Kuwait is a sovereign state in Western Asia located at the head of the Persian Gulf. The geographical region of Kuwait has been occupied by humans since antiquity, particularly due to its strategic location at the head of the Persian Gulf. In the pre-oil era, Kuwait was a regional trade port. In the modern era, Kuwait is best known for the Gulf War (1990–1991).

Kuwait City is the capital and largest city of Kuwait. Located at the heart of the country on the south shore of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf, it is the political, cultural and economic center of the emirate, containing Kuwait's Seif Palace, government offices, and the headquarters of most Kuwaiti corporations and banks.

The House of Sabah is the ruling family of Kuwait.

The Capital Governorate, sometimes referred to as Al Kuwayt, is one of the six governorates of Kuwait. It comprises the historic core of Kuwait City, industrial and port areas such as Shuwaikh and Doha Port, and several offshore islands.
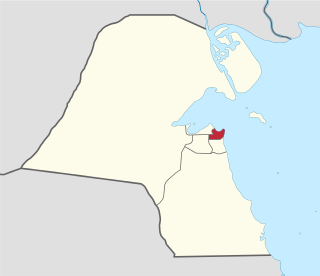
Hawalli Governorate is one of the six governorates of Kuwait, consisting of the following areas:

The Ahmadi Governorate is a governorate in southern Kuwait. It is the second most populated governorate in Kuwait, behind Farwaniya Governorate. Many oil and petroleum companies such as KOC and KNPC have their headquarters here.
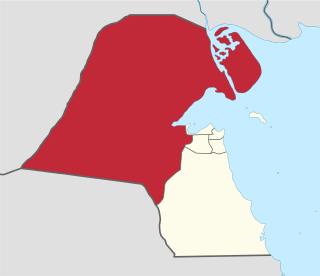
Al-Jahra Governorate is one of the six governorates of Kuwait. It is the largest Governorate in Kuwait accounting for 63 percent of its land area. It includes the town of Al Jahra, most of the northern and western parts of Kuwait, several islands, and also western districts of Kuwait City. It also contains most of Kuwait's arable land. Al Jahra also has some historic relevance to Kuwait's history. The Red Palace or Al Qasr Al Ahmar is the most important historical landmark there.

Mubarak Al-Sabah "the Great", nicknamed "The lion of the peninsula", was the seventh ruler of the Sheikhdom of Kuwait, from 18 May 1896 until his death on 18 November 1915. Mubarak ascended the throne after assassinating his predecessor and half-brother, Muhammad Al-Sabah. Known for his significant role in shaping modern Kuwait, the constitution of the State of Kuwait mandates that the Emir of Kuwait must be a descendant of Mubarak from the ruling Al-Sabah family.

Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the north and Saudi Arabia to the south. With a coastline of approximately 500 km (311 mi), Kuwait also shares a maritime border with Iran, across the Persian Gulf. Most of the country's population reside in the urban agglomeration of Kuwait City, the capital and largest city. As of 2024, Kuwait has a population of 4.82 million, of which 1.53 million are Kuwaiti citizens while the remaining 3.29 million are foreign nationals from over 100 countries. Kuwait has the third largest foreign-born population in the world.
Jleeb Al-Shuyoukh or Jileeb Al-Shiyukh, often shortened to just Jilīb/Jileeb (الجليب), is one of the oldest and most congested areas in Kuwait. It is located within Farwaniya Governorate and borders Kuwait International Airport. It is largely inhabited by expatriates from countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Egypt and Syria. There are even many Dawoodi Bohras residing in Jleeb-Al-Shuyoukh

This page list topics related to Kuwait.
Al Jahra is a city and area located 32 kilometres (20 mi) west of the centre of Kuwait City in Kuwait. Al Jahra is the capital of the Al Jahra Governorate of Kuwait as well as the surrounding Al Jahra District which is agriculturally based. Encyclopædia Britannica recorded the population in 1980 as 67,311. Historically, Jahra was a predominantly agricultural area. There are currently various farms in Jahra.
The community of Indians in Kuwait includes Indian expatriates in Kuwait, as well as Kuwaiti citizens of Indian origin or descent. According to the Indian ministry of external affairs, there are around 1,000,726 Indians as of 2023. The majority of these originate from the south Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, with the former constituting for 66% of the population of Indian nationals.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Cairo, Egypt.

The Sheikhdom of Kuwait was a sheikhdom during the pre-oil era. The sheikhdom became a British protectorate between 1899 and 1961 following the Anglo-Kuwaiti agreement of 1899. This agreement was made between Sheikh Mubarak Al-Sabah and the British Government in India, primarily as a defensive measure against threats from the Ottoman Empire. After 1961, the sheikdom became the state of Kuwait.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Doha, Qatar.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Muscat, Oman.

Sabah Al Ahmad Sea City is a city and area in Al Khiran, Kuwait, built with canals forming 200 kilometres (120 mi) of artificial shoreline. Before construction, the city was expected to house up to 250,000 residents. The city was inaugurated in mid 2016. The concept of the area is unusual because it was built by excavating large channels in the desert rather than on reclaimed land. The city is considered a pioneering project in the region due to its environmentally sustainable construction techniques.













