Carbaryl is a chemical in the carbamate family used chiefly as an insecticide. It is a white crystalline solid previously sold under the brand name Sevin, which was a trademark of the Bayer Company. The Sevin trademark has since been acquired by GardenTech, which has eliminated carbaryl from most Sevin formulations. Union Carbide discovered carbaryl and introduced it commercially in 1958. Bayer purchased Aventis CropScience in 2002, a company that included Union Carbide pesticide operations. Carbaryl was the third-most-used insecticide in the United States for home gardens, commercial agriculture, and forestry and rangeland protection. As a veterinary drug, it is known as carbaril (INN).

Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion.

Trichloroacetic acid is an analogue of acetic acid in which the three hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have all been replaced by chlorine atoms. Salts and esters of trichloroacetic acid are called trichloroacetates.
Chloropicrin, also known as PS and nitrochloroform, is a chemical compound currently used as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, and nematicide. Its chemical structural formula is Cl3CNO2.

Heptachlor is an organochlorine compound that was used as an insecticide. Usually sold as a white or tan powder, heptachlor is one of the cyclodiene insecticides. In 1962, Rachel Carson's Silent Spring questioned the safety of heptachlor and other chlorinated insecticides. Due to its highly stable structure, heptachlor can persist in the environment for decades. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency has limited the sale of heptachlor products to the specific application of fire ant control in underground transformers. The amount that can be present in different foods is regulated.

Temefos or temephos is an organophosphate larvicide used to treat water infested with disease-carrying insects including mosquitoes, midges, and black fly larvae.

Picloram is a systemic herbicide used for general woody plant control. It also controls a wide range of broad-leaved weeds, but most grasses are resistant. A chlorinated derivative of picolinic acid, picloram is in the pyridine family of herbicides.

Fenthion is an organothiophosphate insecticide, avicide, and acaricide. Like most other organophosphates, its mode of action is via cholinesterase inhibition. Due to its relatively low toxicity towards humans and mammals, fenthion is listed as moderately toxic compound in U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and World Health Organization toxicity class.

Methoxychlor is a synthetic organochloride insecticide, now obsolete.

Dichlorvos is an organophosphate widely used as an insecticide to control household pests, in public health, and protecting stored products from insects. The compound has been commercially available since 1961 and has become controversial because of its prevalence in urban waterways and the fact that its toxicity extends well beyond insects. The insecticide has been banned in EU since 1998.

Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide introduced in 1966. It is highly toxic to humans, livestock, pets, and wildlife. The EU and UK imposed a pesticide residue limit of 20 µg/kg for apples and oranges.
Fenamiphos is an organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide.

Thiram is the simplest thiuram disulfide and the oxidized dimer of dimethyldithiocarbamate. It is used as a fungicide, ectoparasiticide to prevent fungal diseases in seed and crops and similarly as an animal repellent to protect fruit trees and ornamentals from damage by rabbits, rodents and deer. It is effective against Stem gall of coriander, damping off, smut of millet, neck rot of onion, etc. Thiram has been used in the treatment of human scabies, as a sun screen and as a bactericide applied directly to the skin or incorporated into soap.
Captafol is a fungicide. It is used to control almost all fungal diseases of plants except powdery mildews. It is believed to be a human carcinogen, and production for use as a fungicide in the United States stopped in 1987. Its continued use from existing stocks was allowed, but in 1999 the Environmental Protection Agency banned its use on all crops except onions, potatoes, and tomatoes. In 2006 even these exceptions were disallowed, so currently its use on all crops is banned in the United States. Several other countries have followed suit since 2000, and as of 2010, no countries are known to allow the use of captafol on food crops. Currently, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health established a recommended exposure limit of 0.1 mg/m3 for dermal exposures.
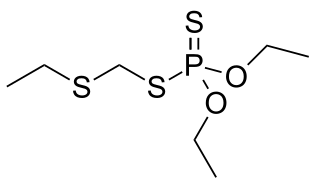
Phorate is an organophosphate used as an insecticide and acaricide.

Sulfotep (also known as tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate and TEDP) is a pesticide commonly used in greenhouses as a fumigant. The substance is also known as Dithione, Dithiophos, and many other names. Sulfotep has the molecular formula C8H20O5P2S2 and belongs to the organophosphate class of chemicals. It has a cholinergic effect, involving depression of the cholinesterase activity of the peripheral and central nervous system of insects. The transduction of signals is disturbed at the synapses that make use of acetylcholine. Sulfotep is a mobile oil that is pale yellow-colored and smells like garlic. It is primarily used as an insecticide.

Metribuzin is an herbicide used both pre- and post-emergence in crops including soy bean, potatoes, tomatoes and sugar cane. It acts by inhibiting photosynthesis by disrupting photosystem II. It is widely used in agriculture and has been found to contaminate groundwater.

Fensulfothion is an insecticide and nematicide. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance. It is widely used on corn, onions, rutabagas, pineapple, bananas, sugar cane, sugar beets, pea nuts, etc.

Fluroxypyr is an herbicide in the class of synthetic auxins. It is used to control broadleaf weeds and woody brush. It is formulated as the 1-methylheptyl ester (fluroxypyr-MHE).