater Manchester. It is one of 19 major stations managed by Network Rail. The station has 14 platforms: 12 terminal and two through platforms. Piccadilly is also a major interchange with the Metrolink light rail system with two tram platforms in its undercroft.

The Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) was formed in the 1860s and became the second-largest joint railway in Great Britain. The committee, which was often styled the Cheshire Lines Railway, operated 143 miles (230 km) of track in the then counties of Lancashire and Cheshire. The railway did not become part of the Big Four during the implementation of the 1923 grouping, surviving independently with its own management until the railways were nationalised at the beginning of 1948. The railway served Liverpool, Manchester, Stockport, Warrington, Widnes, Northwich, Winsford, Knutsford, Chester and Southport with connections to many other railways.

Heaton Mersey is a suburb of Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. It is situated on the north-western border of Stockport, adjacent to Didsbury and Burnage which are in the City of Manchester.

Stockport railway station serves the large town of Stockport in Greater Manchester, England. It is located 6 miles south-east of Manchester Piccadilly, on a spur of the West Coast Main Line to London Euston.

East Didsbury is a suburban railway station in south Manchester, England. It is sited on the Styal Line between Longsight and Wilmslow, providing direct access between Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Airport. East Didsbury tram stop, on the Manchester Metrolink system, is located close by.

Disley Tunnel was built by the Midland Railway in 1902 on its line between New Mills South Junction and Manchester Central, which was more direct than the congested and difficult lines through Stockport Tiviot Dale.

The Sheffield and Midland Railway Companies' Committee was incorporated by Act of Parliament in 1869 as a joint venture between the Midland Railway and the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway.

The Mid-Cheshire line is a railway line in the north-west of England that runs from Chester to Edgeley Junction, Stockport; it connects Chester with Manchester Piccadilly, via Knutsford. After Chester Northgate closed in 1969, the section between Mickle Trafford Junction and Chester was used for freight trains only until it closed in 1992; from Mickle Trafford, passenger trains use the Chester–Warrington line to Chester General instead. The route taken by passenger trains has changed over the years and now differs considerably from the original. Between 2001 and 2014, passenger journeys on the line increased to over 1.7 million per year. A near doubling of the passenger service was expected to occur from December 2018, however this did not materialise.

Chorlton is a stop on the South Manchester Line (SML) and Airport Line of the Metrolink light-rail system in Chorlton-cum-Hardy, Manchester, England. It was built as part of Phase 3a of the network's expansion, and opened on 7 July 2011 on a section of the former Cheshire Lines Committee railway.

The Stockport, Timperley and Altrincham Junction Railway (ST&AJR) was authorised by an Act of Parliament, passed on 22 July 1861 to build a 8 miles 17 chains (13.2 km) railway from Stockport Portwood to Altrincham.

West Didsbury is a tram stop on the South Manchester Line (SML) of Greater Manchester's light-rail Metrolink system. It opened to passengers on 23 May 2013, in West Didsbury, South Manchester, England.

Didsbury railway station is a former station in Didsbury, in the southern suburbs of Manchester, England, United Kingdom. The station was located on Wilmslow Road, just north of the junction with Barlow Moor Road and opposite Didsbury Library. Nothing now remains of the old station buildings, which have been demolished, but the surviving white Portland stone clock tower is a local landmark. Didsbury is now served by Didsbury Village tram stop which is close to the site of the former railway station.
Cheadle LNW railway station was a railway station that served Cheadle, Cheshire, England, between 1866 and its closure in 1917.

East Didsbury is a tram stop on Greater Manchester's light rail Metrolink system and the terminus of the system's South Manchester Line (SML). It is on the east side of Kingsway in East Didsbury, close to Manchester's boundary with Heaton Mersey in the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport. It was built as part of Phase 3b of the network's expansion and opened on 23 May 2013.

Withington is a tram stop on the South Manchester Line (SML) of Greater Manchester's light-rail Metrolink system. It is located on the west side of Princess Road on the fringe of Withington in south Manchester, England.

Burton Road is a stop on the South Manchester Line of Greater Manchester's light rail Metrolink system. It is located on Burton Road, on the border of the suburbs of Withington and West Didsbury in Manchester, England.
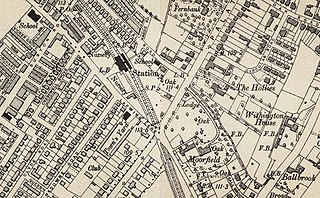
Withington and West Didsbury railway station is a former station in West Didsbury, in the southern suburbs of Manchester, England, United Kingdom. The station was located on Lapwing Lane, close to the junction with Palatine Road and opposite Withington Town Hall. Nothing now remains of the old station buildings, which have been demolished. West Didsbury is now served by West Didsbury tram stop which is approximately 85 metres (279 ft) further down the line from the original railway station.

The South Manchester Line (SML) is a tram line of the Manchester Metrolink in Manchester, England, running from Manchester city centre to Didsbury. The line opened as far as St. Werburgh's Road in 2011 and then to East Didsbury in 2013 as part of phase three of the system's expansion, along a former railway trackbed.

This is a list of confirmed or proposed future developments of the Manchester Metrolink light rail system in Greater Manchester, England.






























