
Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.
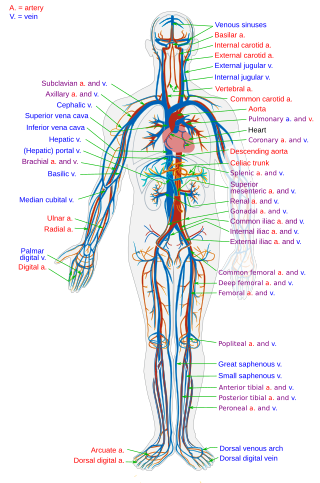
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm. Venous return from the lower half, below the diaphragm, flows through the inferior vena cava. The SVC is located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. It is the typical site of central venous access via a central venous catheter or a peripherally inserted central catheter. Mentions of "the cava" without further specification usually refer to the SVC.

The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.
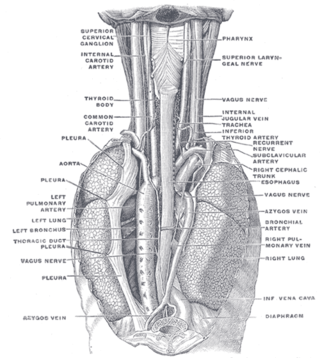
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.

The jugular veins are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

The coronary sinus is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus.
The term Great veins can refer to either —

Scimitar syndrome, or congenital pulmonary venolobar syndrome, is a rare congenital heart defect characterized by anomalous venous return from the right lung. This anomalous pulmonary venous return can be either partial (PAPVR) or total (TAPVR). The syndrome associated with PAPVR is more commonly known as Scimitar syndrome after the curvilinear pattern created on a chest radiograph by the pulmonary veins that drain to the inferior vena cava. This radiographic density often has the shape of a scimitar, a type of curved sword. The syndrome was first described by Catherine Neill in 1960.

The pericardial sinuses are impressions in the pericardial sac formed between the points where great vessels enter it.

The oblique vein of the left atrium is a small vein which descends obliquely on the back of the left atrium and ends in the coronary sinus near its left extremity; it is continuous above with the ligament of the left vena cava, and the two structures form the remnant of the left Cuvierian duct. This obscure region of cardiac perfusion adjacent to the SA node rocks back and forth under systole and diastole thus further influencing cardiac autonomic innervation. Ablation of this channel seems reasonable to many observers.

The valve of the inferior vena cava is a venous valve that lies at the junction of the inferior vena cava and right atrium.
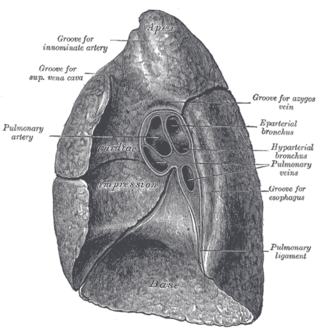
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back than the front. The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura and the visceral pleura is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities.
A cardiac shunt is a pattern of blood flow in the heart that deviates from the normal circuit of the circulatory system. It may be described as right-left, left-right or bidirectional, or as systemic-to-pulmonary or pulmonary-to-systemic. The direction may be controlled by left and/or right heart pressure, a biological or artificial heart valve or both. The presence of a shunt may also affect left and/or right heart pressure either beneficially or detrimentally.
Venous return is the rate of blood flow back to the heart. It normally limits cardiac output.

In anatomy, the venae cavae are two large veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the right atrium. They are located slightly off-center, toward the right side of the body.
The heart is a muscular organ situated in the mediastinum. It consists of four chambers, four valves, two main arteries, and the conduction system. The left and right sides of the heart have different functions: the right side receives de-oxygenated blood through the superior and inferior venae cavae and pumps blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, and the left side receives saturated blood from the lungs.
Raghib syndrome is rare a congenital heart defect where the left superior vena cava (LSVC) is draining into the left atrium in addition to an absent coronary sinus and an atrial septal defect. This can be considered a dangerous heart condition because it puts the individual at a high risk of stroke. Other defects that are often associated with Raghib syndrome can include ventricular septal defects, enlargement of the tricuspid annulus, and pulmonary stenosis. While this is considered an extremely rare developmental complex, cases regarding a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) are relatively common among congenital heart defects. It is also important to note that the PLSVC often drains into the right atrium, and only drains into the left atrium in approximately 10 to 20% of individuals with the defect.












