Related Research Articles
Fundamental analysis, in accounting and finance, is the analysis of a business's financial statements ; health; and competitors and markets. It also considers the overall state of the economy and factors including interest rates, production, earnings, employment, GDP, housing, manufacturing and management. There are two basic approaches that can be used: bottom up analysis and top down analysis. These terms are used to distinguish such analysis from other types of investment analysis, such as quantitative and technical.

A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks, which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include securities listed on a public stock exchange as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies that are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. Investments are usually made with an investment strategy in mind.

A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a major cross-section of a stock market, resulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes are driven by panic selling and underlying economic factors. They often follow speculation and economic bubbles.
A market trend is a perceived tendency of the financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as secular for long time-frames, primary for medium time-frames, and secondary for short time-frames. Traders attempt to identify market trends using technical analysis, a framework which characterizes market trends as predictable price tendencies within the market when price reaches support and resistance levels, varying over time.
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources to achieve later benefits". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream.
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. As a type of active management, it stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of technical analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results. It is distinguished from fundamental analysis, which considers a company's financial statements, health, and the overall state of the market and economy.
The relative strength index (RSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets. It is intended to chart the current and historical strength or weakness of a stock or market based on the closing prices of a recent trading period. The indicator should not be confused with relative strength.
Greed and fear refer to two opposing emotional states theorized as factors causing the unpredictability and volatility of the stock market, and irrational market behavior inconsistent with the efficient-market hypothesis. Greed and fear relate to an old Wall Street saying: "financial markets are driven by two powerful emotions – greed and fear."
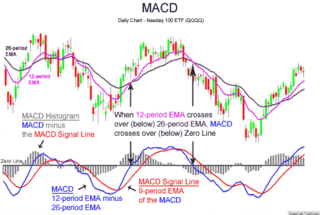
MACD, short for moving average convergence/divergence, is a trading indicator used in technical analysis of securities prices, created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s. It is designed to reveal changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a trend in a stock's price.
On-balance volume (OBV) is a technical analysis indicator intended to relate price and volume in the stock market. OBV is based on a cumulative total volume.
The Negative Volume Index and Positive Volume Index indicators are indicators to identify primary market trends and reversals.
The Hindenburg Omen was a proposed technical analysis pattern, named after the Hindenburg disaster of May 6, 1937. It was created by Jim Miekka, who believed that it predicted stock market crashes.
The Kazakhstan Stock Exchange is a stock exchange located in Almaty, Kazakhstan. The exchange was founded in 1993.
The McClellan oscillator is a market breadth indicator used in technical analysis by financial analysts of the New York Stock Exchange to evaluate the balance between the advancing and declining stocks. The McClellan oscillator is based on the Advance-Decline Data and it could be applied to stock market exchanges, indexes, portfolio of stocks or any basket of stocks.
The TRIN, or Arms index, developed by Richard Arms in the 1970s, is a short-term technical analysis stock market trading indicator based on the Advance-Decline Data. The name is short for TRading INdex. The index is calculated as follows:
The advance–decline line is a stock market technical indicator used by investors to measure the number of individual stocks participating in a market rise or fall. As price changes of large stocks can have a disproportionate effect on capitalization weighted stock market indices such as the S&P 500, the NYSE Composite Index, and the NASDAQ Composite index, it can be useful to know how broadly this movement extends into the larger universe of smaller stocks. Since market indexes represent a group of stocks, they do not present the whole picture of the trading day and the performance of the market during this day. Though the market indices give an idea about what has happened during the trading day, advance/decline numbers give an idea about the individual performance of particular stocks.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
The true strength index (TSI) is a technical indicator used in the analysis of financial markets that attempts to show both trend direction and overbought/oversold conditions. It was first published William Blau in 1991. The indicator uses moving averages of the underlying momentum of a financial instrument. Momentum is considered a leading indicator of price movements, and a moving average characteristically lags behind price. The TSI combines these characteristics to create an indication of price and direction more in sync with market turns than either momentum or moving average. The TSI is provided as part of the standard collection of indicators offered by various trading platforms.
The Advance-Decline data also known as AD data are calculated to show the number of advancing and declining stocks and traded volume associated with these stocks within a market index, stock market exchange or any basket of stocks with purpose of analysis of the sentiment within the analysed group of stocks. Advance-Decline data are used to measure overall market breadth as well as to measure sentiment within the stock market sectors.
Jason Goepfert is an American researcher and columnist focused on the development of behavioral finance. Prior to founding Sundial Capital Research, he was the manager of back office operations for Deephaven Capital Management, a Minnesota-based hedge fund, and Wells Fargo's online brokerage unit.
References
- ↑ Technical Analysis by Charles D. Kirkpatrick, Julie R. Dahlquist 2010 ISBN 0-13-705944-2 page 133