
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that each last from days to weeks. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder.
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together with lability of affect." During a manic episode, an individual will experience rapidly changing emotions and moods, highly influenced by surrounding stimuli. Although mania is often conceived as a "mirror image" to depression, the heightened mood can be either euphoric or dysphoric. As the mania intensifies, irritability can be more pronounced and result in anxiety or anger.
Self-control, an aspect of inhibitory control, is the ability to regulate one's emotions, thoughts, and behavior in the face of temptations and impulses. As an executive function, it is a cognitive process that is necessary for regulating one's behavior in order to achieve specific goals.
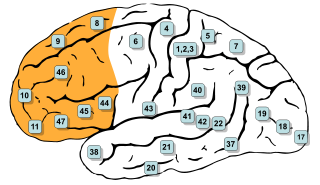
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47.

Delayed gratification, or deferred gratification, is the resistance to the temptation of an immediate pleasure in the hope of obtaining a valuable and long-lasting reward in the long-term. In other words, delayed gratification describes the process that the subject undergoes when the subject resists the temptation of an immediate reward in preference for a later reward. Generally, delayed gratification is associated with resisting a smaller but more immediate reward in order to receive a larger or more enduring reward later. A growing body of literature has linked the ability to delay gratification to a host of other positive outcomes, including academic success, physical health, psychological health, and social competence.

In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence.
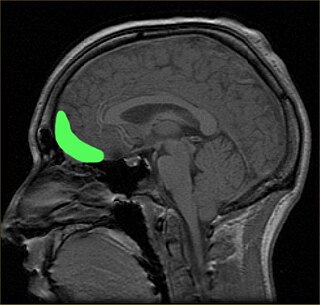
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes of the brain which is involved in the cognitive process of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 12 and 13; in humans it consists of Brodmann area 10, 11 and 47.
Walter Mischel was an Austrian-born American psychologist specializing in personality theory and social psychology. He was the Robert Johnston Niven Professor of Humane Letters in the Department of Psychology at Columbia University. A Review of General Psychology survey, published in 2002, ranked Mischel as the 25th most cited psychologist of the 20th century.
The Iowa gambling task (IGT) is a psychological task thought to simulate real-life decision making. It was introduced by Antoine Bechara, Antonio Damasio, Hanna Damasio and Steven Anderson, then researchers at the University of Iowa. It has been brought to popular attention by Antonio Damasio in his best-selling book Descartes' Error.
Hot cognition is a hypothesis on motivated reasoning in which a person's thinking is influenced by their emotional state. Put simply, hot cognition is cognition coloured by emotion. Hot cognition contrasts with cold cognition, which implies cognitive processing of information that is independent of emotional involvement. Hot cognition is proposed to be associated with cognitive and physiological arousal, in which a person is more responsive to environmental factors. As it is automatic, rapid and led by emotion, hot cognition may consequently cause biased decision making. Hot cognition may arise, with varying degrees of strength, in politics, religion, and other sociopolitical contexts because of moral issues, which are inevitably tied to emotion. Hot cognition was initially proposed in 1963 by Robert P. Abelson. The idea became popular in the 1960s and the 1970s.

The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is a part of the prefrontal cortex in the mammalian brain. The ventral medial prefrontal is located in the frontal lobe at the bottom of the cerebral hemispheres and is implicated in the processing of risk and fear, as it is critical in the regulation of amygdala activity in humans. It also plays a role in the inhibition of emotional responses, and in the process of decision-making and self-control. It is also involved in the cognitive evaluation of morality.
One way of thinking holds that the mental process of decision-making is rational: a formal process based on optimizing utility. Rational thinking and decision-making does not leave much room for emotions. In fact, emotions are often considered irrational occurrences that may distort reasoning.

In psychology, impulsivity is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences," which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. Impulsivity can be classified as a multifactorial construct. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. "When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality." Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least two independent components: first, acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and second, choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.

Inhibitory control, also known as response inhibition, is a cognitive process – and, more specifically, an executive function – that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses and natural, habitual, or dominant behavioral responses to stimuli in order to select a more appropriate behavior that is consistent with completing their goals. Self-control is an important aspect of inhibitory control. For example, successfully suppressing the natural behavioral response to eat cake when one is craving it while dieting requires the use of inhibitory control.
The Stanford marshmallow experiment was a study on delayed gratification in 1972 led by psychologist Walter Mischel, a professor at Stanford University. In this study, a child was offered a choice between one small but immediate reward, or two small rewards if they waited for a period of time. During this time, the researcher left the child in a room with a single marshmallow for about 15 minutes and then returned. If they did not eat the marshmallow, the reward was either another marshmallow or pretzel stick, depending on the child's preference. In follow-up studies, the researchers found that children who were able to wait longer for the preferred rewards tended to have better life outcomes, as measured by SAT scores, educational attainment, body mass index (BMI), and other life measures. A replication attempt with a sample from a more diverse population, over 10 times larger than the original study, showed only half the effect of the original study. The replication suggested that economic background, rather than willpower, explained the other half. The predictive power of the marshmallow test was challenged in a 2020 study.
The neurocircuitry that underlies executive function processes and emotional and motivational processes are known to be distinct in the brain. However, there are brain regions that show overlap in function between the two cognitive systems. Brain regions that exist in both systems are interesting mainly for studies on how one system affects the other. Examples of such cross-modal functions are emotional regulation strategies such as emotional suppression and emotional reappraisal, the effect of mood on cognitive tasks, and the effect of emotional stimulation of cognitive tasks.

The dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC or DMPFC is a section of the prefrontal cortex in some species' brain anatomy. It includes portions of Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA24 and BA32, although some authors identify it specifically with BA8 and BA9 Some notable sub-components include the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, the prelimbic cortex, and the infralimbic cortex.

Bipolar disorder is an affective disorder characterized by periods of elevated and depressed mood. The cause and mechanism of bipolar disorder is not yet known, and the study of its biological origins is ongoing. Although no single gene causes the disorder, a number of genes are linked to increase risk of the disorder, and various gene environment interactions may play a role in predisposing individuals to developing bipolar disorder. Neuroimaging and postmortem studies have found abnormalities in a variety of brain regions, and most commonly implicated regions include the ventral prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Dysfunction in emotional circuits located in these regions have been hypothesized as a mechanism for bipolar disorder. A number of lines of evidence suggests abnormalities in neurotransmission, intracellular signalling, and cellular functioning as possibly playing a role in bipolar disorder.
Present bias is the tendency to rather settle for a smaller present reward than to wait for a larger future reward, in a trade-off situation. It describes the trend of overvaluing immediate rewards, while putting less worth in long-term consequences. The present bias can be used as a measure for self-control, which is a trait related to the prediction of secure life outcomes.
Ozlem Nefise Ayduk is an American social psychologist at U.C. Berkeley researching close relationships, emotion regulation, and the development of self-regulation in children. She is a fellow at the Society of Experimental Social Psychology and the Society for Personality and Social Psychology. She has contributed content to several psychology handbooks, dictionaries, and encyclopedias.










