The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes (endomembranes) that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. In eukaryotes the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that forms a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of plastids or mitochondria, but might have evolved partially from the actions of the latter.

A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote.

Fertilisation or fertilization, also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a zygote and initiate its development into a new individual organism or offspring. While processes such as insemination or pollination, which happen before the fusion of gametes, are also sometimes informally referred to as fertilisation, these are technically separate processes. The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction. During double fertilisation in angiosperms, the haploid male gamete combines with two haploid polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus by the process of vegetative fertilisation.

The egg cell or ovum is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms. The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere. When fertilized, the oosphere becomes the oospore.

During fertilization, a sperm must first fuse with the plasma membrane and then penetrate the female egg cell to fertilize it. Fusing to the egg cell usually causes little problem, whereas penetrating through the egg's hard shell or extracellular matrix can be more difficult. Therefore, sperm cells go through a process known as the acrosome reaction, which is the reaction that occurs in the acrosome of the sperm as it approaches the egg.

Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
Capacitation is the penultimate step in the maturation of mammalian spermatozoa and is required to render them competent to fertilize an oocyte. This step is a biochemical event; the sperm move normally and look mature prior to capacitation. In vivo, capacitation occurs after ejaculation, when the spermatozoa leave the vagina and enter the upper female reproductive tract. The uterus aids in the steps of capacitation by secreting sterol-binding albumin, lipoproteins, and proteolytic and glycosidasic enzymes such as heparin.
Hyperactivation is a type of sperm motility. Hyperactivated sperm motility is characterised by a high amplitude, asymmetrical beating pattern of the sperm tail (flagellum). This type of motility may aid in sperm penetration of the zona pellucida, which encloses the ovum.

Acrosin is a digestive enzyme that acts as a protease. In humans, acrosin is encoded by the ACR gene. Acrosin is released from the acrosome of spermatozoa as a consequence of the acrosome reaction. It aids in the penetration of the Zona Pellucida.

A pronucleus denotes the nucleus found in either a sperm or egg cell during the process of fertilization. The sperm cell undergoes a transformation into a pronucleus after entering the egg cell but prior to the fusion of the genetic material of both the sperm and egg. In contrast, the egg cell possesses a pronucleus once it becomes haploid, not upon the arrival of the sperm cell. Haploid cells, such as sperm and egg cells in humans, carry half the number of chromosomes present in somatic cells, with 23 chromosomes compared to the 46 found in somatic cells. It is noteworthy that the male and female pronuclei do not physically merge, although their genetic material does. Instead, their membranes dissolve, eliminating any barriers between the male and female chromosomes, facilitating the combination of their chromosomes into a single diploid nucleus in the resulting embryo, which contains a complete set of 46 chromosomes.

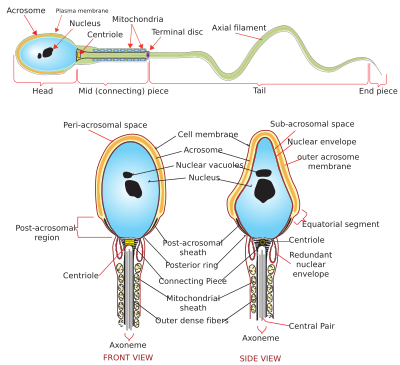
Spermiogenesis is the final stage of spermatogenesis, during which the spermatids develop into mature spermatozoa. At the beginning of the stage, the spermatid is a more or less circular cell containing a nucleus, Golgi apparatus, centriole and mitochondria; by the end of the process, it has radically transformed into an elongated spermatozoon, complete with a head, midpiece, and tail.
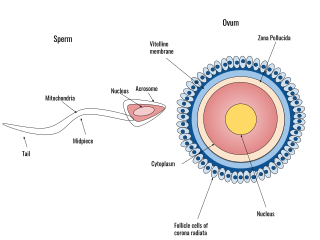
Human fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm, occurring primarily in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The result of this union leads to the production of a fertilized egg called a zygote, initiating embryonic development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the 19th century.

A23187 is a mobile ion-carrier that forms stable complexes with divalent cations. A23187 is also known as Calcimycin, Calcium Ionophore, Antibiotic A23187 and Calcium Ionophore A23187. It is produced at fermentation of Streptomyceschartreusensis.
The hamster zona-free ovum test, or hamster egg-penetration test, or sometimes just hamster test, is an in-vitro test used to study physiological profile of spermatozoa. The primary application of the test is to diagnose male infertility caused by sperm unable to penetrate the ova. The test has limited value, due to expense and a high false negative rate.
The cation channels of sperm also known as Catsper channels or CatSper, are ion channels that are related to the two-pore channels and distantly related to TRP channels. The four members of this family form voltage-gated Ca2+ channels that seem to be specific to sperm. As sperm encounter the more alkaline environment of the female reproductive tract, CatSper channels become activated by the altered ion concentration. These channels are required for proper fertilization. The study of these channels has been slow because they do not traffic to the cell membrane in many heterologous systems.
Teratospermia or teratozoospermia is a condition characterized by the presence of sperm with abnormal morphology that affects fertility in males.
Spermatozoa develop in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. During their development, the spermatogonia proceed through meiosis to become spermatozoa. Many changes occur during this process: the DNA in nuclei becomes condensed; the acrosome develops as a structure close to the nucleus. The acrosome is derived from the Golgi apparatus and contains hydrolytic enzymes important for fusion of the spermatozoon with an egg cell. During spermiogenesis, the nucleus condenses and changes shape. Abnormal shape change is a feature of sperm in male infertility. The acroplaxome is a structure found between the acrosomal membrane and the nuclear membrane. The acroplaxome contains structural proteins including keratin 5, F-actin and profilin IV.
Reproductive immunology refers to a field of medicine that studies interactions between the immune system and components related to the reproductive system, such as maternal immune tolerance towards the fetus, or immunological interactions across the blood-testis barrier. The concept has been used by fertility clinics to explain fertility problems, recurrent miscarriages and pregnancy complications observed when this state of immunological tolerance is not successfully achieved. Immunological therapy is a method for treating many cases of previously "unexplained infertility" or recurrent miscarriage.
Oocyteactivation is a series of processes that occur in the oocyte during fertilization.
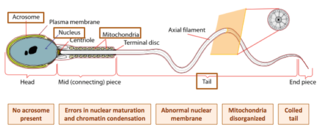
Globozoospermia is a rare and severe form of monomorphic teratozoospermia. This means that the spermatozoa show the same abnormality, and over 85% of spermatozoa in sperm have this abnormality. Globozoospermia is responsible for less than 0.1% of male infertility. It is characterised by round-headed spermatozoa without acrosomes, an abnormal nuclear membrane and midpiece defects. Affected males therefore suffer from either reduced fertility or infertility. Studies suggest that globozoospermia can be either total or partial, however it is unclear whether these two forms are variations on the same syndrome, or actually different syndromes.