
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focuses the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state.
Stress management consists of a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies aimed at controlling a person's level of stress, especially chronic stress, usually for the purpose of improving everyday functioning. Stress produces numerous physical and mental symptoms which vary according to each individual's situational factors. These can include a decline in physical health, such as headaches, chest pain, fatigue, and sleep problems, as well as depression. The process of stress management is named as one of the keys to a happy and successful life in modern society. Life often delivers numerous demands that can be difficult to handle, but stress management provides a number of ways to manage anxiety and maintain overall well-being.

Compassion is a social feeling that motivates people to go out of their way to relieve the physical, mental, or emotional pains of others and themselves. Compassion is sensitivity to the emotional aspects of the suffering of others. When based on notions such as fairness, justice, and interdependence, it may be considered partially rational in nature.

Anger management is a psycho-therapeutic program for anger prevention and control. It has been described as deploying anger successfully. Anger is frequently a result of frustration, or of feeling blocked or thwarted from something the subject feels is important. Anger can also be a defensive response to underlying fear or feelings of vulnerability or powerlessness. Anger management programs consider anger to be a motivation caused by an identifiable reason which can be logically analyzed and addressed.
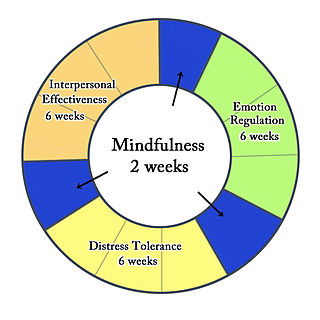
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy that began with efforts to treat personality disorders and interpersonal conflicts. Evidence suggests that DBT can be useful in treating mood disorders and suicidal ideation as well as for changing behavioral patterns such as self-harm and substance use. DBT evolved into a process in which the therapist and client work with acceptance and change-oriented strategies and ultimately balance and synthesize them—comparable to the philosophical dialectical process of thesis and antithesis, followed by synthesis.
Physiological psychology is a subdivision of behavioral neuroscience that studies the neural mechanisms of perception and behavior through direct manipulation of the brains of nonhuman animal subjects in controlled experiments. This field of psychology takes an empirical and practical approach when studying the brain and human behavior. Most scientists in this field believe that the mind is a phenomenon that stems from the nervous system. By studying and gaining knowledge about the mechanisms of the nervous system, physiological psychologists can uncover many truths about human behavior. Unlike other subdivisions within biological psychology, the main focus of psychological research is the development of theories that describe brain-behavior relationships.
Inner peace refers to a deliberate state of psychological or spiritual calm despite the potential presence of stressors. Being "at peace" is considered by many to be healthy (homeostasis) and the opposite of being stressed or anxious, and is considered to be a state where our mind performs at an optimal level, regardless of outcomes. Peace of mind is thus generally associated with bliss, happiness and contentment.

Yoga nidra or yogic sleep in modern usage is a state of consciousness between waking and sleeping, typically induced by a guided meditation.
Coping refers to conscious strategies used to reduce unpleasant emotions. Coping strategies can be cognitions or behaviors and can be individual or social. Coping is to deal with and overcome struggles and difficulties in life. It is a way for us to maintain our mental and emotional well-being. Everybody has a way of handling the hard events that occur in our life and that is what it means to cope. Coping can be healthy and productive, or destructive and unhealthy for you or others. It is recommended that an individual copes in ways that will be beneficial and healthy. "Managing your stress well can help you feel better physically and psychologically and it can impact your ability to perform your best."
Mindfulness is the practice of purposely bringing one's attention to the present-moment experience without evaluation, a skill one develops through meditation or other training. Mindfulness derives from sati, a significant element of Hindu and Buddhist traditions, and is based on Zen, Vipassanā, and Tibetan meditation techniques. Though definitions and techniques of mindfulness are wide-ranging, Buddhist traditions explain what constitutes mindfulness such as how past, present and future moments arise and cease as momentary sense impressions and mental phenomena. Individuals who have contributed to the popularity of mindfulness in the modern Western context include Thích Nhất Hạnh, Herbert Benson, Jon Kabat-Zinn, Richard J. Davidson, and Sam Harris.
Emotion dysregulation is a range of emotional responses that do not lie within a desirable scope of emotive response, considering the stimuli.

The psychological and physiological effects of meditation have been studied. In recent years, studies of meditation have increasingly involved the use of modern instruments, such as fMRI and EEG, which are able to observe brain physiology and neural activity in living subjects, either during the act of meditation itself or before and after meditation. Correlations can thus be established between meditative practices and brain structure or function.

Buddhism includes an analysis of human psychology, emotion, cognition, behavior and motivation along with therapeutic practices. Buddhist psychology is embedded within the greater Buddhist ethical and philosophical system, and its psychological terminology is colored by ethical overtones. Buddhist psychology has two therapeutic goals: the healthy and virtuous life of a householder and the ultimate goal of nirvana, the total cessation of dissatisfaction and suffering (dukkha).
Self-compassion is extending compassion to one's self in instances of perceived inadequacy, failure, or general suffering. Kristin Neff has defined self-compassion as being composed of three main elements – self-kindness, common humanity, and mindfulness.

Crying is the dropping of tears in response to an emotional state or pain. Emotions that can lead to crying include sadness, anger, excitement, and even happiness. The act of crying has been defined as "a complex secretomotor phenomenon characterized by the shedding of tears from the lacrimal apparatus, without any irritation of the ocular structures", instead, giving a relief which protects from conjunctivitis. A related medical term is lacrimation, which also refers to non-emotional shedding of tears. Various forms of crying are known as sobbing, weeping, wailing, whimpering, bawling, and blubbering.

Sport psychology was defined by the European Federation of Sport in 1996, as the study of the psychological basis, processes, and effects of sport. Otherwise, sport is considered as any physical activity where the individuals engage for competition and health. Sport psychology is recognized as an interdisciplinary science that draws on knowledge from many related fields including biomechanics, physiology, kinesiology and psychology. It involves the study of how psychological factors affect performance and how participation in sport and exercise affect psychological and physical factors. Sport psychologists teach cognitive and behavioral strategies to athletes in order to improve their experience and performance in sports.

In psychology, relaxation is the emotional state of low tension, in which there is an absence of arousal, particularly from negative sources such as anger, anxiety, or fear.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) is an eight-week evidence-based program that offers secular, intensive mindfulness training to assist people with stress, anxiety, depression and pain. Developed at the University of Massachusetts Medical Center in the 1970s by Professor Jon Kabat-Zinn, MBSR uses a combination of mindfulness meditation, body awareness, yoga and exploration of patterns of behaviour, thinking, feeling and action. Mindfulness can be understood as the non-judgmental acceptance and investigation of present experience, including body sensations, internal mental states, thoughts, emotions, impulses and memories, in order to reduce suffering or distress and to increase well-being. Mindfulness meditation is a method by which attention skills are cultivated, emotional regulation is developed, and rumination and worry are significantly reduced. During the past decades, mindfulness meditation has been the subject of more controlled clinical research, which suggests its potential beneficial effects for mental health, as well as physical health. While MBSR has its roots in wisdom teachings of Zen Buddhism, Hatha Yoga, Vipassana and Advaita Vedanta, the program itself is secular. The MBSR program is described in detail in Kabat-Zinn's 1990 book Full Catastrophe Living.
The self-transforming brain refers to the ability of the self to consciously use mental activity to change/modify the brain's neural network in order to experience life with more happiness and fulfillment. This capacity of using awareness to do so is based on the assumption that the brain and the mind are closely connected, that one does not change without the other. The phrase "I think therefore I am" is not only a famous proclamation in the eyes of neuroscience. It has been evidenced that mental activities such as fleeting thoughts and feelings can create new neural structures in the brain and thus shape a person's reality. Therefore, it is possible to make use of the brain's neuroplasticity to re-wire or change one's brain and life by consciously activating happy, tranquil and loving mental states.
Trauma-sensitive yoga is yoga as exercise, adapted from 2002 onwards for work with individuals affected by psychological trauma. Its goal is to help trauma survivors to develop a greater sense of mind-body connection, to ease their physiological experiences of trauma, to gain a greater sense of ownership over their bodies, and to augment their overall well-being. However, a 2019 systematic review found that the studies to date were not sufficiently robustly designed to provide strong evidence of yoga's effectiveness as a therapy; it called for further research.













