Terra Sirenum is a large region in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is centered at 39.7°S 150°W and covers 3900 km at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 10 to 70 South and longitudes 110 to 180 W. Terra Sirenum is an upland area notable for massive cratering including the large Newton Crater. Terra Sirenum is in the Phaethontis quadrangle and the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis.

Terra Cimmeria is a large Martian region, centered at 34.7°S 145°E and covering 5,400 km (3,400 mi) at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 15 N to 75 S and longitudes 170 to 260 W. It lies in the Eridania quadrangle. Terra Cimmeria is one part of the heavily cratered, southern highland region of the planet. The Spirit rover landed near the area.
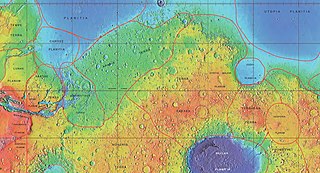
Terra Sabaea is a large area on Mars. Its coordinates are 2°N42°E and it covers 4,700 kilometres (2,900 mi) at its broadest extent. It was named in 1979 after a classic albedo feature on the planet. Terra Sabaea is fairly large and parts of it are found in five quadrangles: Arabia quadrangle, Syrtis Major quadrangle, Iapygia quadrangle, Ismenius Lacus quadrangle, and Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle.

The Noachis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Noachis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-27.

The Ismenius Lacus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 0° to 60° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Ismenius Lacus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-5. The southern and northern borders of the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km (1,905 mi) and 1,500 km (930 mi) wide, respectively. The north-to-south distance is about 2,050 km (1,270 mi). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area. The Ismenius Lacus quadrangle contains parts of Acidalia Planitia, Arabia Terra, Vastitas Borealis, and Terra Sabaea.

The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6. Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km. The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 120° to 180° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Cebrenia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-7. It includes part of Utopia Planitia and Arcadia Planitia. The southern and northern borders of the Cebrenia quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km (1,905 mi) and 1,500 km (930 mi) wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (1,270 mi). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Arcadia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 240° to 300° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Arcadia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-3.

The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' western hemisphere and covers 300° to 360° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-4.

The Iapygia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Iapygia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-21. It was named after the heel of the boot of Italy. That name was given by the Greeks It is part of a region of Italy named Apulia. The name Iapygia was approved in 1958.

The Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. This quadrangle is also referred to as MC-22. It contains parts of the regions Tyrrhena Terra, Hesperia Planum, and Terra Cimmeria.

The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-19. The Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle covers the area from 0° to 45° west longitude and 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle contains Margaritifer Terra and parts of Xanthe Terra, Noachis Terra, Arabia Terra, and Meridiani Planum.

The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 . The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features.

The Eridania quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Eridania quadrangle is also referred to as MC-29.
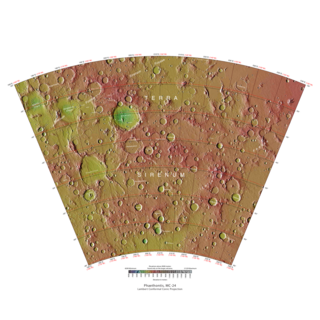
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24.

The Argyre quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Argyre quadrangle is also referred to as MC-26. It contains Argyre Planitia and part of Noachis Terra.

The Mare Australe quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Mare Australe quadrangle is also referred to as MC-30. The quadrangle covers all the area of Mars south of 65°, including the South polar ice cap, and its surrounding area. The quadrangle's name derives from an older name for a feature that is now called Planum Australe, a large plain surrounding the polar cap. The Mars polar lander crash landed in this region.

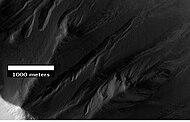
Martian gullies are small, incised networks of narrow channels and their associated downslope sediment deposits, found on the planet of Mars. They are named for their resemblance to terrestrial gullies. First discovered on images from Mars Global Surveyor, they occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Usually, each gully has a dendritic alcove at its head, a fan-shaped apron at its base, and a single thread of incised channel linking the two, giving the whole gully an hourglass shape. They are estimated to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. A subclass of gullies is also found cut into the faces of sand dunes, that are themselves considered to be quite young. Linear dune gullies are now considered recurrent seasonal features.

The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's HiRISE instrument has taken many images that strongly suggest that Mars has had a rich history of water-related processes. Many features of Mars appear to be created by large amounts of water. That Mars once possessed large amounts of water was confirmed by isotope studies in a study published in March 2015, by a team of scientists showing that the ice caps were highly enriched with deuterium, heavy hydrogen, by seven times as much as the Earth. This means that Mars has lost a volume of water 6.5 times what is stored in today's polar caps. The water for a time would have formed an ocean in the low-lying Mare Boreum. The amount of water could have covered the planet about 140 meters, but was probably in an ocean that in places would be almost 1 mile deep.
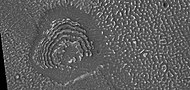
The common surface features of Mars include dark slope streaks, dust devil tracks, sand dunes, Medusae Fossae Formation, fretted terrain, layers, gullies, glaciers, scalloped topography, chaos terrain, possible ancient rivers, pedestal craters, brain terrain, and ring mold craters.