| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Alpaugh, California |
| Reporting mark | WFS |
| Locale | San Joaquin Valley (Tulare County), California |
| Dates of operation | January 7, 1998–present |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
The West Isle Line( reporting mark WFS) is a private railroad and is a wholly owned subsidiary of Nutrien (formerly Western Farm Service). The line is operated by a contractor and the line does not have any employees. The line began service on January 7, 1998, after having been acquired from the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway. The line runs for 5.25 miles from Alpaugh, California, to a connection with the BNSF Railway at Stoil (milepost 936 on BNSF's Bakersfield Subdivision). Western Farm Service is the only customer on the line.
Western Farm Service bought the line from the BNSF in order to avoid having the BNSF's "Alpaugh Branch" abandoned. The line was formerly part of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway and was constructed by the ATSF in 1914. [1]
The railroad, as of 2001, averages 400 carloads per year, primarily chemicals used for fertilizer.
The West Isle Line has one EMD GP9 (serial number 21332) that was manufactured in February 1956 for Southern Pacific Railroad. It is marked in a green paint scheme with yellow marking as "West Isle Line" engine number "3399". It was formerly known as SP 3399, 3472, and 5639. [2]

Alpaugh is a census-designated place (CDP) in Tulare County, California, United States. The population was 1,026 at the 2010 census, up from 761 at the 2000 census.

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 36,000 employees, 33,400 miles (53,800 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Burlington Northern Railroad was a United States-based railroad company formed from a merger of four major U.S. railroads. Burlington Northern operated between 1970 and 1995.

The EMD FP45 is a cowl unit type of C-C diesel locomotive produced in the United States by General Motors Electro-Motive Division (EMD). It was produced beginning in 1967 at the request of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, which did not want its prestigious Super Chief/El Capitan and other passenger trains pulled by freight style hood unit locomotives, which have external walkways.

The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the largest Class 1 railroads in the United States between 1859 and 1996.

The EMD GP30 is a 2,250 hp (1,680 kW) four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division of La Grange, Illinois between July 1961 and November 1963. A total of 948 units were built for railroads in the United States and Canada, including 40 cabless B units for the Union Pacific Railroad.

Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe 3751 is a class "3751" 4-8-4 "Heavy Mountain" type steam locomotive built in May 1927 by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in Eddystone (Philadelphia), Pennsylvania for the Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). No. 3751 was the first 4-8-4 steam locomotive built for the Santa Fe and was referenced in documentation as type: "Heavy Mountain", "New Mountain", or "Mountain 4-wheel trailer". No. 3751 served in passenger duties until being retired in 1957.

The "Beep" is an individual switcher locomotive built in 1970 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway at its Cleburne, Texas, workshops. Technically a rebuild, the Beep originally entered service on the Santa Fe as a Baldwin Model VO-1000. Following its successful CF7 capital rebuilding program, the company hoped to determine if remanufacturing its aging, non-EMD end cab switchers by fitting them with new EMD prime movers was an economically viable proposition. The conversion procedure proved too costly and only the one unit was modified. In 2008-2009, this locomotive was retired and stored operational at Topeka, Kansas. In May 2009 the unit was donated to the Western America Railroad Museum in Barstow, California.

The Pacific Harbor Line was formed in 1998 to take over the Harbor Belt Line (HBL). In 1998, the Alameda Corridor was nearing completion, allowing for a massive amount of railroad traffic from the largest harbors in the Western hemisphere: Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach.
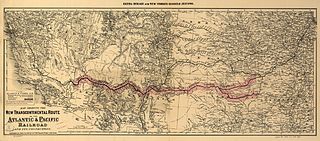
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Needles in Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

Santa Fe Depot is a union station in San Diego, California, built by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway to replace the small Victorian-style structure erected in 1887 for the California Southern Railroad Company. The Spanish Colonial Revival style station is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and is a San Diego Historic Landmark. Its architecture, particularly the signature twin domes, is often echoed in the design of modern buildings in downtown San Diego.
The Denver, Enid and Gulf Railroad (DE&G) was built as a short line railroad operating in Kansas, and Oklahoma. Incorporated in Oklahoma as the Denver, Enid and Gulf Railroad Company, March 31, 1902, by the five Frantz Brothers.

The Southern Transcon is a main line of the BNSF Railway comprising 11 subdivisions between Southern California and Chicago, Illinois. Completed in its current alignment in 1908 by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, when it opened the Belen Cutoff in New Mexico and bypassed the steep grades of Raton Pass, it now serves as a mostly double-tracked intermodal corridor.

The West Texas & Lubbock Railway is a shortline railroad in Texas, owned by Watco. It connects the BNSF in Lubbock with agricultural and oil-producing areas to the west and southwest. The company operates 107 miles of two ex-Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway lines, extending to Whiteface and Seagraves parallel to State Highway 114 and U.S. Highway 62. The primary commodities hauled are fertilizer, construction aggregates, grain, cotton, chemicals, peanuts and plastics.

The Escondido Sub is a 22-mile (35 km) branch railway line between Oceanside, California and Escondido, California, in the North County region of San Diego County. It is primarily used today by the Sprinter hybrid rail and local freight trains serving Escondido industries late at night, after the last Sprinter train of the day is taken out of service.
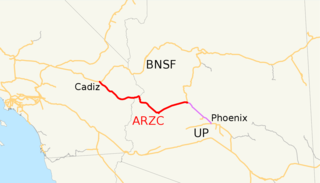
The Arizona and California Railroad is a class III short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by shortline railroad holding company RailAmerica. The Genesee & Wyoming shortline railroad holding company purchased RailAmerica in December 2012. ARZC's main commodities are petroleum gas, steel, and lumber; the railroad hauls around 12,000 carloads per year.

The Southern California Railway Museum, formerly known as the Orange Empire Railway Museum, is a railroad museum in Perris, California, United States. It was founded in 1956 at Griffith Park in Los Angeles before moving to the former Pinacate Station as the "Orange Empire Trolley Museum" in 1958. It was renamed "Orange Empire Railway Museum" in 1975 after merging with a museum then known as the California Southern Railroad Museum, and adopted its current name in 2019. The museum also operates a heritage railroad on the museum grounds.
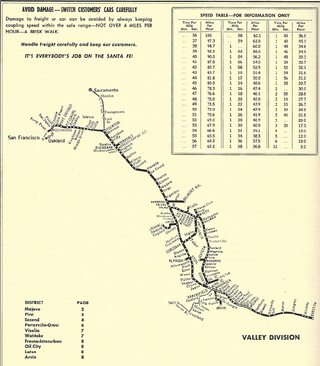
The Valley Division of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway ran from San Francisco to Barstow in California. It is currently in operation as the BNSF Railway's Stockton Subdivision and Bakersfield Subdivision.

The Illinois Northern Railroad was an industrial switching railroad serving Chicago's southwest side. From their yard at 26th St. and Western Ave. the line went southwest to the Santa Fe Railway's Corwith Yard, connecting with most major area railroads and serving on-line customers on the way. They also leased and switched track east of their yard. Incorporated in 1901, it was merged into the Santa Fe Railway in 1975.