Related Research Articles
Shambala or Shambaa is a Bantu language of Tanzania.
Matuumbi, also known as Kimatuumbi and Kimatumbi, is a language spoken in Tanzania in the Kipatimu region of the Kilwa District, south of the Rufiji river. It is a Bantu language, P13 in Guthrie's classification. Kimatuumbi is closely related to the Ngindo, Rufiji and Ndengereko languages. It is spoken by about 70,000 people, according to the Ethnologue.
Ongamo, or Ngas, is a probably extinct Eastern Nilotic language of Tanzania. It is closely related to the Maa languages, but more distantly than they are to each other. Ongamo has 60% of lexical similarity with Maasai, Samburu, and Camus. Speakers have shifted to Chagga, a dominant regional Bantu language.

Kiga is a Great Lakes Bantu language of the Kiga people (Bakiga). Kiga is a similar and partially mutually intelligible with the Nkore language. It was first written in the second half of the 19th century. Kiga is largely spoken in the ancient Kigezi region which includes about 5 districts, namely Rubanda, Rukiga, Kabale, Kanungu and some parts of Rukungiri. As of 2021, Kiga is spoken natively by about 1.3 million people in Uganda.

The Ovambo language is a dialect cluster spoken by the Ovambo people in southern Angola and northern Namibia, of which the written standards are Kwanyama and Ndonga.
Kanamarí, or Katukina-Kanamari, is a Katukinan language spoken by about 650 individuals in Amazonas, Brazil. It is considered endangered.
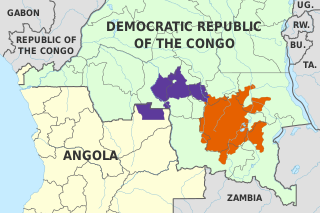
Luba-Katanga, also known as Luba-Shaba and Kiluba, is a Bantu language of Central Africa. It is spoken mostly in the south-east area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo by the Luba people.
Lugbara, or Lugbarati, is the language of the Lugbara people. It is spoken in the West Nile region in northwestern Uganda, as well as the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Orientale Province.
Cuói, known as Thổ, is a dialect cluster spoken by around 70,000 Thổ people in Vietnam and a couple thousand in Laos, mainly in the provinces of Bolikhamsai and Khammouane.
Maʼa is a Bantu language of Tanzania.
The Turu or Nyaturu language, Kinyaturu, also known as RimiKirimi, is a Bantu language of spoken by the Wanyaturu also known as Arimi of the Singida region of Tanzania. Excluding the Bantu language prefixes Ke- and Ki-, other spellings of the language are Limi and Remi. Dialects of the three Turu tribes are Girwana of the Airwana (Wilwana) in the north, Giahi of the Vahi (Wahi) in the south and west, and Ginyamunyinganyi of the Anyiŋanyi (Wanyinganyi) in the east.
The Limba language, Hulimba, is a Niger-Congo language of Sierra Leone and Guinea. It is not closely related to other languages and appears to form its own branch of the Niger–Congo family. Dialects include Tonko, Sela, Kamuke, Wara-wara, Keleng, Biriwa, and Safroko. The eastern variety, spoken primarily in Guinea, is quite distinct. Limba has a system of noun classes, marked by an old, eroded set of prefixes augmented by a newer set of enclitics.
Ma, also known as A-Ma-Lo, Amadi, Madi, Madyo, is a Ubangian language spoken in Haut-Uele Province, the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Wapan or Kororofa, also known as Wukari after the local town of Wukari, is a major Jukunoid language of Nigeria.
The Ki language, Tuki, is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.
Ngam, or Sara Ngam, is a Bongo–Bagirmi language of Chad and the Central African Republic.
Yei Zhuang is a Northern Tai language complex spoken in Wenshan Prefecture, Yunnan, China. Its speakers are also known as the Sha (沙族).
The Tonga language of Mozambique, or Gitonga is a Bantu language spoken along the southern coast of the country. Often thought to be closest to Chopi to its south, the two languages have only a 44% lexical similarity.
Gwamhi-Wuri (Wurə-Gwamhyə-Mba), or Lyase, is a Kainji language of Nigeria. There are three varieties, which have only slight differences. "Lyase-Ne" means 'mother tongue'.
Mbəʼ is a Grassfields language of Cameroon.
References
- ↑ Mba at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)