
Cranham is a residential area of east London, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 17.5 miles (28 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross and comprises an extensive built-up area to the north and a low density conservation area to the south surrounded by open land. It was historically a rural village in the county of Essex and formed an ancient parish. It is peripheral to London, forming the eastern edge of the urban sprawl. The economic history of Cranham is characterised by a shift from agriculture to housing development. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Cranham significantly increased in population, becoming part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1934 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. The 2011 Census population of Cranham was included in Upminster.

Hornchurch is a suburban town in East London in the London Borough of Havering. It is located 15.2 miles (24.5 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. It comprises a number of shopping streets and a large residential area. It historically formed a large ancient parish in the county of Essex that became the manor and liberty of Havering. The economic history of Hornchurch is underpinned by a shift away from agriculture to other industries with the growing significance of nearby Romford as a market town and centre of administration. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Hornchurch significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming an urban district in 1926 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. It is the location of Queen's Theatre, Havering Sixth Form College and Havering College of Further and Higher Education.

Upminster is a suburban town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. Located 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is one of the locally important district centres identified in the London Plan.
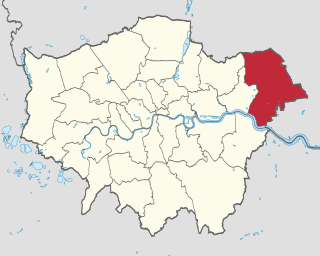
The London Borough of Havering in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities include Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham. The borough is mainly suburban, with large areas of protected open space. Romford is a major retail and night time entertainment centre, and to the south the borough extends into the London Riverside redevelopment area of the Thames Gateway. The name Havering is a reference to the Royal Liberty of Havering which occupied the area for several centuries. The local authority is Havering London Borough Council. It is the easternmost London borough.

Elm Park is a suburban planned community in East London and part of the London Borough of Havering. Located 14.3 miles (23.0 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is identified as a district centre in the London Plan with several streets of shops and a priority for regeneration. Prior to the construction of the extensive Elm Park Garden City development in the 1930s it was a scattered settlement of farms in the south of the parish of Hornchurch. Elm Park has been connected to central London by the electrified District line service since 1935 and the planned development of the area formed part of the interwar private housing boom that was interrupted by World War II. After the war Elm Park expanded with social housing and it has formed part of Greater London since 1965.

Emerson Park is a suburban neighbourhood in the London Borough of Havering, east London. The neighbourhood developed as two large housing estates built on the 550 acres (2.2 km2) estate of Nelmes manor in the parish of Hornchurch. Emerson Park estate to the south started construction in 1895 and Great Nelmes estate to the north was begun in 1901. It is located north of the Romford–Upminster line and a station opened at Emerson Park in 1909. The mansion of Nelmes survived until it was demolished in 1967 to avoid preservation by the Civic Amenities Act and was replaced with a small housing estate called The Witherings. Emerson Park is located 15 miles (24.1 km) northeast of Charing Cross in Central London.

Humphry Repton was the last great designer of the classic phase of the English landscape garden, often regarded as the successor to Capability Brown. His style is thought of as the precursor of the more intricate and eclectic styles of the 19th century. His first name is often incorrectly spelt "Humphrey".

A shrubbery, shrub border or shrub garden is a part of a garden where shrubs, mostly flowering species, are thickly planted. The original shrubberies were mostly sections of large gardens, with one or more paths winding through it, a less-remembered aspect of the English landscape garden with very few original 18th-century examples surviving. As the fashion spread to smaller gardens, linear shrub borders covered up walls and fences, and were typically underplanted with smaller herbaceous flowering plants. By the late 20th century, shrubs, trees and smaller plants tend to be mixed together in the most visible parts of the garden, hopefully blending successfully. At the same time, shrubs, especially very large ones, have become part of the woodland garden, mixed in with trees, both native species and imported ornamental varieties.

North Ockendon is the easternmost settlement of Greater London, England, and part of the London Borough of Havering. It is 18 miles (29 km) east-northeast of Central London and consists of a dispersed settlement within the Metropolitan Green Belt. It was historically an ancient parish in the county of Essex, which was abolished for civil purposes in 1936. North Ockendon is the only inhabited area in Greater London outside the M25 London Orbital Motorway. North Ockendon is north of South Ockendon, in Thurrock, Essex.

Ashton Court is a mansion house and estate to the west of Bristol in England. Although the estate lies mainly in North Somerset, it is owned by the City of Bristol. The mansion and stables are a Grade I listed building. Other structures on the estate are also listed.

Havering, also known as Havering-atte-Bower, was a royal manor and ancient liberty whose area now forms part of, and gives its name to, the London Borough of Havering in Greater London. The manor was in the possession of the Crown from the 11th to the 19th centuries and was the location of Havering Palace from the 13th to the late 17th century. It occupied the same area as the ancient parish of Hornchurch which was divided into the three chapelries of Havering, Hornchurch and Romford.

The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden, is a style of "landscape" garden which emerged in England in the early 18th century, and spread across Europe, replacing the more formal, symmetrical French formal garden which had emerged in the 17th century as the principal gardening style of Europe. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. Created and pioneered by William Kent and others, the "informal" garden style originated as a revolt against the architectural garden and drew inspiration from landscape paintings by Salvator Rosa, Claude Lorrain, and Nicolas Poussin, as well as from the classic Chinese gardens of the East, which had recently been described by European travellers and were realized in the Anglo-Chinese garden.

Hornchurch was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1926 to 1965, formed as an urban district for the civil parish of Hornchurch. It was greatly expanded in 1934 with the addition of Cranham, Great Warley, Rainham, Upminster and Wennington; and in 1936 by gaining North Ockendon. Hornchurch Urban District Council was based at Langtons House in Hornchurch from 1929. The district formed a suburb of London and with a population peaking at 131,014 in 1961, it was one of the largest districts of its type in England. It now forms the greater part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

Hylands House is a Grade II* neo-classical villa situated within Hylands Park a 232-hectare park southwest of Chelmsford in Essex in South East England. It is owned and operated by Chelmsford City Council.

Luscombe Castle is a country house situated near the resort town of Dawlish, in the county of Devon in England. Upon purchasing the land at Luscombe in 1797, Charles Hoare demolished the existing house and commissioned architects John Nash and Humphrey Repton to design a new house and gardens at the site. Nash and Repton came up with an asymmetrical designed building made from Portland stone, with castellated parapets, turrets and pinnacles to create the feel of a picturesque castle.

Brondesbury Park is a suburb and electoral ward of the London Borough of Brent. It is the part of Brondesbury which is not interwoven with Kilburn due to the naming of a major tube station (Kilburn) and is centred on Brondesbury Park railway station and the street, an avenue, which shares its name. The area has a number of open spaces, primarily Queen's Park and Tiverton Green.
Fielders Sports Ground is a cricket ground in Hornchurch, England. It was formerly part of the grounds of Langtons House and was known as Langton Park when it was a first-class cricket ground.
Humphrey Repton was an English amateur cricketer.
Hylands Park is a public park in the London Borough of Havering in northwest Hornchurch, near to Romford. It is owned and managed by Havering London Borough Council and has Green Flag Award status.

Rainham is a suburb of East London, England, in the London Borough of Havering. Historically an ancient parish in the county of Essex, Rainham is 13.6 miles (21.9 km) east of Charing Cross and is surrounded by a residential area, which has grown from the historic village, to the north and a commercial area, fronting the River Thames, to the south. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Rainham significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming part of Hornchurch Urban District in 1934, and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. The economic history of Rainham is underpinned by a shift from agriculture to industry and manufacture and is now in a period of regeneration, coming within the London Riverside section of the Thames Gateway redevelopment area.






















