This article does not cite any sources .(December 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Rush Green | |
|---|---|
 Corner of Rush Green Road and Dagenham Road | |
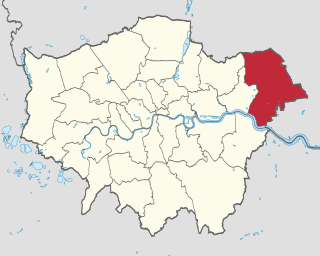
Location within Greater London | |
| OS grid reference | TQ505875 |
| • Charing Cross | 13.5 mi (21.7 km) WSW |
| London borough | |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | ROMFORD |
| Postcode district | RM7 |
| Dialling code | 020 01708 |
| Police | Metropolitan |
| Fire | London |
| Ambulance | London |
| EU Parliament | London |
| UK Parliament | |
| London Assembly | |
Rush Green is a suburban area in Romford in East London, England. It straddles the boundary of the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham and the London Borough of Havering, and is located 13.5 miles (22 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross.

Romford is a large town in east London and the administrative centre of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 14.1 miles (22.7 km) northeast of Charing Cross and is one of the major metropolitan centres identified in the London Plan. Historically Romford was a market town in the county of Essex and formed the administrative centre of the liberty of Havering, until it was dissolved in 1892. Good road links to London and the opening of the railway station in 1839 were key to the development of the town and the economic history of Romford is underpinned by a shift from agriculture to light industry and then to retail and commerce. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Romford significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming a municipal borough in 1937 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965 when the area was transferred from Essex. It now forms one of the largest commercial, retail, entertainment and leisure districts in London and has a developed night-time economy.

East London is a popularly and informally defined part of London, capital of the United Kingdom. By most definitions it is east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames. It broadly comprises the London boroughs of Barking and Dagenham, Hackney, Havering, Newham, Redbridge, Tower Hamlets and Waltham Forest. The East End of London is a subset of East London, consisting of areas close to the ancient City of London. The Eastern (E) Postal District is a different subset of East London; and there is also an "East" sub-region used in the London Plan for planning policy reporting purposes. The most recent (2011) iteration includes seven boroughs north of the Thames, with the addition of three boroughs south of the river.

London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with the largest municipal population in the European Union. Standing on the River Thames in the south-east of England, at the head of its 50-mile (80 km) estuary leading to the North Sea, London has been a major settlement for two millennia. Londinium was founded by the Romans. The City of London, London's ancient core − an area of just 1.12 square miles (2.9 km2) and colloquially known as the Square Mile − retains boundaries that follow closely its medieval limits. The City of Westminster is also an Inner London borough holding city status. Greater London is governed by the Mayor of London and the London Assembly.