Cascading is a software abstraction layer for Apache Hadoop and Apache Flink. Cascading is used to create and execute complex data processing workflows on a Hadoop cluster using any JVM-based language, hiding the underlying complexity of MapReduce jobs. It is open source and available under the Apache License. Commercial support is available from Driven, Inc.
Ganglia is a scalable, distributed monitoring tool for high-performance computing systems, clusters and networks. The software is used to view either live or recorded statistics covering metrics such as CPU load averages or network utilization for many nodes.
In computer science, stream processing is a programming paradigm which views streams, or sequences of events in time, as the central input and output objects of computation. Stream processing encompasses dataflow programming, reactive programming, and distributed data processing. Stream processing systems aim to expose parallel processing for data streams and rely on streaming algorithms for efficient implementation. The software stack for these systems includes components such as programming models and query languages, for expressing computation; stream management systems, for distribution and scheduling; and hardware components for acceleration including floating-point units, graphics processing units, and field-programmable gate arrays.
Apache Hadoop is a collection of open-source software utilities that facilitates using a network of many computers to solve problems involving massive amounts of data and computation. It provides a software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using the MapReduce programming model. Hadoop was originally designed for computer clusters built from commodity hardware, which is still the common use. It has since also found use on clusters of higher-end hardware. All the modules in Hadoop are designed with a fundamental assumption that hardware failures are common occurrences and should be automatically handled by the framework.
An object-based spatial database is a spatial database that stores the location as objects. The object-based spatial model treats the world as surface littered with recognizable objects, which exist independent of their locations.

Solr is an open-source enterprise-search platform, written in Java. Its major features include full-text search, hit highlighting, faceted search, real-time indexing, dynamic clustering, database integration, NoSQL features and rich document handling. Providing distributed search and index replication, Solr is designed for scalability and fault tolerance. Solr is widely used for enterprise search and analytics use cases and has an active development community and regular releases.
Dryad was a research project at Microsoft Research for a general purpose runtime for execution of data parallel applications. The research prototypes of the Dryad and DryadLINQ data-parallel processing frameworks are available in source form at GitHub.
Apache Mahout is a project of the Apache Software Foundation to produce free implementations of distributed or otherwise scalable machine learning algorithms focused primarily on linear algebra. In the past, many of the implementations use the Apache Hadoop platform, however today it is primarily focused on Apache Spark. Mahout also provides Java/Scala libraries for common math operations and primitive Java collections. Mahout is a work in progress; a number of algorithms have been implemented.

Apache ZooKeeper is an open-source server for highly reliable distributed coordination of cloud applications. It is a project of the Apache Software Foundation.

Apache Hama is a distributed computing framework based on bulk synchronous parallel computing techniques for massive scientific computations e.g., matrix, graph and network algorithms. Originally a sub-project of Hadoop, it became an Apache Software Foundation top level project in 2012. It was created by Edward J. Yoon, who named it, and Hama also means hippopotamus in Yoon's native Korean language (하마), following the trend of naming Apache projects after animals and zoology. Hama was inspired by Google's Pregel large-scale graph computing framework described in 2010. When executing graph algorithms, Hama showed a fifty-fold performance increase relative to Hadoop.

Oracle NoSQL Database is a NoSQL-type distributed key-value database from Oracle Corporation. It provides transactional semantics for data manipulation, horizontal scalability, and simple administration and monitoring.
Apache Kafka is a distributed event store and stream-processing platform. It is an open-source system developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Java and Scala. The project aims to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds. Kafka can connect to external systems via Kafka Connect, and provides the Kafka Streams libraries for stream processing applications. Kafka uses a binary TCP-based protocol that is optimized for efficiency and relies on a "message set" abstraction that naturally groups messages together to reduce the overhead of the network roundtrip. This "leads to larger network packets, larger sequential disk operations, contiguous memory blocks [...] which allows Kafka to turn a bursty stream of random message writes into linear writes."
Druid is a column-oriented, open-source, distributed data store written in Java. Druid is designed to quickly ingest massive quantities of event data, and provide low-latency queries on top of the data. The name Druid comes from the shapeshifting Druid class in many role-playing games, to reflect that the architecture of the system can shift to solve different types of data problems.

Apache Spark is an open-source unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. Spark provides an interface for programming clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance. Originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley's AMPLab, the Spark codebase was later donated to the Apache Software Foundation, which has maintained it since.

Apache Samza is an open-source, near-realtime, asynchronous computational framework for stream processing developed by the Apache Software Foundation in Scala and Java. It has been developed in conjunction with Apache Kafka. Both were originally developed by LinkedIn.
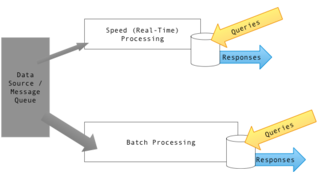
Lambda architecture is a data-processing architecture designed to handle massive quantities of data by taking advantage of both batch and stream-processing methods. This approach to architecture attempts to balance latency, throughput, and fault-tolerance by using batch processing to provide comprehensive and accurate views of batch data, while simultaneously using real-time stream processing to provide views of online data. The two view outputs may be joined before presentation. The rise of lambda architecture is correlated with the growth of big data, real-time analytics, and the drive to mitigate the latencies of map-reduce.

Apache Flink is an open-source, unified stream-processing and batch-processing framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The core of Apache Flink is a distributed streaming data-flow engine written in Java and Scala. Flink executes arbitrary dataflow programs in a data-parallel and pipelined manner. Flink's pipelined runtime system enables the execution of bulk/batch and stream processing programs. Furthermore, Flink's runtime supports the execution of iterative algorithms natively.

SNAMP is an open-source, cross-platform software platform for telemetry, tracing and elasticity management of distributed applications.
StormCrawler is an open-source collection of resources for building low-latency, scalable web crawlers on Apache Storm. It is provided under Apache License and is written mostly in Java.









