| Tantulocarida | |
|---|---|
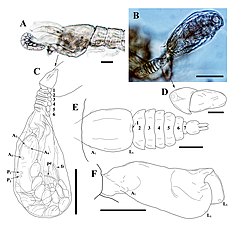 | |
| Microdajus sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Superclass: | Multicrustacea |
| Class: | Tantulocarida G. A. Boxshall & R. J. Lincoln, 1983 [1] |
| Families | |
Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods. [2] [3]