
Fluvastatin is a member of the statin drug class, used to treat hypercholesterolemia and to prevent cardiovascular disease.

Phenprocoumon is a long-acting anticoagulant to be taken by mouth, and a coumarin derivative. It acts as a vitamin K antagonist and inhibits blood clotting (coagulation) by blocking synthesis of coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X. It is used for the prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic disorders such as heart attacks and pulmonary (lung) embolism. The most common adverse effect is bleeding. The drug interacts with a large number of other medications, including aspirin and St John's Wort. It is the standard coumarin used in Germany, Austria, and other European countries.

Silodosin, sold under the brand name Urief among others, is a medication used for the symptomatic treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. It acts as an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
Pazopanib, sold under the brand name Votrient, is an anti-cancer medication marketed worldwide by Novartis. It is a potent and selective multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks tumour growth and inhibits angiogenesis. It has been approved for renal cell carcinoma and soft tissue sarcoma by numerous regulatory administrations worldwide.

Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) is a zinc-binding and proline-rich hydrophilic phosphoprotein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C virus RNA replication. It appears to be a dimeric form without trans-membrane helices.

Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth.
Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and interferon, vary depending on the virus type and whether the person has cirrhosis. It is taken by mouth.

Simeprevir, sold under the brand name Olysio among others, is a medication used in combination with other medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is specifically used for hepatitis C genotype 1 and 4. Medications it is used with include sofosbuvir or ribavirin and peginterferon-alfa. Cure rates are in 80s to 90s percent. It may be used in those who also have HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth once daily for typically 12 weeks.
Ledipasvir is a drug for the treatment of hepatitis C that was developed by Gilead Sciences. After completing Phase III clinical trials, on February 10, 2014, Gilead filed for U.S. approval of a ledipasvir/sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination tablet for genotype 1 hepatitis C. The ledipasvir/sofosbuvir combination is a direct-acting antiviral agent that interferes with HCV replication and can be used to treat patients with genotypes 1a or 1b without PEG-interferon or ribavirin.
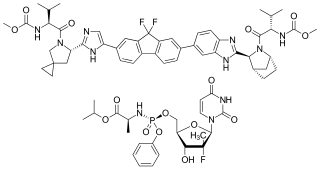
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, sold under the trade name Harvoni among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is a fixed-dose combination of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir. Cure rates are 94% to 99% in people infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. Some evidence also supports use in HCV genotype 3 and 4. It is taken daily by mouth for 8–24 weeks.
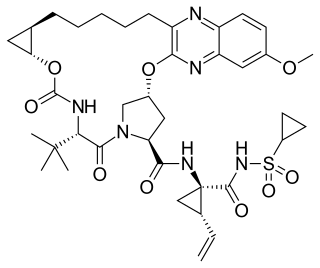
Grazoprevir is a drug approved for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was developed by Merck and completed Phase III trials, used in combination with the NS5A replication complex inhibitor elbasvir under the trade name Zepatier, either with or without ribavirin.

Elbasvir is a drug approved by the FDA in January 2016 for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was developed by Merck and completed Phase III trials, used in combination with the NS3/4A protease inhibitor grazoprevir under the trade name Zepatier, either with or without ribavirin.
Elbasvir/grazoprevir, sold under the brand name Zepatier, is a fixed-dose combination for the treatment of hepatitis C, containing elbasvir and grazoprevir. It is used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1 or 4 infection in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients.
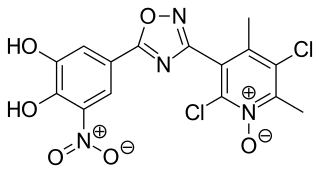
Opicapone, sold under the brand name Ongentys, is a medication which is administered together with levodopa in people with Parkinson's disease. Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor.

Lorlatinib, sold under the brand name Lorbrena in the United States, Canada, and Japan, and Lorviqua in the European Union, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It is an orally administered inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and C-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1), two enzymes that play a role in the development of cancer. It was developed by Pfizer.

Voxilaprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural (NS) protein 3/4A protease inhibitor that is used in combination with sofosbuvir and velpatasvir. The combination has the trade name Vosevi and received a positive opinion from the European Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use in June 2017.
Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, sold under the brand name Epclusa among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of hepatitis C in adults. It combines sofosbuvir and velpatasvir. It is more than 90% effective for hepatitis C genotypes one through six. It also works for hepatitis C in those who also have cirrhosis or HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth.
Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir, sold under the brand name Vosevi, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of hepatitis C. It contains sofosbuvir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitor; velpatasvir, an HCV NS5A inhibitor; and voxilaprevir an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor.
VEGFR-2 inhibitor, also known as kinase insert domain receptor(KDR) inhibitor, are tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitors that reduce angiogenesis or lymphangiogenesis, leading to anticancer activity. Generally they are small, synthesised molecules that bind competitively to the ATP-site of the tyrosine kinase domain. VEGFR-2 selective inhibitor can interrupt multiple signaling pathways involved in tumor, including proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis.
Abametapir, sold under the brand name Xeglyze, is a medication used for the treatment of head lice infestation in people six months of age and older.












