
The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the Zephyrs", and "The Way West".

The EMD SW1 is a 600-horsepower (450 kW) diesel-electric switcher locomotive built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Corporation between December 1938 and November 1953. Final assembly was at EMD's plant at LaGrange (McCook) Illinois. The SW1 was the second generation of 3,402 cu in (55.75 L) switcher from EMD, succeeding the SC and SW. The most significant change from those earlier models was the use of an engine of EMD's own design, the then-new 567 engine, here in 600 hp (450 kW) V6 form. 661 locomotives of this design were built, with a gap in production between March 1943 and September 1945 due to World War II.

Progressive Rail Inc. is a shortline railroad and owner of several other shortlines. PGR is directly operating several separate branches in Minnesota including the Airlake Terminal Railway. Progressive Rail also acquired the Wisconsin Northern Division in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin and operates as a separately-named division. They also own the Chicago Junction Railroad, Clackamas Valley Railway, the Iowa Traction Railway and Iowa Southern Railway in Iowa, the Crab Orchard and Egyptian Railroad in Illinois, the St. Paul & Pacific Northwest Railroad, and the Wisconsin Northern Railroad.

The GE 44-ton switcher is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Electric between 1940 and 1956. It was designed for industrial and light switching duties, often replacing steam locomotives that had previously been assigned these chores.

The Mount Hood Railroad is a heritage and shortline freight railroad located in Hood River, Oregon, 60 miles (97 km) east of Portland, Oregon, United States.

The California Northern Railroad is one of several Class III short-line railroad companies owned by Genesee & Wyoming, Inc. It operates over Southern Pacific Railroad (SP) tracks under a long-term lease.
The BHP Nevada Railroad was a shortline railroad that operated in Nevada from 1996 to 1999. BHP acquired the line from Nevada Northern Railway. Constructed by Utah Construction Company in 1908, the railroad hauled copper ore concentrate from BHP's concentrator at Riepetown to Shafter, Nevada. At Shafter the railroad interchanged with the Union Pacific and the ore continued to BHP's smelter at San Manuel, Arizona. BHP is an Australian-based company that took over Magma Copper, the owner of the Robinson Mine at Ruth, Nevada, in January 1996. The line ran south from a connection with the Union Pacific at Shafter to Ely.

The Western Pacific Railroad Museum (WPRM) in Portola, California, known as the Portola Railroad Museum until January 1, 2006, is a heritage railroad that preserves and operates historic American railroad equipment and preserves documents, photos and information. The museum's mission is to preserve the history of the Western Pacific Railroad and is operated by the Feather River Rail Society, founded in 1983. It is located at a former Western Pacific locomotive facility, adjacent to the Union Pacific's former Western Pacific mainline through the Feather River Canyon.

The Pacific Harbor Line was formed in 1998 to take over the Harbor Belt Line (HBL). In 1998, the Alameda Corridor was nearing completion, allowing for a massive amount of railroad traffic from the largest harbors in the Western hemisphere: Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach.

The McCloud Railway was a class III railroad operated around Mount Shasta, California. It began operations on July 1, 1992, when it took over operations from the McCloud River Railroad. The MCR was incorporated on April 21, 1992.

The Willamette Valley Railway is a short-line railroad that operates in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. It leased a line from Woodburn to Stayton from the Southern Pacific Transportation Company in February 1993, as well as a branch from Geer west to Salem, and purchased the property in 1996. The company also leased a line between Albany and Mill City in 1993, but transferred the lease to the Albany and Eastern Railroad in October 2000.
The Santa Maria Valley Railroad is a 14.8 miles (23.8 km) shortline railroad that interchanges with the Union Pacific Railroad's Coast Line at Guadalupe, California. As of 2006, the Railroad is owned by the Coast Belle Rail Corporation.
B&H Rail Corporation, formerly the Bath & Hammondsport Railroad, is a Class III shortline railroad. Initially the line served the communities of Bath, New York and Hammondsport, New York. In Bath, the railroad connected with the Erie Railroad and the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad. In 1996, the railroad was leased by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad.

The Indian Valley (IV) Railroad was a shortline railroad that was constructed from the Engels Copper Mine to a connection with the Western Pacific Railroad at Paxton, in Plumas County, northeastern California.

The Indiana Northeastern Railroad is a Class III short line freight railroad operating on nearly 130 miles (210 km) in southern lower Michigan, northeast Indiana and northwest Ohio. The Indiana Northeastern Railroad Company began operations in December 1992 and is an independent privately owned company. As of 2017 the railroad hauled more than 7,000 carloads per year. Commodities moved by the railroad include corn, soybeans, wheat and flour. It also handles plastics, fiberboard, aluminum, copper, coal, perlite, stone, lumber, glass, rendering products, as well as agricultural fertilizers and chemicals.

Lake State Railway is a railroad operating in the Saginaw Valley and northeastern quadrant of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The railroad moves large quantities of aggregate and limestone, as well as coal, grain, and chemical products. Some of the company's largest customers include Dow Chemical Company, S. C. Johnson & Son, Lafarge, ConAgra Foods, Archer Daniels Midland, Conrad Yelvington Distributors, and Consumers Energy.

The Crab Orchard and Egyptian Railway is a Class III common carrier shortline railroad that operates in the cities of Marion and Herrin in the Southern Illinois region. It is most historically recognized by the FRA for being the last U.S. railroad of any kind to use steam locomotives exclusively in regular revenue freight service up until March 1986.
The Manufacturers' Junction Railway is a shortline railroad in Cicero, Illinois. Originally a subsidiary of Western Electric used to switch their Hawthorne Works, after the plants were phased out it was sold to OmniTRAX, a company offering railroad management and other services.
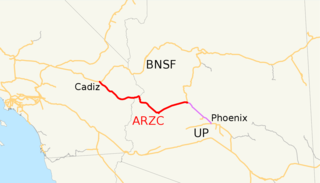
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

The Rogue Valley Terminal Railroad is a 14-mile (23 km) shortline railroad that connects the industrial park in White City, Oregon, United States to the Central Oregon and Pacific Railroad, which hauls its cars to the Union Pacific Railroad at Eugene, Oregon or Black Butte, California via the Siskiyou Summit, or to the Yreka Western Railroad at Montague, California.
















