Related Research Articles

Great Barrier Island lies in the outer Hauraki Gulf, New Zealand, 100 kilometres (62 mi) north-east of central Auckland. With an area of 285 square kilometres (110 sq mi) it is the sixth-largest island of New Zealand and fourth-largest in the main chain. Its highest point, Mount Hobson, is 627 metres (2,057 ft) above sea level. The local authority is the Auckland Council.

The national parks of New Zealand are protected natural areas administered by the Department of Conservation (DOC). The first national parks established in the country were all focused on mountain scenery. Since the 1980s the focus has been on developing a more diverse representation of New Zealand landscapes. The parks are all culturally significant and many also contain historic features. Tongariro National Park is one of the World Heritage Sites that are of both cultural and natural significance, while four of the South Island national parks form Te Wahipounamu, another World Heritage Site. There are currently 13 national parks; a 14th, Te Urewera National Park, was disestablished in 2014.

Coromandel, also called Coromandel Town to distinguish it from the wider district, is a town on the Coromandel Harbour, on the western side of the Coromandel Peninsula, which is in the North Island of New Zealand. It is 75 kilometres east of the city of Auckland, although the road between them, which winds around the Firth of Thames and Hauraki Gulf coasts, is 190 km long. The population was 1,930 as of June 2023.
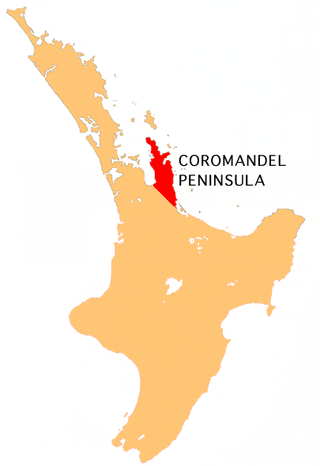
The Coromandel Peninsula on the North Island of New Zealand extends 85 kilometres (53 mi) north from the western end of the Bay of Plenty, forming a natural barrier protecting the Hauraki Gulf and the Firth of Thames in the west from the Pacific Ocean to the east. It is 40 kilometres (25 mi) wide at its broadest point. Almost its entire population lives on the narrow coastal strips fronting the Hauraki Gulf and the Bay of Plenty. In clear weather the peninsula is clearly visible from Auckland, the country's biggest city, which lies on the far shore of the Hauraki Gulf, 55 kilometres (34 mi) to the west. The peninsula is part of the Thames-Coromandel District and the Waikato Region.

The Karangahake Gorge lies between the Coromandel and Kaimai ranges, at the southern end of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. A sharply winding canyon, it was formed by the Ohinemuri River. State Highway 2 passes through this gorge between the towns of Paeroa, Waikino and Waihi. This road is the main link between the Waikato region and the Bay of Plenty.

Waihi Beach is a coastal town at the western end of the Bay of Plenty in New Zealand's North Island. It lies 10 kilometres to the east of the town of Waihi, at the foot of the Coromandel Peninsula. The main beach is 10 kilometres long. The town had a permanent population of 2,780 as of June 2023.

Whitianga is a town on the Coromandel Peninsula, in the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. The town is located on Mercury Bay, on the northeastern coast of the peninsula. The town has a permanent population of 6,440 as of June 2023, making it the second-largest town on the Coromandel Peninsula behind Thames.

Mount Pirongia is an extinct stratovolcano located in the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It rises to 959 m (3,146 ft) and is the highest peak around the Waikato plains. Pirongia's many peaks are basaltic cones created by successive volcanic eruptions between the late Pliocene and early Pleistocene, about 2.5 million years ago. In the adjacent picture, the characteristic profile of the mountain can be seen, along with a prominent accessory cone to the right.

Kauri gum is resin from kauri trees, which historically had several important industrial uses. It can also be used to make crafts such as jewellery. Kauri forests once covered much of the North Island of New Zealand, before early settlers caused the forests to retreat, causing several areas to revert to weeds, scrubs, and swamps. Even afterwards, ancient kauri fields and the remaining forests continued to provide a source for the gum. Between 1820 and 1900, over 90% of Kauri forests were logged or burnt by Europeans.

The Manaia River is a river of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. It flows north from its sources in the Coromandel Range, reaching the Hauraki Gulf at Manaia Harbour, 10 kilometres (6 mi) southwest of Coromandel.

The Tapu River is a river of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. It flows west from the Coromandel Range, reaching the Firth of Thames at the settlement of Tapu, approximately halfway between Thames and Coromandel.

The Te Mata River is a river of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. It flows west to reach the Firth of Thames at the small settlement of Te Mata, 25 kilometres (16 mi) south of Coromandel.

The Waitawheta River is a river of the Waikato Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows from a point south-east of Mount Te Aroha in the Kaimai Range to the Karangahake Gorge at the foot of the Coromandel Peninsula to reach the Ohinemuri River at Karangahake, five kilometres east of Paeroa.

Hapuakohe Range of hills is aligned north–south, between the Waikato River and the Hauraki Plains in the Waikato region of New Zealand. It is separated from the Taupiri Range by an air-gap at Mangawara, where the Waikato flowed about 20,000 years ago.

Tararu is a former gold-mining village on the west coast of the Coromandel Peninsula of New Zealand. State Highway 25 runs through it; Te Puru being about 7 km (4.3 mi) to the north, and Thames about 2 km (1.2 mi) to the south.

Kauaeranga Valley is a valley created by the Kauaeranga River, which flows from the Coromandel Range southwest to the Firth of Thames at Thames, New Zealand in the North Island. It contains the settlement of Kauaeranga on the Coromandel Peninsula. It is located near Thames, in the Thames-Coromandel District in the Waikato region. It covers a land area of 180.51 km2.

Whangaparapara is a harbour and coastal community on Great Barrier Island in New Zealand's Hauraki Gulf.

Coromandel Forest Park is a protected area and conservation park administered by the Department of Conservation, covering 71,899 hectares of the Coromandel Peninsula, in the Thames Coromandel District of the Waikato Region.
Endeavour Inlet is a large inlet of Queen Charlotte Sound, part of New Zealand's Marlborough Sounds. It lies north-east of Bay of Many Coves / Miritū Bay and south-west of Resolution Bay. The inlet is home to a number of retreats, including Furneaux Lodge and Punga Cove.
The Kaihu Forest is a forested area located in the Northland region of New Zealand, near the Kaihu River and the settlement of Kaihu. The forest is part of the broader ecological landscape of the region, which historically included vast stands of native Kauri trees, one of New Zealand’s most iconic tree species.
References
- 1 2 3 "Wires Track". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "The Maratoto Valley". Ohinemuri Regional History Journal. 3. April 1965.
- 1 2 "Maratoto/Old Wires Track, Sunday 9 February 2020". Women's Outdoor Pursuits. 9 February 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 "Maratoto Mine". mindat.org. Hudson Institute of Mineralogy.
- 1 2 "Maratoto". climbnz.org.nz. Climbing NZ.
- ↑ "Maratoto is open". nz4wheeling.com. NZ4Wheeling. 21 January 2017.
- ↑ "Golden Cross Track". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation.
- ↑ "Wentworth Track". doc.govt.nz. Department of Conservation.
- ↑ "Maratoto". thecrag.com. The Crag.