
The Great Central Railway (GCR) is a heritage railway in Leicestershire, England, named after the company that originally built this stretch of railway. It runs for 8.25 miles (13.28 km) between the town of Loughborough and a new terminus in the north of Leicester. It has period signalling, locomotives and rolling stock.

Sanday is one of the inhabited islands of Orkney that lies off the north coast of mainland Scotland. With an area of 50.43 km2 (19.5 sq mi), it is the third largest of the Orkney Islands. The main centres of population are Lady Village and Kettletoft. Sanday can be reached by Orkney Ferries or by plane from Kirkwall on the Orkney Mainland. On Sanday, an on-demand public minibus service allows connecting to the ferry.

The Welsh Highland Railway is a 25-mile (40.2 km) long, restored 1 ft 11+1⁄2 in narrow gauge heritage railway in the Welsh county of Gwynedd, operating from Caernarfon to Porthmadog, and passing through a number of popular tourist destinations including Beddgelert and the Aberglaslyn Pass. At Porthmadog it connects with the Ffestiniog Railway and to the short Welsh Highland Heritage Railway. In Porthmadog it uses the United Kingdom's only mixed gauge flat rail crossing.

Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles and aircraft.
Brush Traction was a manufacturer and maintainer of railway locomotives in Loughborough, England whose operations have now been merged into the Wabtec company's Doncaster UK operations.
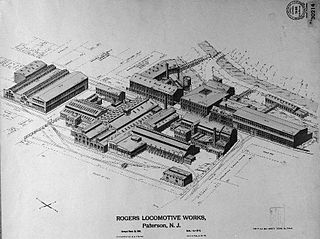
Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works was a manufacturer of railroad steam locomotives based in Paterson, in Passaic County, New Jersey, in the United States. Between its founding in 1832 and its acquisition in 1905, the company built more than 6,000 steam locomotives for railroads around the world. Most 19th-century U.S. railroads owned at least one Rogers-built locomotive. The company's most famous product was a locomotive named The General, built in December 1855, which was one of the principals of the Great Locomotive Chase of the American Civil War.

The South Devon Railway (SDR) is a 6.64-mile (10.69 km) heritage railway from Totnes to Buckfastleigh in Devon. Mostly running alongside the River Dart, it was initially known as the Dart Valley Railway. The railway is now operated by the South Devon Railway Trust, a registered charity.

The Sittingbourne and Kemsley Light Railway in Kent is a 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge heritage railway that operates from Sittingbourne to the banks of The Swale.

The LSWR N15 class was a British 2–cylinder 4-6-0 express passenger steam locomotive designed by Robert Urie. The class has a complex build history spanning three sub-classes and ten years of construction from 1918 to 1927. The first batch of the class was constructed for the London and South Western Railway (LSWR), where they hauled heavy express passenger trains to the south coast ports and further west to Exeter. After the Lord Nelsons, they were the second biggest 4-6-0 passenger locomotives on the Southern Railway. They could reach speeds of up to 90 mph (145 km/h).

The Abbey Light Railway was a 2 ft narrow gauge railway in Kirkstall, Leeds, West Yorkshire, England. Built by enthusiasts, the Railway ran from the nearby Bridge Road commercial area into the grounds of Kirkstall Abbey, operating most Sundays.

The SR West Country and Battle of Britain classes, collectively known as Light Pacifics or informally as Spam Cans, or "flat tops", are air-smoothed 4-6-2 Pacific steam locomotives designed for the Southern Railway by its Chief Mechanical Engineer Oliver Bulleid. Incorporating a number of new developments in British steam locomotive technology, they were amongst the first British designs to use welding in the construction process, and to use steel fireboxes, which meant that components could be more easily constructed under wartime austerity and post-war economy.

The New Zealand DF class locomotive of 1954 was the first class of mainline diesel-electric locomotives built for New Zealand's national railway network, built by English Electric. It should not be confused with General Motors Electro-Motive Division DF class of 1979.

Scarborough North Bay Railway (SNBR) is a ridable miniature railway in Scarborough, North Yorkshire, England. It was built in 1931, to the gauge of 20 in, and runs for approximately 7⁄8 mile (1.4 km) between Peasholm Park and Scalby Mills in the North Bay area of the town. The railway attracted approximately 200,000 visitors in the 2014–2015 season, and remains popular with tourists.

For more than a century, the Swiss locomotive, multiple unit, motor coach and railcar classification system, in either its original or updated forms, has been used to name and classify the rolling stock operated on the railways of Switzerland. It started out as a uniform system for the classification and naming of all rolling stock, powered and unpowered, but had been replaced and amended by the UIC classification of goods wagons.

Sir Haydn is a narrow gauge steam locomotive, built by Hughes's Locomotive & Tramway Engine Works, Loughborough in 1878. It operated on the Corris Railway in Wales, until closure in 1948, and since 1951 has operated on the nearby Talyllyn Railway. It has carried the operating number 3 under four successive owners.

Edward Thomas is a narrow gauge steam locomotive. Built by Kerr Stuart & Co. Ltd. at the California Works, Stoke-on-Trent in 1921, it was delivered new to the Corris Railway where it ran until 1948. After that railway closed, the locomotive was brought to the Talyllyn Railway in 1951, then restored, and remains in working order at the heritage railway. It has carried the operating number 4 under four successive owners.

The Ness Islands Railway is a 7+1⁄4 in gauge miniature railway in Inverness, Scotland, opened in 1983.
Carnforth MPD (Motive Power Depot) is a former London Midland and Scottish Railway railway depot located in the town of Carnforth, Lancashire, England.

St. Nicholas Abbey Heritage Railway (SNAHR) is a 1.5 kilometres (0.9 mi) long heritage narrow gauge railway with a 2 ft 6 in gauge, in the parish of Saint Peter on the Eastern Caribbean island of Barbados.

Crowle Peatland Railway is a fledgling railway museum based on the peat moors at Crowle in North Lincolnshire, England.


















