
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after some superclusters (of which only one, the Shapley Supercluster, is known to be bound). They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. One of the key features of clusters is the intracluster medium (ICM). The ICM consists of heated gas between the galaxies and has a peak temperature between 2–15 keV that is dependent on the total mass of the cluster. Galaxy clusters should not be confused with galactic clusters (also known as open clusters), which are star clusters within galaxies, or with globular clusters, which typically orbit galaxies. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. The galaxy groups and clusters can themselves cluster together to form superclusters.
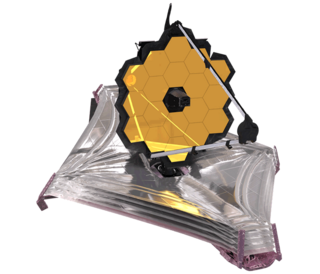
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. Its high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the first stars and the formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.

The Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey, or GOODS, is an astronomical survey combining deep observations from three of NASA's Great Observatories: the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, along with data from other space-based telescopes, such as XMM Newton, and some of the world's most powerful ground-based telescopes.

Abell 2744, nicknamed Pandora's Cluster, is a giant galaxy cluster resulting from the simultaneous pile-up of at least four separate, smaller galaxy clusters that took place over a span of 350 million years, and is located approximately 4 billion light years from Earth. The galaxies in the cluster make up less than five percent of its mass. The gas is so hot that it shines only in X-rays. Dark matter makes up around 75 percent of the cluster's mass.

MACS0647-JD is a galaxy with a redshift of about z = 10.7, equivalent to a light travel distance of 13.26 billion light-years. If the distance estimate is correct, it formed about 427 million years after the Big Bang.

EGSY8p7 (EGSY-2008532660) is a distant galaxy in the constellation of Boötes, with a spectroscopic redshift of z = 8.68, a light travel distance of 13.2 billion light-years from Earth. Therefore, at an age of 13.2 billion years, it is observed as it existed 570 million years after the Big Bang, which occurred 13.8 billion years ago, using the W. M. Keck Observatory. In July 2015, EGSY8p7 was announced as the oldest and most-distant known object, surpassing the previous record holder, EGS-zs8-1, which was determined in May 2015 as the oldest and most distant object. In March 2016, Pascal Oesch, one of the discoverers of EGSY8p7, announced the discovery of GN-z11, an older and more distant galaxy.

GN-z11 is a high-redshift galaxy found in the constellation Ursa Major. It is among the farthest known galaxies from Earth ever discovered. The 2015 discovery was published in a 2016 paper headed by Pascal Oesch and Gabriel Brammer. Up until the discovery of JADES-GS-z13-0 in 2022 by the James Webb Space Telescope, GN-z11 was the oldest and most distant known galaxy yet identified in the observable universe, having a spectroscopic redshift of z = 10.957, which corresponds to a proper distance of approximately 32 billion light-years. Data published in 2024 established that the galaxy contains the most distant, and therefore earliest, black hole known in the universe, estimated at around 1.6 million solar masses.

WHL0137-LS, also known as Earendel, is a star located in the constellation of Cetus. Discovered in 2022 by the Hubble Space Telescope, it is the earliest and most distant known star, at a comoving distance of 28 billion light-years. The previous furthest known star, MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1, also known as Icarus, at a comoving distance of 14.4 billion light-years, was discovered by Hubble in 2018. Stars like Earendel can be observed at cosmological distances thanks to the large magnification factors involved, that can exceed 1000. Other stars have been observed through this technique, such as Godzilla.

Webb's First Deep Field is the first operational image taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The deep-field photograph, which covers a tiny area of sky visible from the Southern Hemisphere, is centered on SMACS 0723, a galaxy cluster in the constellation of Volans. Thousands of galaxies are visible in the image, some as old as 13 billion years. It is the highest-resolution image of the early universe ever taken. Captured by the telescope's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the image was revealed to the public by NASA on 11 July 2022.

SMACS J0723.3–7327, commonly referred to as SMACS 0723, is a galaxy cluster about 4 billion light years from Earth, within the southern constellation of Volans. It is a patch of sky visible from the Southern Hemisphere on Earth and often observed by the Hubble Space Telescope and other telescopes in search of the deep past. It was the target of the first full-color image to be unveiled by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), imaged using NIRCam, with spectra included, showing objects lensed by the cluster with redshifts implying they are 13.1 billion years old. The cluster has been previously observed by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) as part of the Southern MAssive Cluster Survey (SMACS), as well as Planck and Chandra.

GLASS-z12 is a Lyman-break galaxy discovered by the Grism Lens-Amplified Survey from Space (GLASS) observing program using the James Webb Space Telescope's NIRCam in July 2022. Spectroscopic observations of GLASS-z12 by the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) in August 2022 confirmed that the galaxy has a spectroscopic redshift of 12.117±0.012, making it one of the earliest and most distant galaxies ever discovered, dating back to just 350 million years after the Big Bang, 13.6 billion years ago. ALMA observations detected an emission line associated with doubly ionized oxygen at 258.7 GHz with a significance of 5σ, suggesting that there is very low dust content in GLASS-z12, if not the early universe as well. Also based on oxygen-related measurements, the age of the galaxy is confirmed.
CEERS-93316 is a high-redshift galaxy with a spectroscopic redshift z=4.9. Significantly, the redshift that was initially reported was photometric and would have made CEERS-93316 the earliest and most distant known galaxy observed.

JADES-GS-z13-0 is a high-redshift Lyman-break galaxy discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) during NIRCam imaging for the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) on 29 September 2022. Spectroscopic observations by JWST's NIRSpec instrument in October 2022 confirmed the galaxy's redshift of z = 13.2 to a high accuracy, establishing it as the oldest and most distant spectroscopically-confirmed galaxy at the time, with a light-travel distance of 13.4 billion years. Due to the expansion of the universe, its present proper distance is approximately 33 billion light-years. In 2024, two older and more distant galaxies, JADES-GS-z14-0 and JADES-GS-z14-1, were found.
F200DB-045 is a candidate high-redshift galaxy, with an estimated redshift of approximately z = 20.4, corresponding to 168 million years after the Big Bang. If confirmed, it would be one of the earliest and most distant known galaxies observed.

UHZ1 is a background galaxy containing a quasar. At a redshift of approximately 10.1, UHZ1 is at a distance of 13.2 billion light-years, seen when our universe was about 3 percent of its current age. This redshift made it the most distant, and therefore earliest known quasar in the observable universe as of 2023. To detect this object, astronomers working at the Chandra X-ray Observatory used the Abell 2744's cluster mass as a gravitational lens in order to magnify distant objects directly behind it. At the time of discovery, it exceeded the distance record of QSO J0313−1806.

Maisie's Galaxy is a distant galaxy located at z=11.4 that existed 390 million years after the beginning of the universe.

JADES-GS-z7-01-QU is a Lyman-break galaxy, first identified in 2010, located in the constellation Fornax. It formed around 700 million years after the birth of the universe, after which it suddenly stopped creating new stars. It experienced rapid star formation around 80 million years before the epoch of observation, lasting for at least 30 million years, before ending around 10-20 million years before the epoch of observation. It is the oldest and most distant "dead" galaxy so far discovered.

JADES-GS-z14-0 is a high-redshift Lyman-Break galaxy in the constellation Fornax that was discovered in 2024 using NIRcam as part of the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) program. It has an estimated redshift of 14.32, making it the furthest galaxy ever discovered.

UNCOVER-z12 is a high-redshift Lyman-break galaxy discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) during NIRCam imaging for the JWST Ultradeep NIRSpec and NIRCam Observations before the Epoch of Reionization (UNCOVER) project in November 2023. UNCOVER-z12 is within the Abell 2744 supercluster in the constellation Sculptor. It is the 5th-most distant object ever discovered as of 2024, and is estimated to be 32.21 giga-lightyears from Earth.



















