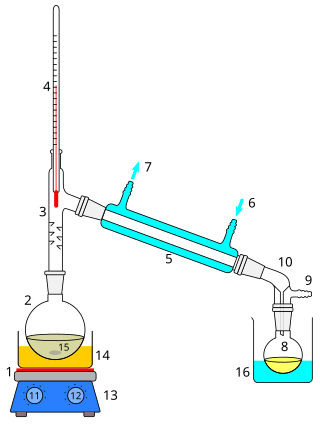
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products ; this may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation, or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components; in either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction. An installation used for distillation, especially of distilled beverages, is a distillery. Distillation includes the following applications:

Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.

Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds and fog.

Lindane, also known as gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane (γ-HCH), gammaxene, Gammallin and benzene hexachloride (BHC), is an organochlorine chemical and an isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane that has been used both as an agricultural insecticide and as a pharmaceutical treatment for lice and scabies.

Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is an international environmental treaty, signed on 22 May 2001 in Stockholm and effective from 17 May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs).

Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic compounds that are resistant to degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. They are toxic chemicals that adversely affect human health and the environment around the world. Because they can be transported by wind and water, most POPs generated in one country can and do affect people and wildlife far from where they are used and released.

Biomagnification, also known as bioamplification or biological magnification, is the increase in concentration of a substance, e.g a pesticide, in the tissues of organisms at successively higher levels in a food chain. This increase can occur as a result of:

Dieldrin is an organochlorine compound originally produced in 1948 by J. Hyman & Co, Denver, as an insecticide. Dieldrin is closely related to aldrin, which reacts further to form dieldrin. Aldrin is not toxic to insects; it is oxidized in the insect to form dieldrin which is the active compound. Both dieldrin and aldrin are named after the Diels-Alder reaction which is used to form aldrin from a mixture of norbornadiene and hexachlorocyclopentadiene.
Scrubber systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove some particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams. An early application of a carbon dioxide scrubber was in the submarine the Ictíneo I, in 1859; a role for which they continue to be used today. Traditionally, the term "scrubber" has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to wash unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. Recently, the term has also been used to describe systems that inject a dry reagent or slurry into a dirty exhaust stream to "wash out" acid gases. Scrubbers are one of the primary devices that control gaseous emissions, especially acid gases. Scrubbers can also be used for heat recovery from hot gases by flue-gas condensation. They are also used for the high flows in solar, PV, or LED processes.

Toxaphene was an insecticide used primarily for cotton in the southern United States during the late 1960s and the 1970s. Toxaphene is a mixture of over 670 different chemicals and is produced by reacting chlorine gas with camphene. It can be most commonly found as a yellow to amber waxy solid.

In chemistry, volatility is a material quality which describes how readily a substance vaporizes. At a given temperature and pressure, a substance with high volatility is more likely to exist as a vapour, while a substance with low volatility is more likely to be a liquid or solid. Volatility can also describe the tendency of a vapor to condense into a liquid or solid; less volatile substances will more readily condense from a vapor than highly volatile ones. Differences in volatility can be observed by comparing how fast substances within a group evaporate when exposed to the atmosphere. A highly volatile substance such as rubbing alcohol will quickly evaporate, while a substance with low volatility such as vegetable oil will remain condensed. In general, solids are much less volatile than liquids, but there are some exceptions. Solids that sublimate such as dry ice or iodine can vaporize at a similar rate as some liquids under standard conditions.

β-Hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) is an organochloride which is one of the isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). It is a byproduct of the production of the insecticide lindane (γ-HCH). It is typically constitutes 5–14% of technical-grade lindane, though it has not been produced or used in the United States since 1985. As of 2009, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants classified α-hexachlorocyclohexane and β-HCH as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), due to the chemical's ability to persist in the environment, bioaccumulative, biomagnifying, and long-range transport capacity.

Arctic haze is the phenomenon of a visible reddish-brown springtime haze in the atmosphere at high latitudes in the Arctic due to anthropogenic air pollution. A major distinguishing factor of Arctic haze is the ability of its chemical ingredients to persist in the atmosphere for significantly longer than other pollutants. Due to limited amounts of snow, rain, or turbulent air to displace pollutants from the polar air mass in spring, Arctic haze can linger for more than a month in the northern atmosphere.

An evaporator is a type of heat exchanger device that facilitates evaporation by utilizing conductive and convective heat transfer to provide the necessary thermal energy for phase transition from liquid to vapor. Within evaporators, a circulating liquid is exposed to an atmospheric or reduced pressure environment, causing it to boil at a lower temperature compared to normal atmospheric boiling.

α-Hexachlorocyclohexane (α-HCH) is an organochloride which is one of the isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). It is a byproduct of the production of the insecticide lindane (γ-HCH) and it is typically still contained in commercial grade lindane used as insecticide. Lindane, however, has not been produced or used in the United States for more than 20 years. At ambient temperatures it is a stable, white, powdery solid substance. As of 2009, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants classified (α-HCH) and (β-HCH) as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), due to the chemical's ability to persistence in the environment, bioaccumulative, biomagnifying, and long-range transport capacity.

Pentachlorobenzene (PeCB) is a chlorobenzene compound with the molecular formula C6HCl5 which is a chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbon. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with five chlorine atoms. PeCB was once used industrially for a variety of uses, but because of environmental concerns there are currently no large scale uses of PeCB. Pentachlorobenzene is a known persistent organic pollutant (POP) and banned globally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2009.
Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic substances (PBTs) are a class of compounds that have high resistance to degradation from abiotic and biotic factors, high mobility in the environment and high toxicity. Because of these factors PBTs have been observed to have a high order of bioaccumulation and biomagnification, very long retention times in various media, and widespread distribution across the globe. Most PBTs in the environment are either created through industry or are unintentional byproducts.
Pollution in the Arctic Ocean is primarily the result of economic activities carried out on land, which is sources from locally, regionally, and globally origins. There is also the inclusion of industrial development in the Arctic region, northern rivers, and the effects of military activities, particularly nuclear activity – as well as the influx of pollutants from other regions of the world.However, the Arctic Ocean remains relatively clean compared to other marine regions of the world.
Brynjulf Ottar (1918–1988) was a Norwegian atmospheric chemist who served as the first director of the Norwegian Institute for Air Research. In the 1970s, his work on the long-range transport of air pollution helped to alert the world to the problem of acid rain; later, he was one of the first scientists to describe the mechanism of global distillation, by which pollutants travel from mid-latitude parts of Earth to the Arctic.
















