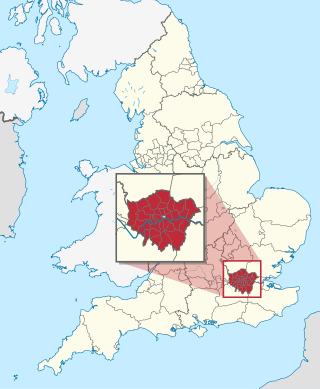
The London boroughs are the 32 local authority districts that together with the City of London make up the administrative area of Greater London, England; each is governed by a London borough council. The present London boroughs were all created at the same time as Greater London on 1 April 1965 by the London Government Act 1963 and are a type of local government district. Twelve were designated as Inner London boroughs and twenty as Outer London boroughs. The City of London, the historic centre, is a separate ceremonial county and sui generis local government district that functions quite differently from a London borough. However, the two counties together comprise the administrative area of Greater London as well as the London Region, all of which is also governed by the Greater London Authority, under the Mayor of London.
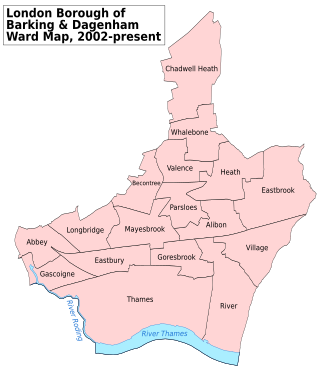
Barking and Dagenham London Borough Council in London, England is elected every four years. Since the last boundary changes in 2022 the council has comprised 51 councillors representing 19 wards, with each ward electing two or three councillors. Elections are held every four years.

Havering London Borough Council, also known as Havering Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Havering in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under no overall control since 2014; since 2022 it has been run by a coalition of the Havering Residents Association and Labour. The council is based at Havering Town Hall in Romford.

Hackney London Borough Council, also known as Hackney Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Hackney, in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2002. Since 2002 the council has been led by a directly elected mayor. The council meets at Hackney Town Hall and has its main offices in the adjoining Hackney Service Centre.

Newham London Borough Council also known as Newham Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Newham in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 1971. It has been led by a directly elected mayor since 2002. The council meets at Newham Town Hall in East Ham and has its main offices at 1000 Dockside Road, overlooking the Royal Albert Dock.

Waltham Forest London Borough Council, also known as Waltham Forest Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Waltham Forest in London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2010. The council is based at Waltham Forest Town Hall in Walthamstow.

Redbridge London Borough Council, also known as Redbridge Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Redbridge in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2014. The council meets at Redbridge Town Hall in Ilford and has its main offices nearby at Lynton House.

Barnet London Borough Council, also known as Barnet Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Barnet in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2022. The council meets at Hendon Town Hall and has its main offices at 2 Bristol Avenue in Colindale.

Sutton London Borough Council, also known as Sutton Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Sutton in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Liberal Democrat majority control since 1990. The council is based at the Civic Offices in Sutton.

Hounslow London Borough Council, also known as Hounslow Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Hounslow in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2010. The council is based at Hounslow House on Bath Road in Hounslow.
Merton London Borough Council, which styles itself Merton Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Merton in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2014. The council is based at Merton Civic Centre in Morden.

Wandsworth London Borough Council, also known as Wandsworth Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Wandsworth in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2022. It is based at Wandsworth Town Hall in the centre of Wandsworth.

Bexley London Borough Council, also known as Bexley Council is the local authority for the London Borough of Bexley in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Conservative majority control since 2006. It is based at Bexley Civic Offices in the Bexleyheath area of the borough.

Bromley London Borough Council, also known as Bromley Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Bromley in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Conservative majority control since 2001. It is based at the Civic Centre at Bromley Palace, but is in the process of moving to Churchill Court in the centre of Bromley, which is anticipated to open later in 2024.

Croydon London Borough Council, which styles itself Croydon Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Croydon in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. Croydon is divided into 28 wards, electing 70 councillors. Since 2022 the council has been led by a directly elected mayor. The council has been under no overall control since 2022, being run by a Conservative minority administration. The council meets at Croydon Town Hall and has its main offices in the adjoining Bernard Weatherill House.

Ealing London Borough Council, which styles itself Ealing Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Ealing in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2010. The council meets at Ealing Town Hall and has its main offices in the adjoining Perceval House.

Enfield London Borough Council, which styles itself Enfield Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Enfield in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 2010. It is based at Enfield Civic Centre.

Harrow London Borough Council, also known as Harrow Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Harrow in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Conservative majority control since 2022. Full council meetings are held at the Harrow Arts Centre and the council's main offices are at the Council Hub in Wealdstone.

Hillingdon London Borough Council, which styles itself Hillingdon Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Hillingdon in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Conservative majority control since 2006. The council is based at Hillingdon Civic Centre in Uxbridge.

Kingston upon Thames London Borough Council is the local authority for the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in the United Kingdom capital of London.






















