
Menthol is an organic compound, more specifically a monoterpenoid, made synthetically or obtained from the oils of corn mint, peppermint, or other mints. It is a waxy, clear or white crystalline substance, which is solid at room temperature and melts slightly above.
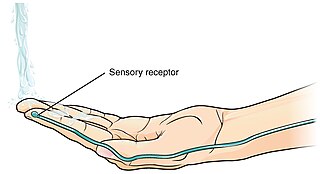
A thermoreceptor is a non-specialised sense receptor, or more accurately the receptive portion of a sensory neuron, that codes absolute and relative changes in temperature, primarily within the innocuous range. In the mammalian peripheral nervous system, warmth receptors are thought to be unmyelinated C-fibres, while those responding to cold have both C-fibers and thinly myelinated A delta fibers. The adequate stimulus for a warm receptor is warming, which results in an increase in their action potential discharge rate. Cooling results in a decrease in warm receptor discharge rate. For cold receptors their firing rate increases during cooling and decreases during warming. Some cold receptors also respond with a brief action potential discharge to high temperatures, i.e. typically above 45 °C, and this is known as a paradoxical response to heat. The mechanism responsible for this behavior has not been determined.
Transient receptor potential channels are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. Most of these are grouped into two broad groups: Group 1 includes TRPC, TRPV, TRPVL, TRPM, TRPS, TRPN, and TRPA. Group 2 consists of TRPP and TRPML. Other less-well categorized TRP channels exist, including yeast channels and a number of Group 1 and Group 2 channels present in non-animals. Many of these channels mediate a variety of sensations such as pain, temperature, different kinds of taste, pressure, and vision. In the body, some TRP channels are thought to behave like microscopic thermometers and used in animals to sense hot or cold. Some TRP channels are activated by molecules found in spices like garlic (allicin), chili pepper (capsaicin), wasabi ; others are activated by menthol, camphor, peppermint, and cooling agents; yet others are activated by molecules found in cannabis or stevia. Some act as sensors of osmotic pressure, volume, stretch, and vibration. Most of the channels are activated or inhibited by signaling lipids and contribute to a family of lipid-gated ion channels.

The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a biological system composed of endocannabinoids, which are endogenous lipid-based retrograde neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors, and cannabinoid receptor proteins that are expressed throughout the vertebrate central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endocannabinoid system remains under preliminary research, but may be involved in regulating physiological and cognitive processes, including fertility, pregnancy, pre- and postnatal development, various activity of immune system, appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory, and in mediating the pharmacological effects of cannabis. The ECS plays an important role in multiple aspects of neural functions, including the control of movement and motor coordination, learning and memory, emotion and motivation, addictive-like behavior and pain modulation, among others.
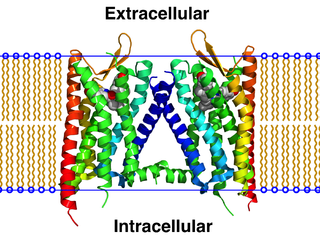
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP for its ligand ketazocine, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the OPRK1 gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction.
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems.

The transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1), also known as the capsaicin receptor and the vanilloid receptor 1, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRPV1 gene. It was the first isolated member of the transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor proteins that in turn are a sub-family of the transient receptor potential protein group. This protein is a member of the TRPV group of transient receptor potential family of ion channels. Fatty acid metabolites with affinity for this receptor are produced by cyanobacteria, which diverged from eukaryotes at least 2000 million years ago (MYA). The function of TRPV1 is detection and regulation of body temperature. In addition, TRPV1 provides a sensation of scalding heat and pain (nociception). In primary afferent sensory neurons, it cooperates with TRPA1 to mediate the detection of noxious environmental stimuli.
TRPM is a family of transient receptor potential ion channels (M standing for wikt:melastatin). Functional TRPM channels are believed to form tetramers. The TRPM family consists of eight different channels, TRPM1–TRPM8.

Capsazepine is a synthetic antagonist of capsaicin. It is used as a biochemical tool in the study of TRPV ion channels.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 2, also known as TRPM2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM2 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1, also known as transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, TRPA1, or The Wasabi Receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPA1 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 5 (TRPM5), also known as long transient receptor potential channel 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM5 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 is an ion channel protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPV4 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M (melastatin) member 8 (TRPM8), also known as the cold and menthol receptor 1 (CMR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM8 gene. The TRPM8 channel is the primary molecular transducer of cold somatosensation in humans. In addition, mints can desensitize a region through the activation of TRPM8 receptors.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM3 gene.

Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 3, also known as TRPV3, is a human gene encoding the protein of the same name.

Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1D subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNA1D gene. Cav1.3 channels belong to the Cav1 family, which form L-type calcium currents and are sensitive to selective inhibition by dihydropyridines (DHP).
Diana M. Bautista is an American neuroscientist known for her work on the molecular mechanisms underlying itch, touch and pain. She is a full professor of cell and developmental biology in the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology and is affiliated with the Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute at the University of California, Berkeley.

HC-067047 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the TRPV4 receptor. It has been used to investigate the role of TRPV4 receptors in a number of areas, such as regulation of blood pressure, bladder function and some forms of pain, as well as neurological functions.

RQ-00203078 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective blocker of the TRPM8 ion channel, which is the main receptor responsible for the sensation of cold. It was developed as a potential analgesic, and blocks the development of hyperalgesia following exposure to cold temperatures or chronic morphine administration.
















