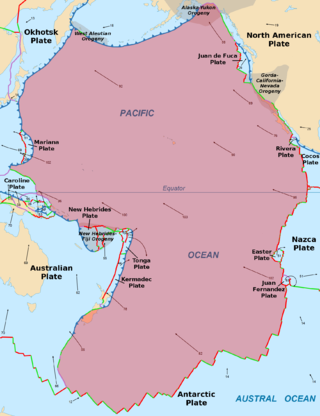
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million km2 (40 million sq mi), it is the largest tectonic plate.

The Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately 100 million years ago when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica had begun rifting by 96 million years ago and completely separated a while after this, some believing as recently as 45 million years ago ,but most accepting presently that this had occurred by 60 million years ago.

The Bismarck Sea lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean within the nation of Papua New Guinea. It is located northeast of the island of New Guinea and south of the Bismarck Archipelago. It has coastlines in districts of the Islands Region, Momase Region, and Papua Region.
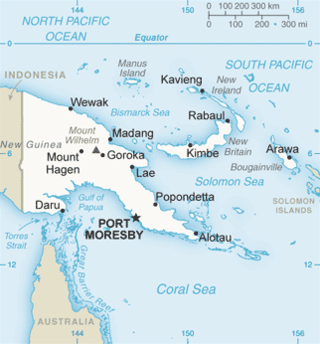
The Solomon Sea is a sea located within the Pacific Ocean. It lies between Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. Many major battles were fought there during World War II.
The Solomon Sea Plate is a minor tectonic plate to the northwest of the Solomon Islands archipelago in the south Pacific Ocean. It roughly corresponds with the Solomon Sea east of Papua New Guinea. The plate boundaries are associated with high earthquake activity as part of the New Britain subduction zone.

The 1,600 kilometres (990 mi) long Macquarie Fault Zone is a major right lateral-moving transform fault along the seafloor of the south Pacific Ocean which runs from New Zealand southwestward towards the Macquarie Triple Junction. It is also the tectonic plate boundary between the Australian Plate to the northwest and the Pacific Plate to the southeast. As such it is a region of high seismic activity and recorded the largest strike-slip event on record up to May 23, 1989, of at least 8.0

The Caroline Plate is a minor tectonic plate that straddles the Equator in the eastern hemisphere located north of New Guinea. It forms a subduction zone along the border with the Bird's Head Plate and other minor plates of the New Guinea region to the south. A transform boundary forms the northern border with the Pacific Plate. Along the border with the Philippine Sea Plate is a convergent boundary that transitions into a rift.

The Mariana Plate is a micro tectonic plate located west of the Mariana Trench which forms the basement of the Mariana Islands which form part of the Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc. It is separated from the Philippine Sea Plate to the west by a divergent boundary with numerous transform fault offsets. The boundary between the Mariana and the Pacific Plate to the east is a subduction zone with the Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Mariana. This eastern subduction is divided into the Mariana Trench, which forms the southeastern boundary, and the Izu–Ogasawara Trench the northeastern boundary. The subduction plate motion is responsible for the shape of the Mariana plate and back arc.

The North Bismarck Plate is a small tectonic plate located in the Bismarck Sea off the northeast coast of New Guinea. It is currently regarded as a relic or inactive plate by most. At one time it was called the Manus Plate, but this term was later used for a modelled microplate at the south east boundary of the North Bismarck Plate.
The South Bismarck Plate is a small tectonic plate located mainly in the southern Bismarck Sea. The eastern part of New Guinea and the island of New Britain are on this plate. It is associated with high earthquake and volcanic activity as part of the New Britain subduction zone within the Pacific Ring of Fire.
The 2000 New Ireland earthquakes occurred off the coast of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea on November 16 and 17.

The Woodlark Plate is a small almost triangular shaped tectonic plate located east of the island of New Guinea and situated mainly within the northern half of the Woodlark Basin. It is located in a very complex tectonic environment, that because of associated features, has been extensively studied since it was first proposed to exist. It is now known to be much smaller than originally proposed, mainly because of information from GPS stations on islands and sea floor studies that have fully defined its margins.
The 1996 Biak earthquake, or the Irian Jaya earthquake, occurred on 17 February at near Biak Island, Indonesia. The earthquake, which occurred on the New Guinea Trench, had a moment magnitude of 8.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). The run-up height of the generated tsunami reached 7.7 m (25 ft). The disaster left at least 108 people dead, 423 injured, and 58 missing. It damaged or destroyed 5,043 houses which subsequently made another 10,000 homeless. At Korim, 187 houses were destroyed. Various countries and organizations provided aid and relief in the aftermath of the earthquake.

The Kilinailau Trench is an oceanic trench delineating the former oceanic crust boundary between the Pacific Plate and the now inactive North Bismarck Plate, in the area to the west of Papua New Guinea. To its south west is the inactive North Solomon Trench. The collision of the Ontong Java Plateau in the then subducting oceanic crust ot the Pacific Plate, initially to the trench's south-east, changed the plate collision dynamics relative to the then Indo-Australian Plate to the west. Now the Ontong Java Plateau is just to the east of the trench and its great depth of crust appears to explain why subduction stalled here, and moved to the opposite direction along the far side of New Britain and the Solomons. The Melanesian ocean arc ridge structures formed when the trench was active are to its west and would include the north eastern part of New Ireland.

The New Britain Trench has formed due to subduction of the floor of the Solomon Sea and has some of the highest current seismic activity in the world.

The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific Plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth.

The Woodlark Basin is a young geologic structural basin located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, found to the southeast of the island country of Papua New Guinea. The basin is an extensional basin that is actively spreading and has a seafloor spreading center. The basin formed between the then Indo-Australian Plate and the Solomon microplate creating the presently independent Woodlark Plate. The Woodlark Basin has a complex geologic history dating back twenty million years to the initial opening of the basin but most of the spreading has happened in the last 3.6 million years.

The Trobriand Plate was, and likely is, an independent microplate between New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. It has some unique geology, having the presence of the youngest metamorphic core complexes on earth. If there is presently active subduction between it and the Solomon Plate, at the Trobriand Trough, it continues to be an active microplate. Otherwise in the latest tectonic models it has merged with the Solomon Sea Plate, which becomes somewhat larger that predicted by Bird's 2003 model of Tectonic Plates. As a smaller Solomon Sea Plate is totally underwater, global positioning data can not resolve this issue. The area of the plate is associated with earthquake and volcanic activity as part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
The New Britain subduction zone is one of the most recently formed and most active subduction zones on earth, producing great earthquakes, with potential for tsunami hazard, and being associated with active volcanism, as part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. It has a close relationship to an area of subduction tectonic activity that extends south eastward from New Britain to the Vanuatu subduction zone, involving the north eastern portion of the Australian Plate and its complicated collision dynamics with the south-western portion of the Pacific Plate.











