
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera Neogale and Mustela and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the American mink and the European mink. The extinct sea mink was related to the American mink but was much larger.

Avian influenza, also known as avian flu, is a bird flu caused by the influenza A virus, which can infect people. It is similar to other types of animal flu in that it is caused by a virus strain that has adapted to a specific host. The type with the greatest risk is highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI).

Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus which can cause illness in humans and many other species. A bird-adapted strain of H5N1, called HPAI A(H5N1) for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus of type A of subtype H5N1, is the highly pathogenic causative agent of H5N1 flu, commonly known as avian influenza. It is enzootic in many bird populations, especially in Southeast Asia. One strain of HPAI A(H5N1) is spreading globally after first appearing in Asia. It is epizootic and panzootic, killing tens of millions of birds and spurring the culling of hundreds of millions of others to stem its spread. Many references to "bird flu" and H5N1 in the popular media refer to this strain.

Bernard Matthews Foods Limited is a British farming and food products business with its headquarters in Great Witchingham, Norfolk, England, which specialises in turkey products.

The global spread of H5N1 influenza in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat. While other H5N1 influenza strains are known, they are significantly different on a genetic level from a recent, highly pathogenic, emergent strain of H5N1, which was able to achieve hitherto unprecedented global spread in 2008. The H5N1 strain is a fast-mutating, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAI) found in multiple bird species. It is both epizootic and panzootic. Unless otherwise indicated, "H5N1" in this timeline refers to the recent highly pathogenic strain of H5N1.

Influenza A virus subtype H7N2 (A/H7N2) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus. This subtype is one of several sometimes called bird flu virus. H7N2 is considered a low pathogenicity avian influenza (LPAI) virus. With this in mind, H5 & H7 influenza viruses can re-assort into the Highly Pathogenic variant if conditions are favorable.

H5N8 is a subtype of the influenza A virus and is highly lethal to wild birds and poultry. H5N8 is typically not associated with humans. However, seven people in Russia were found to be infected in 2021, becoming the first documented human cases.

The social impact of H5N1 is the effect or influence of H5N1 in human society, especially the financial, political, social, and personal responses to both actual and predicted deaths in birds, humans, and other animals. Billions of dollars are raised and spent to research H5N1 and prepare for a potential avian influenza pandemic. Over ten billion dollars were lost, and over two hundred million birds were killed to contain H5N1. People reacted by buying less chicken causing poultry sales and prices to fall. Many individuals stockpiled supplies for a possible flu pandemic.

The global spread of H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat.

The global spread of H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat.

The 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak was an occurrence of avian influenza in England caused by the H5N1 subtype of Influenza virus A that began on 30 January 2007. The infection affected poultry at one of Bernard Matthews' farms in Holton in Suffolk. It was the third instance of H5N1-subtype detected in the United Kingdom and a range of precautions were instituted to prevent spread of the disease including a large cull of turkeys, the imposition of segregation zones, and a disinfection programme for the plant.

The global spread of H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat.
In reaction to the 2009 flu pandemic, governments around the world have responded with sometimes extreme reactions against pigs, which has included the official extermination of all domestic pigs in Egypt and the culling of three wild boars at the Baghdad Zoo in Iraq. Many of these slaughters occurred in Muslim countries, and religious restrictions on the consumption of pork have been cited as influencing the decision to take such action. Many other countries have banned international trade in pigs and pork products.

The birds of Cornwall are in general a selection of those found in the whole of the British Isles, though Cornwall's position at the extreme south-west of Great Britain results in many occasional migrants. The nightingale is one English bird which is virtually absent from Cornwall.

Charles George Eustice is a British politician and former public relations executive who held office as Secretary of State for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs between 2020 and 2022. A member of the Conservative Party, he has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Camborne and Redruth since 2010.

H5N6 is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus. Infected birds shed the virus in their saliva, mucous, and feces. The virus was first detected in poultry in 2013, since then spreading among wild bird populations and poultry around the world. Humans can be infected through unprotected contact with infected birds or contaminated surfaces. The virus transmits by getting into a person's eyes, nose, mouth, and through inhalation. Human infections are rare. Since 2014, at least 87 cases have occurred in humans. 29 people have died. A spike in human cases was reported in 2021. There have been no confirmed cases of human-to-human transmission. Some infections have been identified where no direct contact with infected birds or contaminated surfaces has been known to had occurred. Only one infected woman has said that she never came into any contact with poultry.
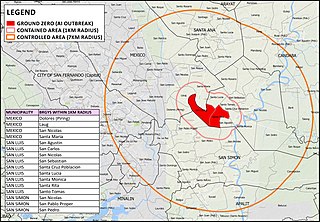
From April to September 2017 in the Philippines, an outbreak of H5N6 avian influenza or bird flu affected poultry in at least three towns in Central Luzon; San Luis in Pampanga and Jaen and San Isidro in Nueva Ecija.

In the early 2020s, an ongoing outbreak of avian influenza subtype H5N8 has been occurring at poultry farms and among wild bird populations in several countries and continents, leading to the subsequent cullings of millions of birds to prevent a pandemic similar to that of the H5N1 outbreak in 2008. The first case of human transmission of avian flu, also known as bird flu, was reported by Russian authorities in February 2021, as several poultry farm workers tested positive for the virus.
The Wild Bird Fund is a non-profit animal hospital on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. It is the city's first and only wild animal hospital.









